What is Operations?
To fully understand what operations management is, we must first understand what is meant by operations. The series of activities that take place in the creation of the product or how the services are provided is what is called as “operations.” Used by companies to transform resources into goods or services, operations answers the question, “What does the company do?”
Back office in a bank; manufacturing of IKEA furniture; ordering products from Amazon—these are all operations. Looking around you is the best way to begin understanding the nature of operations. Every service or product you have used today is created by operations.
Companies and organizations need to ensure that their product or service is of good quality and useful to their clients before offering it. How can they ensure that the products and services rendered meet client expectations?—through operations management.
What is Operations Management (OM)?
Operations management is in charge of everything that goes into making goods and delivering services. It manages resources like materials, machines, technology, and people, and produces the goods and services that people want in the market.
Either production or the provision of services is the main focus of OM. It puts emphasis mostly on planning and organizing projects, as well as supervising them. Simply defined: Operations management is how resources are turned into goods and services in the most efficient way possible to fulfill the demand of consumers or clients.
The whole organization exists to support activities such as facilities management, human resource management, catering to inquiries and requests, and so on—all of these are under the responsibilities of operations management. To be able to compete in the world nowadays, businesses need to manage their operations well and have efficient processes in place.
Achieve operational excellence
Cultivate a culture of excellence with our digital solutions that enhance efficiency, agility, and continuous improvement across all operations.
Explore now3 Components of Operations
Operations management is systemizing the direction and control of a business process in transforming resources, which are called inputs, into finished goods or services for consumers or clients (outputs). This basic transformation model applies equally to manufacturing and service businesses and in both the corporate and non-profit sectors.
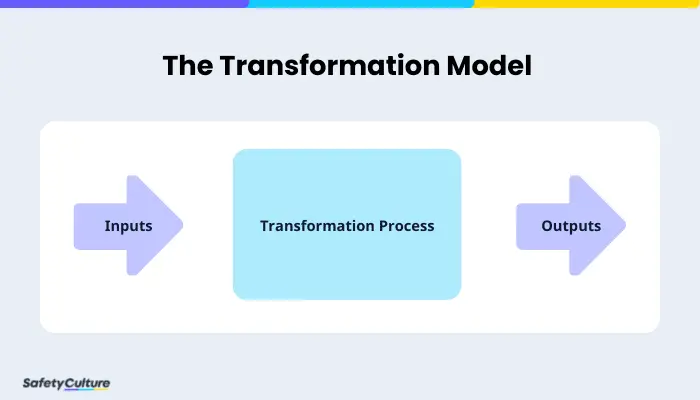
The Transformation Model of Operations Management | SafetyCulture
Inputs
Input resources are usually classified as: transformed and transforming resources.
- Transformed resources – pertains to those that are transformed by the operation to produce the goods or services. This includes materials, information, and customers.
- Transforming resources – pertains to those that are used in the transformation process. There are two types of transforming resources—The first are the staff or workers and the second are the facilities or the locations where the transformation process takes place. Inputs include different types of both transformed and transforming resources.
Outputs
The outputs in the transformation model may be in the form of either goods or services or can be both goods and services. Transformation processes should result in good outputs (e.g., minimizing inputs to be wasted). To minimize the environmental impact of waste over the entire product life cycle, outputs must be designed to last up to the point of final disposal.
Transformation Processes
Taking one or more inputs, making changes to it, adding value, and producing outputs for consumers or clients is referred to as the transformation process. An example of this is changing a raw material to create a new item out of it.
Foundations of Operations Management
Two key terms can help define operations management more precisely: supply chain management and logistics. Operations management has firm foundations in both of these areas.
-
Supply Chain Management
The best way for businesses to better service their customers is to make supply chain management a strategic priority. The supply chain includes all the activities required to move a product from inception to the customer. The end goal is simple: meet the customer’s request and foster satisfaction.
