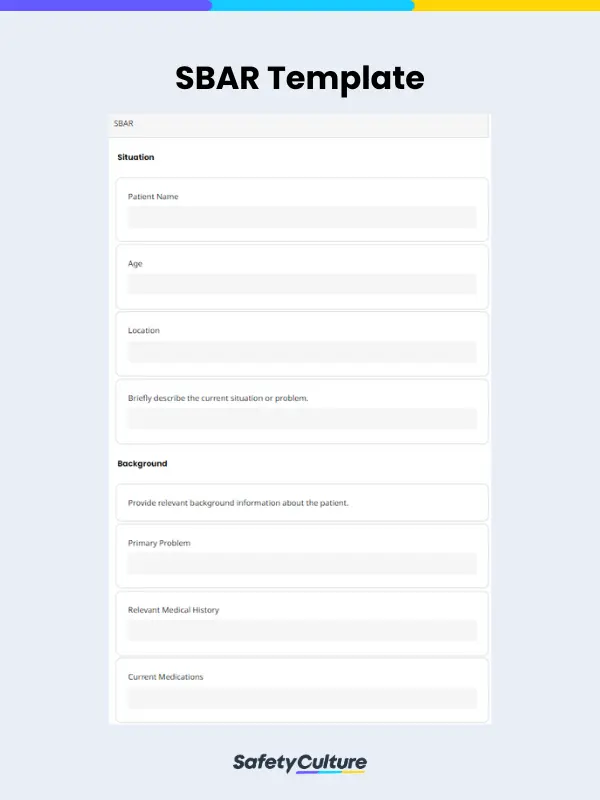
What is an SBAR Template?
An SBAR template is a tool used to standardize documentation done by healthcare professionals to structure their communication using the Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation (SBAR) framework. The template provides a guide for organizing and conveying essential information in a clear and concise manner to ensure streamlined continuity of patient care.
What are the 4 Steps of SBAR?
As a straightforward framework, the steps of SBAR are as follows:
- Situation – This step prompts the healthcare professional to provide a brief summary of the current situation or problem.
- Background – This is where the healthcare professional indicates essential background information about the patient’s history and current status.
- Assessment – This is where the assessment or evaluation of the patient’s condition is presented.
- Recommendation – The final step involves providing recommendations or suggestions for actions to be taken.
Benefits of Using an SBAR Template
Using an SBAR format template offers the following benefits mainly in healthcare communication and other industries that require structured communication models:
- Standardization – SBAR templates provide a standardized format for communication, ensuring consistency and uniformity in the information exchange process. This promotes clarity and reduces the risk of miscommunication or misunderstanding among healthcare professionals.
- Efficiency – Templates streamline the communication process by providing a structured framework. Healthcare professionals can quickly fill in the required information in the designated sections, saving time and facilitating efficient communication during busy and time-sensitive situations.
- Improved Patient Safety – Clear and concise communication through SBAR templates reduces the potential for errors, misunderstandings, and delays in care. Also, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions and take appropriate actions promptly, thereby enhancing patient safety.
- Enhanced Interprofessional Collaboration – The standardized format of templates for SBAR allows for easier comprehension and understanding of information, promoting teamwork and coordinated care.
How to Create One
It’s important to remember that SBAR templates can be customized and refined based on the specific needs and preferences of the healthcare organization or individual users. Generally, creating a template when using the SBAR framework involves the following steps:
- Divide the template into the four main sections of SBAR: Situation, Background, Assessment, and Recommendation. Clearly label these sections that will serve as the framework for organizing information.
- Within each section, determine the specific information fields that need to be included. For example, the Situation section may include fields for patient name, age, and location if necessary.
- Include optional fields or sections that capture additional information that may be relevant in the given context, such as other pertinent clinical information and interventions needed.
- Review the template for clarity, completeness, and usability. Seek feedback from other healthcare professionals to ensure the template captures the essential information effectively.
- Test and implement the use of the template and gather feedback from users. Make any necessary revisions based on their feedback before finalizing and distributing for regular use.
- Offer training or educational sessions to professionals to ensure they understand the purpose, structure, and benefits of using the SBAR template.
How Do You Write an SBAR Report Using a Template?
To help you write an SBAR report using a template, you may follow these steps:
- Begin by providing a brief summary of the current situation or problem. Include key details such as the patient’s name, location, and the reason for the report.
- Provide relevant background information about the patient. Include their medical history, current diagnosis, recent treatments or procedures, allergies, and any other essential details.
- Present your assessment or evaluation of the patient’s condition. Include objective data such as vital signs, laboratory results, symptoms, and subjective observations.
- Suggest specific actions or interventions to be taken based on your assessment. Provide clear and concise recommendations for further diagnostic tests, medication changes or adjustments, interventions, or consultations with specialists.
- Review the completed SBAR report for accuracy, clarity, and completeness.
- Share the SBAR report with the appropriate healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care.
- Record the SBAR report in the patient’s medical record or communication logs as per your organization’s policies. This ensures that the information is documented for future reference and continuity of care.
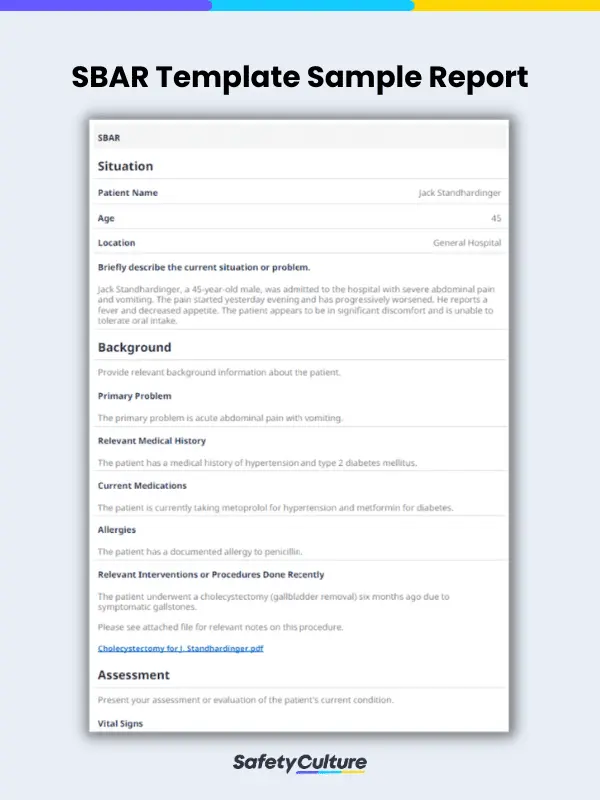
Check out this filled-out SBAR template example using SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor):
FAQs About SBAR Templates
While SBAR was originally developed for healthcare communication, its principles can be applied in various industries and non-clinical settings where structured communication is essential. These include project management, team coordination, or emergency response. By adapting the concept of SBAR to specific contexts, organizations can promote effective information exchange, enhance collaboration, and minimize errors or misunderstandings using SBAR form templates.
To enhance communication, reduce the risk of errors or misinterpretations, and promote efficient and effective collaboration among the healthcare team, here are some common instances when a nurse should use SBAR:
- Handoffs or shift changes
- Patient transfers
- Consultations with physicians or specialists
- Rapid response or emergency situations
- Reporting significant changes
- Communicating with ancillary staff
While not universally mandatory, SBAR is a recommended practice in healthcare settings due to its effectiveness in enhancing communication during shift changes and patient safety. Many healthcare organizations have implemented it as a standard practice and provide training and resources to support its use. Also, the decision to make SBAR mandatory may vary depending on the healthcare facility, policies, and regulations.