What is Lean Process Improvement?
Lean process improvement follows the principles of Lean to establish a continuous, proactive method of identifying opportunities for improvement, implementing changes based on such opportunities, measuring the impact of such changes, and eliminating waste from an organization’s processes to focus on those that bring more value to customers. Hence, this practice aims to define which processes are efficient and valuable, as well as those that bring no advantage to customers and the business.
Why is Lean Process Improvement Important?
Lean process improvement is of utmost importance to any organization that aims to implement continuous, incremental changes to both existing and proposed systems in a strategic manner. These can be done by making workflows more efficient, thus eliminating waste from the processes. Apart from that, this practice also builds and sustains value-adding activities for customers, the business, and its stakeholders.
Implementing Lean process improvement principles is crucial in mitigating risks of errors or variation in the organization’s overall operations. In return, the benefits of lean process improvement bring about favorable results such as effective production processes, quality services, and top-notch customer satisfaction are achieved.
Lean process improvement is utilized across a wide cross section of industries, including manufacturing, construction, healthcare, and service companies. Although it was born out of the automotive industry, its foundational principles are universal; serving as a holistic guide in ensuring that no protocol is left unchecked and that every opportunity is carefully analyzed for improvement.
5 Principles of Lean and Their Practical Application
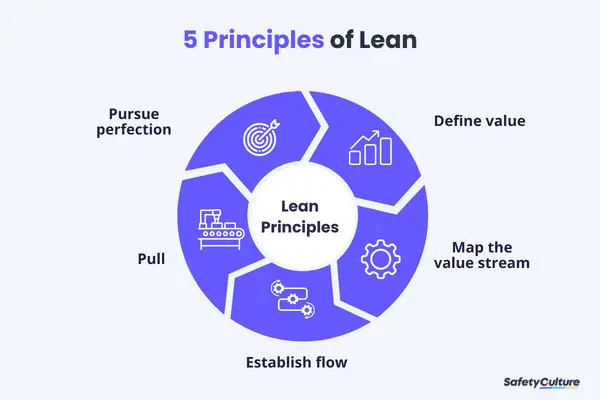
5 Principles of Lean
Here, learn about the Lean principles based on their importance to the overall improvement process.
1. Value
What is considered valuable by customers?
Looking from the customer’s perspective, an organization must be able to define what value is. Value is defined as something the customer is willing to pay for and, from a process standpoint, there is a transformation of raw materials towards finished goods. Everything else is considered waste and should be reduced or eliminated.
Here lies the ultimate goal to identify their needs and offer solutions that satisfy them. Some Lean process improvement examples that fall under this principle include:
- Focus Group Discussions (FGDs)
- Customer surveys
- Web analytics
2. Value Stream
How can we achieve customer value?
Achieving process flow is about balancing production lines through the elimination of waste and the reallocation of resources in order to make each step in the process move at the same speed. This greatly reduces downtime and inventory between process steps. To do this correctly, identify the greatest bottleneck. Once that constraint is broken, find the new biggest bottleneck. With Lean, you’re constantly chasing the bottleneck throughout the system as processes are improved.
3. Flow
How can we ensure smooth-flowing processes?
Now that you’ve removed or reduced wastes from the value stream, it’s time for you to ensure that the rest of the process runs with little to no delays, faults, and risks. Doing this helps you sustain and continuously improve what works. Some strategies you can consider under this principle include comprehensively training employees and standardizing tasks according to quality standards.
4. Pull
How can we limit inventory as waste?
Pull is about producing goods at the rate of customer demand with just enough overproduction to account for variation in that demand. Batch sizes must be kept as small as possible, which requires the ability to change production lines quickly and make the different products the customer demands.
5. Perfection
What are our steps to building a sustainable culture of Lean thinking?
Now that there’s a clear flow of how the principles of Lean apply to Lean process improvement, it’s important to remember that these must contribute to an organization’s efforts toward building a culture of Continuous Process Improvement (CPI) among stakeholders. That said, employees, managers, and leaders must always strive to perfect their processes and how they execute their tasks so that wastes are kept to a minimum and customer value is prioritized.
As these principles collectively help make the overall Lean process improvement more tailored to the goals of organizations, it pays to note that it doesn’t stop there. Instead, it must:
- be a mindset;
- be practiced across the organization;
- help maximize customer value; and
- follow the practice of continuous improvement (kaizen).
8 Lean Process Improvement Steps
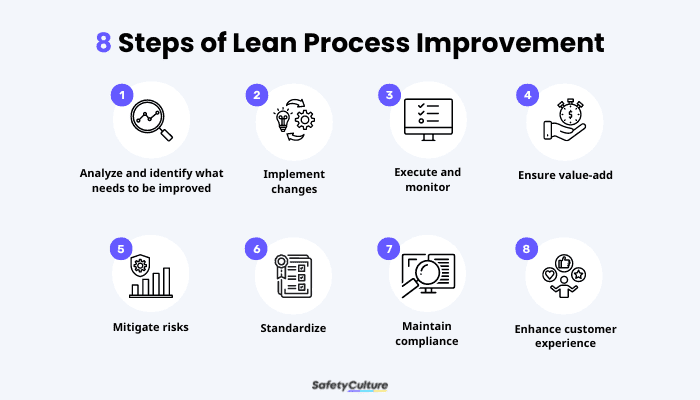
8 Steps of Lean Process Improvement
- Analyze and identify what needs to be improved – This involves looking at the current processes of the organization to help pinpoint the delays, bottlenecks, or inefficiencies and thus create corrective and preventive actions for improvement.