-
Logistics
Logistics are used to manage, coordinate and monitor the resources needed to move the products in a timely and cost-effective manner. Transportation, shipping and receiving, importing and exporting operations, warehousing, managing of inventory, purchasing, and customer service are all part of logistics. Logistics’ long-term goal is to get the right thing to the right location at the right time.
High-quality products or services attract customers, give businesses a competitive edge in the market, increase their revenue, and make them a force in their industry.
Digitize the way you Work
Empower your team with SafetyCulture to perform checks, train staff, report issues, and automate tasks with our digital platform.
Get Started for FreeWhat is Operations Management Training?
Operations management training focuses on equipping employees with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively manage and optimize various operational aspects of an organization. It can help your operations managers contribute to the efficient and effective functioning of the organization and drive improvements in operational processes and outcomes.
Here’s an overview of what you can expect from an operations management training program:
- Process Understanding: Training often begins with an understanding of core business processes and their interdependencies. This includes processes related to production, procurement, inventory management, distribution, and customer service.
- Efficiency and Productivity: Training emphasizes methods and strategies for improving operational efficiency and productivity. This may involve topics like lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, Total Quality Management (TQM), and process optimization.
- Supply Chain Management: Operations managers are often responsible for overseeing the supply chain, which includes sourcing raw materials, managing suppliers, logistics, and distribution. Training covers supply chain strategies, vendor management, and inventory control.
- Quality Control: Ensuring the quality of products and services is a critical aspect of operations management. Training includes techniques for quality control, quality assurance, and continuous improvement methodologies.
- Resource Allocation: Operations managers need to allocate resources effectively, whether it’s labor, materials, equipment, or capital. Training covers resource allocation models and strategies.
- Project Management: Project management skills are essential for overseeing operational projects, such as process improvements or system implementations. Training may include project management methodologies like Agile, Scrum, or traditional project management frameworks.
Take your operations management training to the next level using the Training feature from SafetyCulture platform. With this feature, you can transform your SOPs and technical standards into interactive, bite-sized training that your team can easily complete in minutes—not days or weeks. Get started with over 1,000 templates from the course library, or build your own using the creator tool’s drag-and-drop functionality.
Recent Trends
Digital innovations are already making the management of operations more effective. These innovations boost the organizations’ performance higher, more efficiently, and to greater profitability. Below are recent trends in operations. While most of them have been around for some time, they continue to be popular trends in operations management:
- Business process reengineering, or BPR, is a strategy that helps businesses in restructuring their organizations.
- Lean manufacturing (5S Lean), Six Sigma, and agile manufacturing are all disciplines that emphasize efficient, adaptive production and have remained popular over the years.
- Manufacturing processes, such as changing the way a furniture is constructed, can be reconfigured in response to market changes.
- Behavioral operations management is an approach that focuses on human behavior or employee involvement.
- Business sustainability is the policy of adhering to ecologically sustainable practices in compliance to changing regulations.
One of the digital innovations that employers could take advantage of is employee GPS tracking. This technology allows managers to see their employees’ exact locations and how long they are working at a specific job site, then provide them with safety alarms as needed.
Increase Operational Efficiency with SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor)
SafetyCulture is an operations management software that businesses use to conduct inspections, collect data accurately, manage tasks, streamline processes, implement workflow management, and ensure operational efficiency in all departments in organizations across different industries.
Explore alternative operations trends and provide your team with the tools they need to innovate efficiently with SafetyCulture. Project managers, supervisors, supply chain managers, and operations professionals are among those who use this tool. Below are the features your business can have by using SafetyCulture:
- Monitor processes, production, sales, and distribution of specific goods and services, such as by conducting a supply chain management audit
- Streamline both internal and external communications with clear, descriptive, and rich media messaging and specific access permissions using Heads Up
- Conduct quality management of goods and services, such as by following Total Quality Management (TQM)
- Track the movements of raw materials, shipping, and finished goods through inventory management
- Manage, train, and assess employees with human resource management



