What is a Factory Acceptance Test Checklist?
A factory acceptance test checklist is a comprehensive document that outlines the criteria, procedures, and requirements to assess and verify equipment and system quality, functionality, and conformity. Quality managers, design engineers, operators, and maintenance personnel use this as a tool to test and ensure that newly produced equipment works according to design specifications before installation and operation.
Why Use a Factory Acceptance Test Checklist?
Overlooked equipment discrepancies can lead to installation problems on site, which can wreak havoc on a project schedule. Prior to shipment, quality managers should resolve nonconformity at the factory so that the clients’ new processing lines are up and ready to go on time.
When FATs are conducted with the help of checklists, the following issues can be proactively identified and avoided:
- Poor Machine Quality or Craftsmanship
- Nonconformity to Regulatory or Sanitary Specifications (e.g., American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC))
- Lack of Appropriate Machine Guarding and Labels (e.g., Lock Out Tag Out (LOTO) labels and procedures, compliance with Occupational Health & Safety Administration (OSHA) standards)
- Lower than Expected Throughput
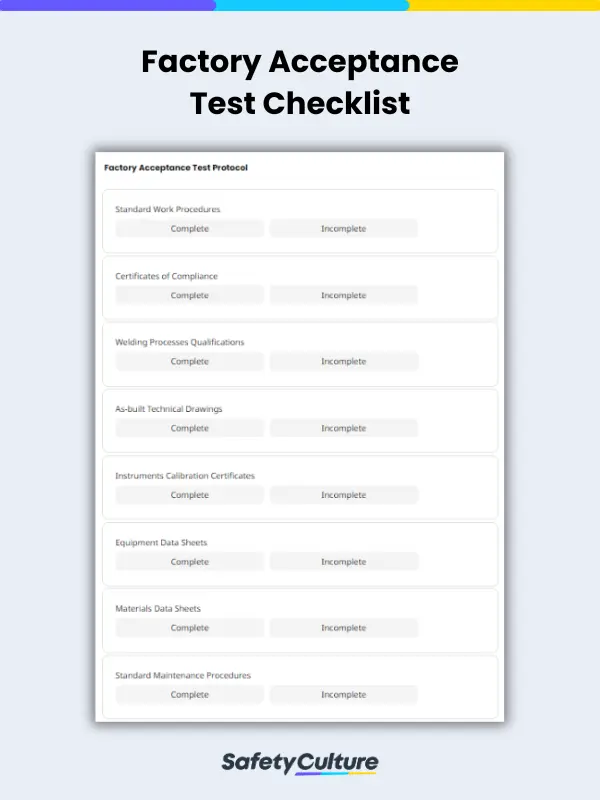
Hence, using a factory acceptance test checklist template can reduce costly project delays by ensuring the completion of FAT protocol, such as standard work procedures, certificates of compliance, and welding process qualifications, and implementing the proper factory acceptance test procedure.
What Should Be Included in a Factory Acceptance Test Checklist?
A good factory acceptance test checklist should enable quality managers to verify the following and more:
- Conformance to specifications
- Certificates of compliance
- Welding processes qualifications
- As-built technical drawings
- Instruments calibration certificates
- Standard work procedures
- Equipment data sheets
- Materials data sheets
- Control system
- Standard maintenance procedures
- Training materials
- Ergonomic assessment
Some other elements you must consider including in the checklist are personnel checks, post-FAT checklist, completion page, and sign-off.
How to Conduct FAT Using a Checklist
Conducting a factory acceptance test using a checklist is a critical step to ensure that equipment or systems meet specified requirements and quality standards before they are delivered to the customer. Hence, properly following a structured process is essential to achieving the desired outcomes and avoiding potential issues.
Follow these steps to effectively carry out a FAT with the help of a checklist:
1. Prepare for the FAT testing
Ensure that all parties involved, including the customer and the manufacturer, have reviewed and agreed upon the FAT checklist. Also, verify that the testing environment is set up and that all necessary documentation, tools, and personnel are in place.
2. Perform the tests
Test the equipment or system’s various functions, performance parameters, and safety measures. Make sure to document the results of each test, including any deviations or discrepancies from the checklist.
3. Document real-time observation
Designated individuals, including customers and third-party inspectors, must observe and document their real-time observations during the tests using the checklist. They can verify that these are conducted impartially and that the equipment meets the acceptance criteria.
4. Address deviations and issues
If the equipment fails to meet any of the acceptance criteria or if discrepancies are found during testing, develop a plan to address them. The manufacturer is responsible for rectifying the problems and retesting the equipment until it complies with the requirements specified in the checklist.
5. Finalize documentation and obtain approval
Once all tests have been successfully completed, and any issues resolved, finalize the documentation of the FAT results. This should include a summary of the tests, deviations, resolutions, and any relevant observations. Make sure to obtain approval from all parties involved before proceeding with the shipment of the equipment or system.
FAT Report Example
A factory acceptance test report serves as a crucial documentation tool, summarizing the results and findings of the FAT and helping you understand how it supports the assurance of a successful project outcome.
Here’s a factory acceptance test example when exported as a PDF report:
FAQs About Factory Acceptance Test Checklists
An FAT checklist is focused on verifying that the equipment or system meets design and quality standards at the manufacturer’s facility, while an SAT checklist is used to confirm that the equipment functions correctly in the real-world environment at the customer’s site. Both checklists play essential roles in quality assurance and risk mitigation at different stages of the equipment’s lifecycle.
Documentation serves as a comprehensive record of the FAT, capturing the procedures, results, deviations, and observations. This isn’t only essential for compliance with industry standards and contractual obligations but also facilitates issue identification and resolution.
Yes, a third-party inspector or expert can provide an impartial and expert assessment of the testing procedures and ensure that the equipment or system complies with industry standards, contractual requirements, and best practices. This adds an extra layer of credibility to the FAT process, enhances quality assurance, and instills confidence in the evaluation’s objectivity.