What is Risk Avoidance?
Risk avoidance in risk management is a strategy or approach that individuals, organizations, or societies use to minimize or eliminate exposure to potential risks and their negative consequences. It involves taking proactive measures to prevent or steer clear of situations, activities, or decisions that carry a significant level of risk.
Risk avoidance focuses on avoiding or completely refraining from engaging in activities that may lead to potential harm, loss, or adverse outcomes. This approach aims to mitigate the likelihood of risks materializing by eliminating any involvement or exposure to them.
When is Risk Avoidance the Right Strategy?
While risk avoidance can be applied in various contexts, such as personal life, business, finance, and project management, knowing when to implement it is highly crucial. Commonly, this approach is considered the right strategy in certain situations where the potential negative consequences outweigh the potential benefits or when the risks involved are deemed unacceptable.
Further, here are some scenarios where it’s often the preferred approach in risk management:
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance – If engaging in a particular activity or decision poses a high risk of violating laws, regulations, or ethical standards, risk avoidance is typically the best choice to help prevent legal complications, fines, reputational damage, and potential lawsuits.
- High Probability of Failure – This could apply to projects, investments, or ventures that have a low chance of success or are deemed economically unviable.
- Uncertainty and Limited Information – Risk avoidance helps prevent potential harm or loss in situations where the risks are difficult to quantify or predict accurately.
- Value Misalignment – If engaging in a particular activity or decision conflicts with an individual’s or organization’s values, principles, or mission, risk avoidance can help ensure alignment with ethical standards and prevent compromising one’s integrity.
In implementing risk avoidance strategies, it’s important to note that this approach may also entail missed opportunities or potential benefits that could arise from taking calculated risks. Therefore, striking a balance between risk avoidance, risk-taking, and other types of approaches is often a key consideration in decision-making processes.
Risk Avoidance vs Other Risk Management Types
Now, how does risk avoidance differ from other approaches in risk management that organizations consider implementing? Here’s a quick guide on risk avoidance vs. risk acceptance, risk avoidance vs. risk transference, risk avoidance vs. risk reduction, risk avoidance vs. risk sharing, and risk avoidance vs. risk mitigation:
- Risk avoidance – preventing or eliminating exposure to potential risks
- Risk acceptance – acknowledging and embracing risks
- Risk transference – shifting the responsibility for managing risks to another party (e.g., insurance provider)
- Risk reduction – mitigating the impact or likelihood of risks by implementing measures and strategies to minimize their potential negative consequences
- Risk sharing – distributing the potential negative consequences of risks among multiple parties
- Risk mitigation – implementing various measures to minimize the impact or likelihood of risks
Process
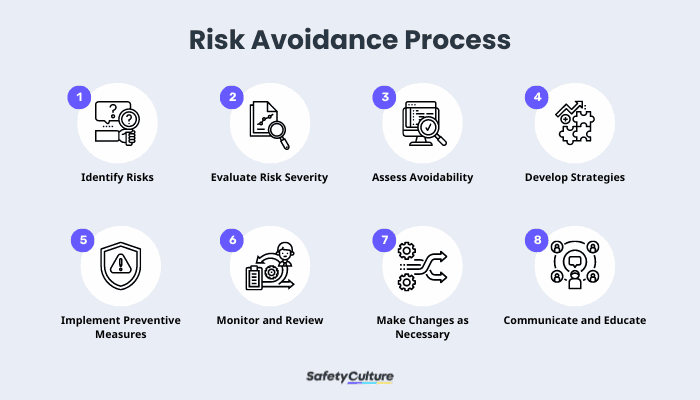
Risk Avoidance Process
Risk avoidance is an intentional, comprehensive process that involves a series of steps aimed at preventing or eliminating exposure to potential risks. Generally, organizations can follow these steps to implement this approach in risk management:
- Identify Risks – This step involves thoroughly analyzing the context, understanding the potential negative consequences, and recognizing the factors that contribute to the potential risks associated with a specific activity, decision, or situation.
- Evaluate Risk Severity – Determine the potential impact or harm a risk could cause and evaluate the likelihood of its occurrence to help prioritize which requires immediate attention and avoidance measures.
- Assess Avoidability – Consider whether there are feasible alternative strategies, processes, or decisions that would eliminate or significantly reduce the exposure to the risks.
- Develop Risk Avoidance Strategies – These strategies may involve alternative approaches, revised processes, or refraining from engaging in certain activities or decisions altogether.
