A Comprehensive Guide to Warehouse Management
What is warehouse management? What is its main difference with inventory management? Why is it important? What are its processes and common challenges?

Published 18 Nov 2025
Article by
7 min read
What is Warehouse Management?
Warehouse management is the overall process of overseeing the day-to-day operations of a warehouse. This generally includes the procedures involved to carry out activities such as receiving, storage, packing, and shipping of products in and out of warehouses. Moreover, warehouse managers, inventory managers, and logistics providers employ warehouse management to streamline product tracking, show accurate inventory levels, and increase warehouse efficiency.
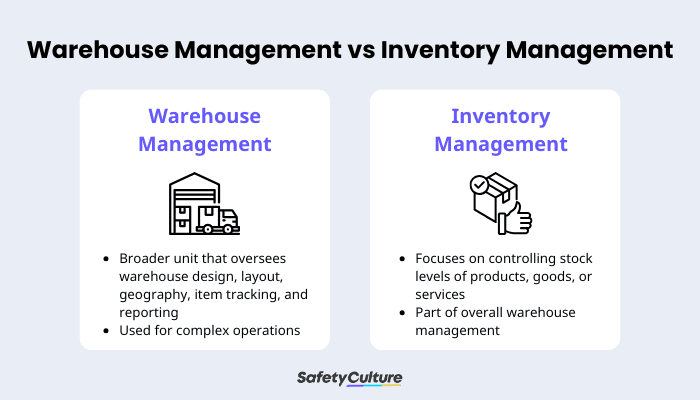
Warehouse Management vs Inventory Management
Warehouse management and inventory management are often used in tandem with one another, which sometimes leads to confusion over their primary purpose and distinctions. So, what is the main difference between the two?
Inventory management
Inventory management focuses on controlling stock levels of products, goods, or services. It uses information such as sales trends, historical data, and seasonal demands to keep the right products available without overstocking. It’s a crucial part of the overall supply chain and is part of overall warehouse management.
Warehouse management
Warehouse management, on the other hand, is a broader unit that oversees how materials move through the facility. It covers warehouse design, layout, geography, item tracking, and reporting. It also observes the policies and procedures involved in efficient warehouse operations through resources, including people, equipment, and finished products.
Additionally, warehouse management is ideal for bigger companies with complex operations, while inventory management is sufficient for smaller businesses’ needs.
Why is it Important?
According to a study released by Oracle, 82% of American consumers say delays in deliveries or other forms of disruption in the supply chain affect their daily life. As an essential component of the transport and logistics industry, warehouse management plays a huge role in ensuring the supply chain runs smoothly, whether it's small-scale or across multiple warehouses.
Businesses implement warehouse management for various reasons, but why is it an important factor in achieving highly efficient business logistics?
Controlled inventory levels – Real-time information from a well-managed warehouse gives teams clear visibility of stock on hand. Accurate counts mean fewer shortages, reduced discrepancies between the demand and supply of the products, and lower holding costs for the company.
Improved customer service – When orders are prepared, delivered, and fulfilled in a timely and accurate manner, this can create a lasting positive impact on customers. When in-demand items are always available and orders are shipped on time, it leads to satisfied and happier customers.
Increased productivity – Data-driven layouts and material flow reduce wasted movement and handling time. Placing commonly used materials near production, packing, or shipping areas keeps throughput high and teams focused on value-adding work.
Achieve operational excellence
Cultivate a culture of excellence with our digital solutions that enhance efficiency, agility, and continuous improvement across all operations.
Warehouse Management Process
The warehouse management process is composed of six major steps that are highly dependent on each other. Each stage in the process would affect how the next ones would perform, so it’s crucial to ensure that each one is operating according to its ideal functions. Below are the six core processes of warehouse management:
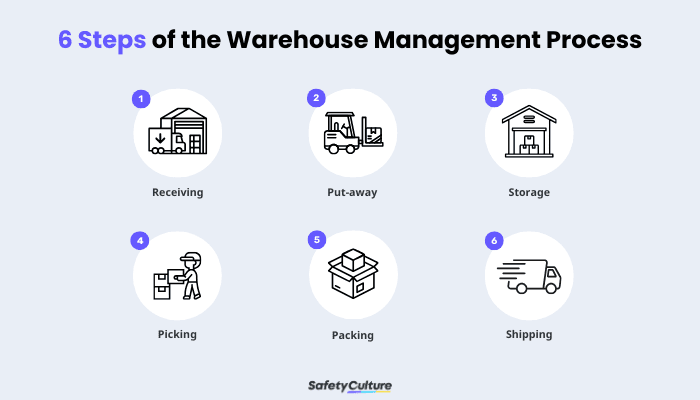
Step 1: Receiving
Warehouse receiving is the first checkpoint for quality and accuracy. During this step, receivers check incoming shipments to ensure the right quantity, condition, and timing.
It serves as the business’ first layer of protection against costly errors or damaged goods. During this stage, warehouse receivers can identify items that aren’t at par with expectations, send them back to the suppliers, and therefore save the company from potentially costly damages.
Step 2: Put-away
Put-away is the process of moving received items from the receiving docks onto their most ideal storage locations. An efficient and accurate put-away process ensures the safety of employees and the safe storage of items. It also helps maximize space allocation, eases tracking of items, and minimizes traveling time of products—which all ultimately enhance the whole warehouse experience.
Step 3: Storage
In the storage process, it’s important to keep items in their most appropriate location throughout the warehouse. Considerations include safety, space, and efficiency. To achieve optimum use of the facilities, warehouse managers can ask questions along the lines of:
Are the items safely stored in the appropriate location in the warehouse?
Are perishable items stored in areas with appropriate climate control ?
Are items stored in a way that maximizes the storage spaces available?
Are items stored in a manner that they are easy to track and are highly visible?
Are items easily accessible to employees as needed?
Step 4: Picking
