What is Warehouse Safety?
Warehouse safety is a set of regulatory guidelines and industry best practices to help warehousing personnel ensure a safe work environment and reinforce safe behavior when working in warehouses. For sustainable warehouse operations, health and safety should be prioritized as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) revealed that the fatal injury rate for the warehousing industry is higher than the national average for all industries.
Importance
Warehouses can be dangerous places to work in. It is important to understand common warehouse dangers and hazards because they can cause injuries and in extreme cases death. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics reported an average of 16 fatalities every year in the U.S. warehousing and storage sector and a reported injury and illness rate of 5 out of every 100 warehouse and storage workers.
Warehouse Safety Regulations and Standards
While there are no explicit OSHA warehousing regulations, warehouse operations fall under the general industry requirements which include the following OSHA standards:
- Hazard Communication – Warehouse operators should prepare and implement a written Hazard Communication (HazCom) program and warehouse workers who may be exposed to hazardous chemicals should know about them and how to protect themselves.
- Emergency Action Plan (EAP) – If warehouse owners do not have an in-house fire brigade, then they should have a detailed plan describing the actions warehousing employees should take in the event of a fire or other emergency situations.
- Fire Safety – Warehouse management employing more than 10 workers should have a written fire prevention plan, kept in the warehouse and made available to warehouse personnel for review.
- Exit Routes – Warehouses should have at least two well-designed and well-constructed emergency exit routes—located as far away as practical from each other in case one is blocked by fire or smoke—that are regularly inspected for maintenance, safeguards, and operational features.
- Walking / Working Surfaces – Warehouse and storage facility workers working at heights, especially on elevated platforms, should have fall protection systems to protect themselves from falls which is among the leading causes of serious work-related injuries and deaths.
- Medical and First Aid – OSHA requires warehouse operators to provide medical and first-aid personnel and supplies commensurate with warehouse hazards such as faulty pallet racks and racking falls due to unsafe use of forklifts, among others.
Hazards and Controls
Here are 8 of the most common warehouse safety hazards and safety tips and resources to help you identify and control them:
- Forklifts are critical pieces of equipment used in warehousing and storage facilities. Ensure all operators are certified and undergo regular refresher training. Perform daily pre-start inspections for equipment damage. Unsafe use of forklifts is the most often cited hazard in warehousing operations by OSHA
- Loading Docks are a common venue for accidents. Operators must drive slowly on dock plates and ensure edges are clear and safe. Implement warning signs and mechanisms to keep people away from loading docks.
- Conveyors pose serious dangers to workers including getting caught in equipment and being struck by falling objects. Warehouse facilities must use proper safeguarding equipment to prevent entanglement and follow lockout tag-out procedures during maintenance.
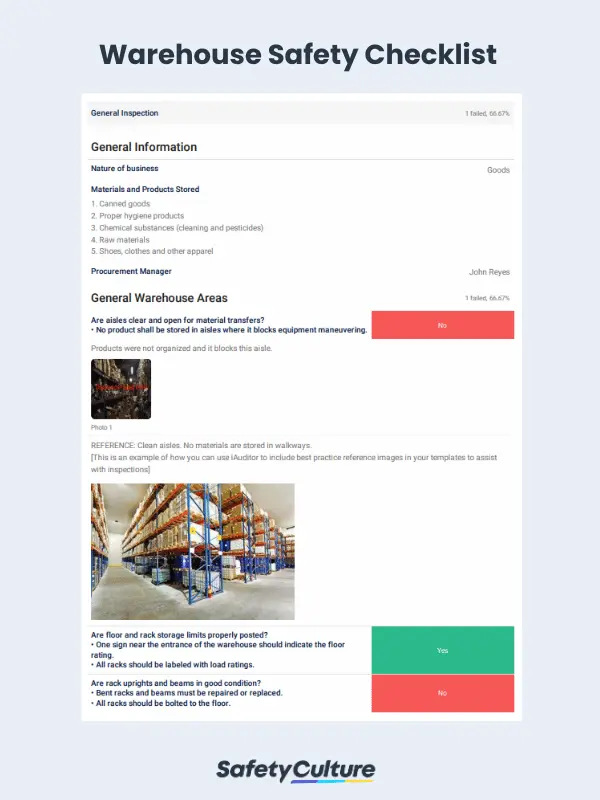
- Materials Storage keeps aisles and passageways clear to prevent slips, trips, and falls. Improper stacking of loads and storage of materials on shelves can result in unintended slip and trip hazards for nearby workers. Stack loads evenly, with heavier loads on lower or middle shelves.
- Manual Lifting/Handling is also a common venue for physical injuries such as musculoskeletal disorders. Workers must practice proper ergonomic posture and minimize lifting through good engineering design.