- Implement Preventive Measures – These may include revising plans, modifying processes, or establishing guidelines and protocols to ensure the risks are avoided effectively.
- Monitor and Review – Regularly review and assess the progress to ensure that the intended risk avoidance measures are being followed and that any potential new risks are promptly addressed.
- Adjust as Necessary – If new risks emerge or the effectiveness of the risk avoidance measures is not satisfactory, make adjustments or improvements to the strategies. This can be done by updating protocols, enhancing training, or revising processes.
- Communicate and Educate – Ensure that all relevant stakeholders are aware of the risks, the risk avoidance strategies in place, and their roles and responsibilities in implementing them.
Risk Avoidance Examples
Some practical examples of how risk avoidance is applied in certain situations and industries are the following:
Construction
Example: Fall Protection Measures
Risk Avoidance in Construction: Falls from heights are a significant risk in construction projects, leading to severe injuries or fatalities.
Measures:
- Use of scaffolding systems to provide workers with a stable platform so they can perform tasks at elevated levels
- Use of guardrails and toeboards on elevated work platforms, such as balconies or scaffolds
- Changing the scope of a construction project altogether to eliminate the need for working at heights, if possible
Manufacturing
Example: Hazardous Material Handling
Risk Avoidance in Manufacturing: Mishandling or improper storage of hazardous materials can pose significant risks, including chemical spills, fires, explosions, and health hazards to workers.
Measures:
- Substituting hazardous materials with less hazardous alternatives to reduce the overall risk profile of a manufacturing process
- Training employees involved in handling hazardous materials to cover proper handling techniques, use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), emergency procedures, and safe storage practices
- Having adequate ventilation systems to help control the concentration of potentially harmful substances and reduce the risk of exposure to employees
Retail
Example: Point-of-Sale (POS) Security
Risk Avoidance in Retail: Unauthorized access to customer payment information, data breaches, and fraudulent activities can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities for retailers.
Measures:
- Implementing secure payment processing systems that comply with industry standards such as Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
- Granting data access privileges based on the principle of least privilege, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access critical systems and sensitive information
- Deciding not to collect certain types of data that have limited to no known protection measures
Project Management
Example: Procurement Risk Avoidance
Risk Avoidance in Project Management: Potential risks in the procurement process can include delays, cost overruns, quality issues, and supplier failures, which can significantly impact project timelines, budgets, and deliverables.
Measures:
- Avoiding partnering with vendors that have a history of poor performance or questionable practices
- Prequalifying suppliers based on predefined criteria such as experience, financial stability, and relevant certifications
- Diversifying the supplier base to spread the risk and prevent disruptions in case of supplier failures, capacity issues, or other unforeseen circumstances
Cyber Security
Example: Network Segmentation
Risk Avoidance in Cyber Security: Unauthorized access to critical systems and sensitive data can lead to data breaches, loss of intellectual property, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Measures:
- Creating barriers or firewalls between different parts of the network, preventing unauthorized lateral movement of threats
- Implementing strong authentication methods, such as Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) or Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Implementing strong encryption protocols for sensitive data both in transit and at rest
Tips and Best Practices
To aid your risk management initiatives and make your risk avoidance strategy more effective, keep in mind and implement the following:
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential risks and their impact on your organization. This helps prioritize which risks require immediate attention and which need to be completely eliminated.
- Adopt a holistic approach to risk avoidance by considering all aspects of your organization’s operations, processes, and environment.
- Establish clear and effective communication channels within your organization to ensure that risk avoidance strategies are understood and implemented by all stakeholders. Regularly communicate their importance and encourage employees to report or register other potential risks or hazards that need to be avoided from the get-go.
- Ensure that your risk avoidance strategies align with regulatory requirements to minimize legal and compliance risks.
- Regularly evaluate their implementation and adjust as necessary based on feedback, lessons learned, and emerging risks.
- Maintain a record of risk assessments, mitigation plans, and changes made to demonstrate compliance, track progress, and facilitate future improvements.
- Foster a culture of risk awareness and engagement, training and encouraging employees to actively participate in identifying and addressing potential risks.
- Regularly review and update your risk avoidance strategies to reflect changes in your organization, industry, or operating environment.
Create Your Own Risk Management Checklist
Eliminate manual tasks and streamline your operations.
Get started for FREE


