Published 26 Sept 2025
Article by
5 min read
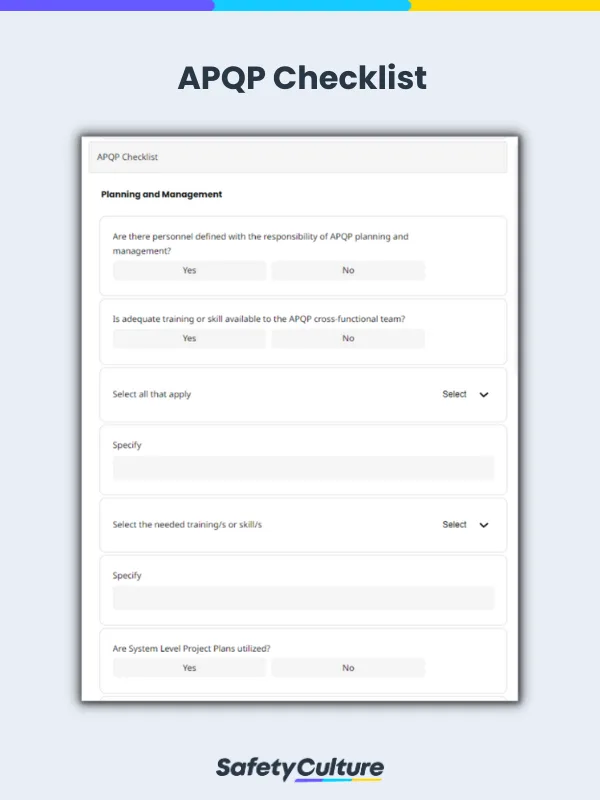
What is an APQP Checklist?
APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning) checklists are tools used by Cross-Functional Teams (CFTs) to achieve optimum results throughout the APQP process—pre-planning, designing, developing, and validating the product and the process, launching the product, and assessing it for continuous improvement. Using an APQP checklist can help ensure the on-time production of quality products at the lowest cost and increase customer satisfaction.
What is Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)?
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) is a structured process employed when introducing a new product in the market or incorporating changes in the product after its release. This method helps detect defects during production and ensures that there is proper documentation of the processes involved when manufacturing new products.
A Cross-Functional Team (CFT) composed of engineering, manufacturing, quality, procurement, and distribution professionals performs an APQP to ensure that products meet or even exceed customer requirements. Primarily practiced in the automotive industry, it has been adopted by other manufacturing sectors such as aerospace, defense, medical, and pharmaceutical since this method is proven effective.
What’s Included in an APQP Checklist?
An APQP checklist ensures that all aspects of product development and production meet quality standards. The checklist should typically include:
Planning and Management : Define project scope, goals, timelines, and resources. Establish quality objectives and risk management strategies.
Product Design and Development : Ensure design specifications meet customer and regulatory requirements. Validate designs through testing and analysis.
Process Design and Development : Document production processes and identify potential failures using FMEA. Validate processes to ensure consistent quality.
Validation and Verification : Validate both design and process to meet specifications. Conduct thorough testing and maintain detailed records.
Production and Post-Delivery : Implement production controls and plan for customer support. Ensure consistent quality during production.
By following these steps, there is an increased chance that an APQP checklist will be a valuable asset to your company.

What is the Difference Between APQP and PPAP?
PPAP, which stands for Production Part Approval Process is one of the components and output of an APQP. But what really is the main difference between the two?
APQP | PPAP |
Advanced Product Quality Planning | |
What are the 5 phases of implementing APQP? Phase 1:Plan and Define ProgramPhase 2:Product Design and Development VerificationPhase 3:Process Design and Development VerificationPhase 4:Product &Process Validationand Production FeedbackPhase 5:Launch, Assessment &Corrective Action | PPAP belongs to the 4th phase of APQP: Product & Process Validation and Production Feedback |
APQP is a process for introducing a new product in the market or for incorporating changes in the product after its release. | The goal of PPAP is to provide evidence that the manufacturer and supplier have understood the customer’s specifications and that they can produce products that consistently meet those specifications. |
APQP and PPAP both have essential importance, especially to the aerospace and automotive manufacturing industry. They help ensure that quality materials and products are created, released, and continually improved.
5 Common APQP Challenges and Cost-efficient Solutions
Manufacturing products based on APQP requirements can be challenging, but it enables Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and the entire supply chain to gain long-term, high yields. Here is how CFTs can proactively solve the 5 common challenges of advanced product quality planning:
1. IATF 16949:2016 Compliance
IATF 16949:2016 is an international standard for automotive quality management systems. Compliance with the IATF standard requires the proper documentation of processes implemented, inspections conducted, and actions taken for nonconformance. Perform regular IATF audits using a digital IATF 16949:2016 Audit Checklist to schedule routine compliance checks, assign corrective actions, and secure records in the cloud.
2. Clear Direction and Responsibilities
Management should oversee the advanced product quality planning process based on the quality policy of the company. Project managers should facilitate communication and collaboration among cross-functional teams to remove the guesswork and address unresolved issues. Take advantage of a mobile-ready APQP documents checklist to easily manage priorities and ensure the completion of all deliverables from pre-planning to production.
3. Adequate Knowledge and Resources
Engineering, manufacturing, and quality personnel should understand what APQP requirements entail and how to deliver them. Here are some of the most widely used APQP tools for designing, developing, and validating products and processes:
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a systematic method of anticipating potential failures in manufacturing processes and mitigating their impact on customers. In conducting Design and Process FMEAs , utilizing an easy-to-use FMEA template can help properly identify the mechanism of failure, accurately compute the Risk Priority Number (RPN), and regularly monitor corrective actions.
First Article Inspection (FAI) is the process of verifying design requirements of a product from the first production run, including part number accountability, materials/processes, special processes, functional tests, and design characteristics. An FAI report form converted into a SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) mobile app empowers quality inspectors to automatically generate a shareable report from the moment an FAI is completed.
Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) is used to verify that newly produced equipment works according to its construction code and customer purchase order specifications. It is performed in the manufacturing facility before delivery and installation at the customer’s site. Immediately resolve equipment nonconformities and keep the project on track and within its budget by using an intuitive FAT checklist .
4. Time Management
As a strategy for actionable data, ascertain all inspections/tests are recorded and analyzed to develop and implement corrective and preventive actions. To save time and effort, project managers should create automated workflows and easily manage reporting procedures, especially for visual inspections and risk assessments.
5. Discipline and Team Accountabilit y
CFTs should meet on a regular basis to review APQP priorities and check the status of the entire advanced product quality planning process. Together with a record of open issues, risk and opportunity lists should also be maintained and presented to management.
Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.