- Hazardous Chemicals pose potential risks that depend on the type of hazardous chemical, but it is usually catastrophic. It’s very important to implement a hazard communication program to ensure workers are trained in safety inspections and chemical handling.
- Charging Stations in warehouse facilities are used to refuel or recharge powered equipment to function. The risks involved in these are usually fires and explosions. Keep stations away from open flames and strictly prohibit smoking in the facility. Ensure fire extinguishers are available, ventilation systems are in place, and proper PPE is worn.
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
Explore nowTips and Best Practices
Depending on the type of business, there are specific safety rules to be followed due to hazards that are also specific to the type of work people do. Below are a few general tips to follow to ensure warehouse safety, regardless of business or industry.
- Reinforce proper ergonomics at all times.
Warehouse employees do a lot of heavy lifting, and it is important that they are trained in the proper lifting procedures so that they avoid hurting others and themselves. Your warehouse safety program should cover ergonomics in the workplace. If they have to do manual lifting, train them in the proper techniques that will help protect the back and knees from injury. - Ensure that all fire hazards are minimized and that appropriate fire safety measures are in place.
If you have an operating warehouse facility, you probably have all the necessary fire alarms, extinguishers, and sprinklers as required by safety regulations in your area. But it’s still important to schedule regular training and inspections to ensure that all employees are knowledgeable in fire safety processes and that all fire safety measures are in place and functioning as required. - Minimize cutting dangers and enforce safe handling of sharp objects.
Workers in a warehouse environment handle a lot of packing and unpacking tasks; they constantly use a lot of corrugated, metal, and plastic straps and plastic pallet wrappings. This is why it’s vital that they use proper PPE and safety knives to avoid serious injury or death. All workers should also be trained in the proper cutting techniques to ensure warehouse safety at all times.
Example of a Program Overview
Setting and maintaining warehouse safety programs is an ongoing process of identifying barriers to safe work and removing them from the warehouse operations. Any warehouse safety program should be tailored to the current condition, needs, and culture of the warehousing workers, but it should at least contain:
- Warehouse Safety Rules include OSHA requirements such as appropriate PPE, mandatory safety signages, HazCom program, fire prevention plan, and emergency action plan. You can also take advantage of a warehouse safety checklist to do regular safety observation checks to ensure safety protocols are being followed by employees in the warehouse.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) – especially applies to certain job tasks and for operating specialized pieces of machinery or new equipment
- Warehouse Safety Training – generally includes forklift operator certification, hazardous material handling and storage training, and proper ergonomics and hazard identification in warehousing
- Warehouse Inspections and Record-keeping – crucial warehousing checks such as racking inspections, 5S audits, daily pre-use forklift inspections, and warehouse tools and equipment preventive maintenance should be adequately documented and kept for a certain period.
Create Your Own Warehouse Safety Checklist
Eliminate manual tasks and streamline your operations.
Get started for FREEWarehouse Safety Topics to Discuss with Your Team
Apart from having the required certifications and appropriate training, facilitating regular warehouse safety meetings or toolbox talks can help engage with frontline workers better, foster collaboration, and build a safety culture from the ground up.
Listed below are relevant warehouse safety meeting topics you can discuss with your team:
- Identifying and Complying with PPE-related Warehouse Safety Signages
- Warehouse Safety Equipment for Proper Handling and Storage of Hazardous Materials
- Distinguishing between Forklift Pre-operation and Operational Safety Checks
- Warehouse Health and Safety Regulations for Working at Heights
- Emergency Procedures for Warehouse Fires caused by Faulty Electrical Distribution
If safety procedures and workplace hazards are disregarded in warehouses to cut costs, it exposes workers to serious risks of accidents and injury. Providing workers training on hazard awareness, conducting safety inspections, and implementing warehouse safety measures can help maintain a safe and healthy working environment.
FAQs About Warehouse Safety
According to data from OSHA, the biggest safety issue that warehousing establishments face is accidents relating to forklifts. As per the latest statistics, it is estimated that between 35,000 and 62,000 injuries happen annually involving forklifts, some of which, unfortunately, is fatal.
A warehouse safety checklist is a comprehensive document that enumerates the measures and procedures that should be observed to ensure the safety of workers and visitors in a warehouse establishment. The checklist typically covers all the areas of the warehouse, including storage areas, interior and exterior dock areas, equipment checks, and offices, among others.
Some of the most common PPEs used when working in warehouses include hard hats, steel-toed boots or safety shoes, safety glasses or goggles, gloves, and high-visibility vets or clothing. These PPEs, however, still depend on the specific hazards present in the environment of the particular warehouse.