What is Procurement Management?
Procurement management refers to the method of ensuring that there’s an efficient way of acquiring supplies of goods and services needed for the success of an organization’s projects and processes. Also known as the Source-to-Settle (S2S) process, this approach helps organizations integrate their sourcing and purchasing stages.
Why is Procurement Management Important?
Procurement and supply chain management come hand in hand. The former ensures that all goods and services an organization needs are properly acquired, while the latter is the process of efficiently transforming and distributing those into products to customers. Hence, procurement management is key to making sure that both functions are well-performing and successful.
Since procurement plays a critical role in the financial health and overall performance of an organization, effectively managing this function is needed to help streamline the activities and processes involved in it.
For instance, implementing good procurement management strategies fit for the business is essential for efficient invoicing and expense tracking. Companies can also discover opportunities and eliminate low-value activities to improve their procurement management processes and supplier relationships. This way, cost savings can be forecasted and taken into account during strategic planning.
Effectively managing procurement processes also contributes to how efficiently the organization’s stakeholders can address issues and mitigate risks that may arise during each stage or step.
Key Benefits
Now, how does effective procurement management benefit businesses? Here are a few areas where it makes a significant impact:
Strategic Sourcing
Part of an organization’s procurement management plan is to identify and select external providers. Being able to establish your criteria and guidelines on effective sourcing plans is helpful in implementing procurement strategies that are aligned and valuable to your organization.
Optimized Purchasing
An inefficient purchasing process can lead to substantial delays in acquiring the goods and services your organization needs for the production stage. To avoid this, procurement management helps standardize your purchase requisition, approval, and finalization workflows.
Proactive Risk Management
Organizations must always keep their supplier relationships in check to aid in mitigating risks involved in any unforeseen costs and expenses. Aside from that, incorporating best practices in how you manage your procurement process allows you to improve inventory management and contingency planning.
Reduced Costs
Having an efficient way of managing procurement activities can also result in cost savings. Ensuring that there’s a system in place helps avoid delays, redundancies, and ineffective procurement practices. Hence, additional processes and the need to go through the previous stages can be eliminated.
Sustainable Roster of Suppliers
Ensuring that you are partnering with suppliers with their own sustainable strategy can help support your own strategy. This is where the importance of working with suppliers who maintain a good, ethical code of conduct comes in. Also, collaborating with third-party suppliers can reduce the overall impact of your business activities on the environment.
Steps
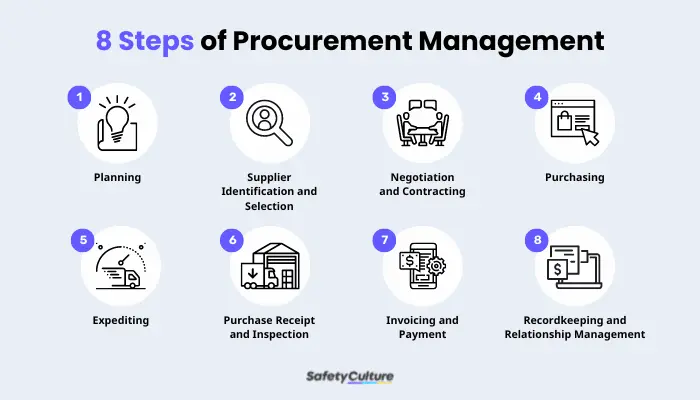
8 Steps of Procurement Management
As a comprehensive process, managing procurement entails various steps and activities under each. In a general sense, here are the 8 steps of procurement management:
1. Planning
This step revolves around the process of identifying the product or service need so that the specifics can be planned out. Also, this is where forecasting is done based on current or existing projections and historical data on how the supplies for the product or service shall be ordered.
2. Supplier Identification and Selection
Ensuring that suppliers meet your product requirements is covered in this step. Identifying and selecting suppliers can be based on your established relationships with vendors, research for new ones, and reaching out for requisition.
3. Negotiation and Contracting
Competitive bidding is one of the ways organizations can conduct their negotiations with suppliers when it comes to the best price and terms for their products. Suppliers present their quotations to the companies, and then the companies present their requirements. Contract finalization and signing will take place once all the terms and conditions have been agreed upon.
4. Purchasing
For this stage, creating purchase orders is a must to effectively track the purchases and expenses of a business. The purchase order is a document that defines the exact price, product specifications, items, quantities, and terms of the products being purchased or supplied.
To guide you, here’s a sample purchase order template you can download and use.
Create Your Own Purchase Order Template
Eliminate manual tasks and streamline your operations.
Get started for FREE5. Expediting
Depending on the needs of your business, accelerating orders may be necessary. Some factors that contribute to this are schedule changes, product demand, and other unforeseen circumstances.
6. Purchase Receipt and Inspection
Once the goods have been delivered, acknowledgment of receipt and inspection should be conducted. The purchase order must be double-checked with the received supplies to see if there are any discrepancies or errors. In any case, reports must be created and submitted for proper documentation.
7. Invoicing and Payment
The next step is to clear invoices and align them with accounts payables. These are crucial to complete the purchase.
8. Recordkeeping and Relationship Management
Lastly, keeping a record of all processes is important not just to track expenses but also for auditing and tax purposes. Also, documentation provides opportunities for businesses to assess data and provide feedback to suppliers.
To help you promote efficiency in your procurement management system, having and using a procurement checklist is a must. Since there are a lot of stages involved, things may get overlooked, which can then jeopardize the quality of your processes. From a business perspective, this can mean delays in production, the risk of not meeting customer expectations, and higher costs due to inefficiencies.
FAQs About Procurement Management
Purchasing is under the overall process of procurement. It pertains to the actual method of buying goods and services. Procurement, on the other hand, tackles the act of dealing with other factors revolving around supplier identification and selection, contract negotiation, and purchasing.
Procure-to-pay or P2P refers to the process of requisitioning, purchasing, paying for, and receiving goods or products from suppliers, and integrating them into a holistic system for maximum efficiency. Typically, it involves 5 key stages:
- Processing of requisition
- Sourcing
- Processing of purchase order
- Receiving of goods
- Management of accounts payables
Ensuring a successful procurement management program should be part of an organization’s key goals to contribute to business growth. With this, you must consider the 5 P’s of procurement management, namely:
- Proposal
- Planning
- Pricing
- People
- Project management
Some of the golden rules of procurement are the following:
- Proper timing – Strategic procurement management—one that’s not rushed yet too slow—is key to smooth-flowing operations.
- Innovation – Organizations must always strive for continuous improvement and leave room for innovation.
- Rethink and renegotiate – Similar to innovation, rethinking helps pinpoint areas to improve and reassess.