- Implement changes – Careful planning on how certain changes and improvements must be made is encouraged as a solid foundation for the implementation. Process owners, among others, are the ones to lead initiatives and ensure everything is scheduled, monitored, and documented.
- Execute and monitor – Related to the second step, this phase also deals with improving how changes are done to fit the goals and objectives of the organization. Those in charge in this stage must also note any issues uncovered during execution.
- Ensure value-add – To further reinforce one of the Lean principles—Value—this step is all about assessing if processes are contributing to the end goal of meeting and surpassing customer value. This is where the act of reducing waste and continuously improving systems is greatly enforced.
- Mitigate risks – Since the nature of some activities involves risks, the method of streamlining operations as part of Lean process improvement is essential to establish activities that are risk-averse.
- Standardize – Repeating processes must have proper documentation, and their guidelines must be stored securely and easily accessible. This is so employees and other stakeholders can efficiently replicate processes and do their work effectively.
- Maintain compliance – Most especially when an organization’s dedicated employee maintains a Lean process improvement certification, establishing a system and implementing standard activities must become a significant part of company culture. This helps ensure that government-mandated protocols are strictly followed across the organization.
- Enhance customer experience – To fully realize the effectiveness of the overall Lean process improvement, the favorable results that represent achieving customer value must be present to be able to improve customer satisfaction.
Digitize the way you Work
Empower your team with SafetyCulture to perform checks, train staff, report issues, and automate tasks with our digital platform.
Get Started for FreeTechniques
These are some of the most common Lean process improvement techniques you can use:
- Kanban – As a visual process workflow tool using boards, Kanban allows individuals and teams to establish a shared understanding of an organization’s processes with the aim of effective work management.
- Hoshin – Mainly used for strategic planning, Hoshin is a Lean process improvement tool that empowers organizational communication when it comes to setting objectives and achieving them by getting everyone on board to work towards a common goal.
- 5S – This refers to the systematic approach to organizing workplaces through visual management practices by applying these 5 principles: Sort (seiri), Set in order (seiton), Shine (seiso), Standardize (seiketsu), and Sustain (shitsuke), which were originally pioneered by Toyota Motor Company.
- 5 Whys – As a common root cause analysis tool, the 5 Whys method is also good for Lean process improvement. By simply asking the question “Why?” typically 5 times, organizations can reach or identify the root cause of a problem which can help apply lean thinking and practices.
- Six Sigma – Six Sigma focuses on near-perfect quality and the elimination of variation and helps enhance Lean process improvement through a data-driven approach to eliminating errors and defects to aid problem-solving.
- Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA)and Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC) – When looking into a holistic approach, these two tools can be used for problem-solving and eliminating waste in business processes.
- Gemba Walk – This is a workplace walkthrough method used to observe employees, learn about their tasks, and see where the “actual work” happens. Doing this helps organizations see processes in action and identify areas for improvement using Lean principles and productivity enhancement efforts.
Training
Another sustainable approach is conducting comprehensive Lean process improvement training programs. Depending on the specific and overall goals and objectives of the organization, the kind of guidance and learning opportunities that must be available for employees must be part of its initiatives toward continuous improvement. A Lean process improvement course can also help make the learning experience more targeted and less complicated.
Training is a micro-learning solution designed to improve the way organizations train workers toward quality and safety. Check out this free editable course on Think Lean that you can download from our Course Library to help you get started on conducting Lean process improvement.
FAQs about Lean Process Improvement
The Lean process is the method of building and sustaining a culture of continuous improvement in processes, workflows, and systems in an organization. It typically involves a long-term approach to help carry out sets of activities that bring value to customers and the business as well as remove wastes from the process.
In this context, the Lean approach aims to emphasize streamlining systems with the aim of creating value. On the other hand, Six Sigma focuses on eliminating defects and waste by reducing process variability. When applied together, organizations can have a holistic way of meeting customer needs and making business operations more efficient in the long run.
Some examples of Lean process improvement tools and techniques, as described earlier in this guide, include:
- Kanban
- Hoshin
- 5S
- 5 Whys
- Six Sigma
- PDCA
- DMAIC
- Gemba Walk
These are essential in efficiently conducting each step of the process toward continuous improvement.
One of the most common examples of how Lean process improvement is applied in industries is how process visualization gets enhanced. Using tools like the ones listed in the previous FAQ, you can analyze and assess your organization’s current workflows by making everyone involved understand them better with the help of visuals like charts, boards, and value maps.



