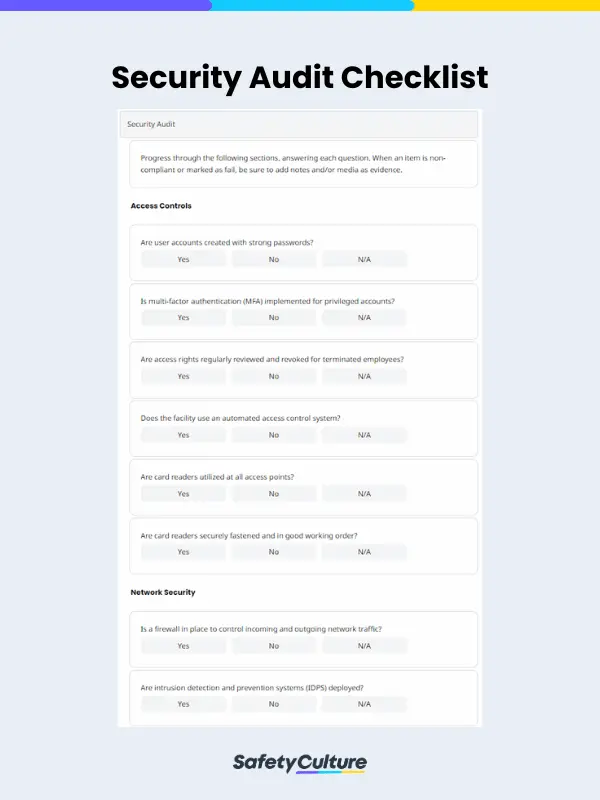
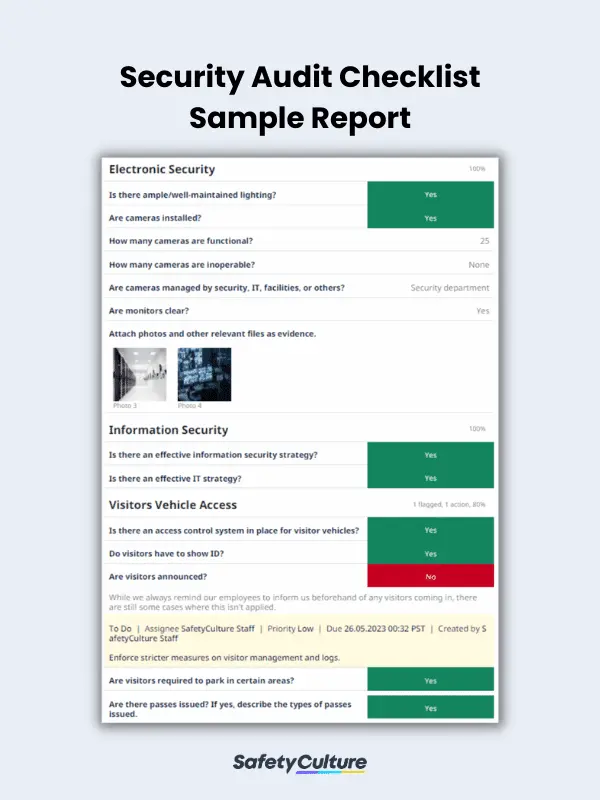
What is a Security Audit Checklist?
A security audit checklist is a comprehensive tool used to assess the security measures and controls in an organization’s systems, processes, and infrastructure. It typically includes a list of security requirements, best practices, and industry standards that organizations need to meet and review during the audit process to help them implement appropriate remediation measures for any vulnerabilities or threats.
Types of Security Audits
There are various approaches to conducting a security audit that organizations can apply to gain comprehensive insights into their security posture and help identify and address vulnerabilities and risks. Also, it’s common for organizations to use a combination of the following types of security audits to achieve a robust and well-rounded security assessment:
- External Audits – performed by independent third-party organizations or auditors to identify vulnerabilities or weaknesses that could be exploited by external threats
- Penetration Tests – also known as ethical hacking and involve authorized attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in the organization’s systems and infrastructure to simulate real-world attacks and assess the effectiveness of existing security measures
- Vulnerability Scans – use automated tools to determine and evaluate potential security vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems, networks, and applications with the aim of prioritizing and remedying identified vulnerabilities
- Internal Audits – conducted by the organization’s own internal audit team or designated personnel to assess the organization’s adherence to security policies, procedures, regulatory requirements, access privileges, data handling practices, and overall compliance with security standards
Why Conduct Security Audits Using a Checklist
Security audits and the various approaches in which they can be performed are often comprehensive in nature and require a clear understanding of the importance of protecting an organization’s security system. Also, a good number of factors, aspects, and elements need to be considered during the systematic audit.
