A Quick Guide on Quality Standards
Learn what quality standards are, how they relate to quality assurance and quality control, the principles, and some examples.

Published 18 Jan 2024
Article by
4 min read
What are Quality Standards?
Quality standards refer to sets of guidelines, systems, methods, requirements, and specifications followed by an organization to ensure consistent process and product quality. Mostly prevalent in manufacturing, quality standards are established by industry regulatory boards to help drive customer satisfaction and maintain compliance. Globally, ISO quality standards are the most widely accepted set of standards applicable to various industries.
Why are Quality Standards Important?
Any product or service that’s free from any manufacturing defect, deficiency, or process variation is considered of good quality. This is achieved through the holistic process of quality assurance and quality control.
Thus, to ensure and maintain good manufacturing practices, a set of manufacturing quality standards must be established and followed for the purpose of uniformity across the entire manufacturing process.
Additionally, some of the benefits of quality standards include the following:
Continuous improvement of quality outcomes
Efficient adherence to regulatory requirements and compliance
Reduced process variation and product defects by focusing on your Critical to Quality factors
Improved worker productivity and safety
Enhanced customer satisfaction
Seamless flow of operations
Principles
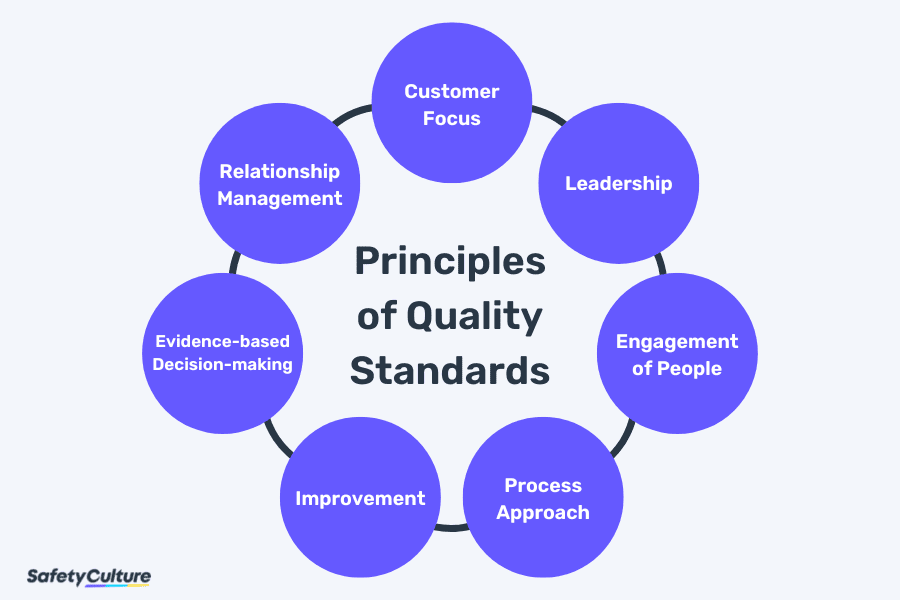
Principles of Quality Standards
In setting quality assurance standards, the 7 principles of quality management also apply to help establish a more fitting Quality Management Standard (QMS) based on your business and industry. That said, the principles of quality standards are the following:
Customer Focus – This guides the organization in ensuring that customer needs and expectations are met by setting quality standards aligned with them.
Leadership – This pertains to the organization’s commitment to implement leadership principles across the organization to promote a healthy culture of collaboration.
Engagement of People – This is key to maintaining worker engagement toward providing better value to the organization and customers.
Process Approach – This refers to the way of treating all projects and processes as part of a holistic functioning system to drive all efforts into sustaining the business.
Improvement – This emphasizes the need for an organization to continuously improve by encouraging proactive innovation and consistent recognition of successful initiatives.
Evidence-based Decision-making – This empowers people to value the importance of data and analysis and how they can put them into practical applications such as maintaining quality standards.
Relationship Management – This enables organizations to look at the overall supply chain management and how it affects the processes, stakeholders, and suppliers.
What are Examples of Quality Standards?
Learn more about this list of quality standards most widely used in the manufacturing, healthcare, food, and automotive industries.
ISO 9000 and 9001
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) published the ISO 9000, the family of good management practices standards for QMS. The ISO sets quality control standards for manufacturing companies to adhere to so that they can maintain compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Under ISO 9000 is ISO 9001, which sets out detailed requirements for establishing a QMS that specifically suits their industry needs.
Create your own Quality Audit Checklist
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
GMP and GLP
Another set of notable quality standards examples is Good Manufacturing Practices ( GMP ) and Good Laboratory Practice ( GLP ).
GMP refers to the system of processes and documentation to ensure that manufacturing products are being produced and controlled consistently against quality standards. On the other hand, GLP is a set of principles that ensures non-clinical laboratory studies are following quality standards and maintaining the integrity of safety test data.
US FDA
Both the GMP and GLP are enforced by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). That said, the US FDA sets out regulations that address manufacturing practices, including personal hygienic practices, facility maintenance guidelines, sanitary operations, and process controls during food manufacturing.
IATF 16949
The International Automotive Task Force (IATF) 16949 was created specifically for the automotive industry. Apart from helping organizations maintain the quality of automotive services and assembly parts, IATF 16949 also guides in continuously improving how manufacturers carry out their processes toward reducing defects and waste.
IAQG 9100
The International Aerospace Quality Group (IAQG) 9100 is a specific set of QMS requirements for aviation, space, and defense organizations in the aerospace industry. This can be applied to all supply chain levels to achieve optimal quality and efficiency.
Ensure and Maintain Quality with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
Enforcing and monitoring quality standards in your organization requires an optimized approach to ensure you’re not missing out on critical process issues, system improvements, and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). To help you with these, use a powerful mobile solution such as SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) and leverage the following features for your QMS:
Conduct quality inspections and process audits to ensure all teams, leaders, and employees are complying with quality standards for maximum efficiency
Use quality control inspection checklists to easily spot issues , assign corrective actions , and standardize regular inspections for a streamlined QMS
Maximize your inspection data , audit results, and overall analytics reports to generate actionable insights that are crucial for your continuous improvement efforts
For a more holistic overview of your organization’s QMS, connect other QMS and Business Intelligence (BI) tools to SafetyCulture, such as the following:
Google Calendar for seamlessly scheduling your inspections and audits
KiSSFLOW for efficiently managing workflows and approving process requests quickly for any action related to your overall quality management
Asana for proactively managing tasks and projects in your organization
Disseminate quality standards, policies, and guidelines across the board while encouraging real-time collaboration via Heads Up
Improve and maintain compliance with QMS standards by conducting regular Training sessions with your organization
Ensure all Assets are compliant with QMS standards
You may also download and customize these ready-to-use checklist templates for your quality checks:
Related articles
Quality Management
Quality

Critical to Quality (CTQ): Guide to Customer-Driven Excellence
Learn the basics of Critical to Quality, its benefits, parameters, and specific applications in this comprehensive guide.
Quality
Quality Management

A Guide to Understanding Management Reviews
Learn about what a management review is, its importance, its key inputs and outputs, its process, and some FAQs.
Quality
Quality Management

5 Core Tools of Quality: The Ultimate Guide
Learn how the 5 core tools of quality work together to reduce risk, improve consistency, and drive continuous operational improvement.