Picking, as the name suggests, is the warehouse management process where employees locate and pick up individual items across the warehouse to fulfill orders. This is one of the most crucial steps in the whole process because it’s directly tied to customer satisfaction.
This process is also one of the most labor-intensive and most expensive activities for warehouses. As such, optimizing this step not only enables businesses to efficiently manage orders but also to reduce errors, drive profit, and strengthen company reputation.
Step 5: Packing
Next, we have the process of packing or packaging. This is the part where all the picked items for a specific customer are consolidated and prepared to be delivered. Considerations that have to be observed include components such as accurate packing slip, appropriate packaging materials (especially for fragile items), and the ideal packaging weight.
The primary goal of packing is to ensure that items will be safe and damage-free the moment they leave the premises of the warehouse until they are delivered to the customers. Warehouse managers can use tools such as checklists or standardized packing procedures to ensure quality packaging consistency for all items and reduce damage-related costs.
Create your own packaging quality control checklist
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
Step 6: Shipping
Shipping or delivery marks the final step of the warehouse management process. It’s where the finalized orders are shipped out using the correct transportation mode to bring the items to the customers.
Shipping is only considered successful if the items are delivered with the correct documentation, at the right time, and according to the expected quality.
Top Challenges of Warehouse Management
Because there are several processes, people, and strategies involved to ensure its smooth operation, warehouse management encounters numerous challenges. Aside from issues with warehouse safety,food warehousing, and other sensitive goods, the following are some of the top challenges that the warehouse sector commonly faces:
Skills gap – Currently, one of the top challenges that the industry of warehouse, transport, logistics, and the whole supply chain faces is the skills gap and driver shortage. In the United States, there’s a historic truck driver shortage of 80,000 just in the year 2021 alone. While the UK continues to experience Heavy Goods Vehicle (HGV) driver shortage caused by an aging workforce, lack of diversity in the industry, and reliance on the international workforce.
Low visibility – Minimal visibility can also lead to overstocks, inadequate use of space, and inaccurate inventory. To address this, businesses have the option of utilizing tracking tags such as Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) tags, barcodes, IoT devices , or QR codes.
Delays in processes – An unoptimized warehouse operation is prone to inefficiencies and slower progress of activities. These issues not only affect the warehouse process itself but can also impact customer satisfaction if delays are noted during order fulfillment.
Damaged products – If warehouse items are received, stored, or shipped improperly, this causes significant damages to products and goods. Accumulating damaged items is a costly expense for businesses and their reputation would be at stake if it frequently affects customers.
Demand volatility – A lot of factors go into the concept of supply and product demand—holidays, seasonal changes, extreme weather, and economic situation are just some of these. Having accurate and real-time information while ensuring that the supply chain is managed properly, can help combat this challenge.
Non-automated process – Warehouses that still rely on manual processes of checking, inspecting, tracking, and documenting warehouse items are at numerous disadvantages. These weaknesses can be along the lines of higher labor costs, larger inventory discrepancies, and slower order fulfillment.
To combat these challenges, businesses can always utilize tools or new technologies that could streamline warehouse operations and improve efficiency.
Conduct Effective Warehouse Management with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, enhance resource utilization, and build an agile and scalable infrastructure with SafetyCulture. Strive for operational excellence to boost competitive advantage, foster sustainable growth, and deliver long-term value.
✓ Save time and reduce costs
✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents
✓ Boost productivity and efficiency
✓ Enhance communication and collaboration
✓ Discover improvement opportunities
✓ Make data-driven business decisions
FAQs About Warehouse Management
Related articles
Digital Tool
Operations

Types of Forms: What You Need to Know
Learn about the types of forms your business can use to standardize processes, collect valuable and actionable data, and ensure compliance.
Logistics
Operations

Warehousing Logistics (Storage Logistics)
Understand warehousing logistics and manage the storage, movement, and handling of inventory to effectively meet supply and demand.
Operations
Human Resources

The Role of HR in Workplace Health and Safety Management
Learn what an HR health and safety program covers, its key responsibilities, and the best practices for creating safer working environments.