Hence, using a tool like security audit checklists is highly recommended to help streamline the step-by-step process and ensure no key details are missing and left unaddressed. Apart from that, conducting security audits using a checklist offers the following benefits:
- Comprehensive Coverage – ensures that no critical areas or security controls are overlooked during the audit as it serves as a systematic guide toward a comprehensive evaluation of the organization’s security posture
- Consistency – promotes consistency and standardization in the audit process, which allows for fair and unbiased evaluations across different systems, departments, or locations within the organization
- Compliance with Standards – helps organizations meet the requirements outlined in relevant standards to demonstrate compliance, address regulatory obligations, and fulfill industry-specific security requirements
- Efficiency and Time Savings – streamlines the audit process by reviewing and assessing specific checklist items without having to brainstorm or remember all the necessary aspects to consider repeatedly
- Documentation and Evidence – serves as a recordkeeping and documentation tool, allowing auditors to record observations, findings, and evidence during the audit
- Risk Identification and Prioritization – enables auditors to prioritize findings and allocate resources for remediation based on their severity and potential impact on the organization’s security
- Continuous Improvement – provides a basis for ongoing security improvements and helps track progress over time by comparing results from multiple audits
What to Include in a Security Audit Checklist
Organizations may have varying needs and requirements when it comes to establishing security systems depending on the industry they’re in and the type of data or information they must protect. Generally, though, security audit checklists should at least have the following elements and sections:
- Audit Title Page
- Access Controls
- Network Security
- Data Protection
- Physical Security
- Incident Response
- Employee Awareness and Training
- Compliance
- Electronic Security
- Information Security
- General Facility Impressions and Security Posture
- Visitors Vehicle Access
- Completion/Sign-off
How to Create and Use One: 8 Steps
To guide you on how you can prepare and maximize a checklist for your security audits, here are some steps and tips you can consider:
- Clearly outline the scope of the security audit, specifying the systems, networks, processes, and locations to be assessed. Identify the applicable security standards, regulations, and best practices that will be used as a reference.
- Create a comprehensive checklist based on the selected relevant standards. Include specific items to review categorized in sections, actions to take, and evidence to collect during the audit process.
- Determine who will be responsible for conducting the audit and using the checklist. Assign roles and responsibilities to ensure the audit is performed effectively. This may involve internal audit teams, third-party auditors, or a dedicated security team.
- Evaluate the organization’s security controls, policies, and procedures against the checklist. Identify gaps or areas of non-compliance and gather information through interviews, document reviews, and system inspections.
- Prioritize checklist items based on their importance and relevance to your organization’s security posture. Focus on critical controls and areas of higher risk and consider assigning weights or levels of severity to prioritize findings.
- Create remediation plans to address the identified issues. Assign responsibilities, set timelines, and establish action plans for resolving the vulnerabilities and implementing necessary security improvements.
- Prepare a comprehensive audit report to summarize the results and communicate them to the management, stakeholders, and relevant teams.
- Monitor and review the progress of remediation efforts by tracking the implementation of security measures and evaluating their effectiveness through regular audits.
FAQs About Security Audit Checklists
Organizations can follow unique steps and processes when conducting a security audit based on their industry standards, goals, and requirements. Commonly, its phases or stages include the following:
- Planning
- Information Gathering
- Risk Assessment
- Audit Execution
- Findings and Analysis
- Reporting
- Remediation and Follow-up
- Continuous Improvement and Monitoring
In general, security audits should be conducted at least annually. However, organizations may choose to perform audits more frequently, such as quarterly or bi-annually. This decision may depend on various factors, including industry regulations, organizational risk tolerance, and the evolving threat landscape, that may warrant a security audit to be conducted more frequently or even earlier than scheduled.
Regardless of the frequency, continuous monitoring and regular vulnerability assessments should be implemented to complement periodic security audits and ensure ongoing security effectiveness.
The ISO standard for security audits is ISO 27001, which provides a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It sets out the criteria for assessing the organization’s security risks, implementing appropriate security controls, and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets, among others.