What is FMEA?
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a systematic method of anticipating potential failures in business processes and mitigating their impact on customers. An FMEA usually starts with a brainstorming session composed of an experienced team and ends with a re-analysis of failure risks after corrective actions have been applied. Ultimately, FMEAs can help prevent costly manufacturing failures, improve product and service reliability, and increase customer satisfaction.
Types of FMEA
While there are a variety of FMEA types, all follow the same principles—focusing on detection, elimination, and/or mitigation of critical risk events. The 2 most common types of FMEA are:
- Design FMEA (DFMEA)
DFMEA or Design FMEA is applied during the early or end stage of product design. It aims to uncover potential failures associated with product design that could result in risks to health and safety, financial stability, and the environment. - Process FMEA (PFMEA)
PFMEA or Process FMEA is done prior to the start-up of a new process or an existing process. It aims to discover risks associated with process changes that can negatively impact product quality, process reliability, customer satisfaction, public safety, and the environment.
What is an FMEA Template?
An FMEA template (or FMEA form) is used by product design or process improvement teams to determine the risk priority number (RPN) of the mechanism of equipment or process failures and monitor the corrective actions delegated to key personnel. Using specific FMEA templates such as a design FMEA template or a process FMEA template can help easily determine more potential failures at the onset and prevent avoidable losses in manufacturing operations.
FMEA Success Factors
To achieve optimum results from FMEAs, it should be done correctly—performed on the correct parts, by the correct team, in the correct time frame, and with the correct procedure. Here are the essential ingredients for success in implementing FMEAs:
- Proper Identification of the Mechanism of Failure
Key information such as the functions (process step or input) should be available before conducting meetings and visible during brainstorming. The mechanism of failure (potential failure modes, effects, and causes) can be identified properly when FMEA teams account for past failures, agree upon certain assumptions, and establish ground rules. Inviting customers and suppliers is a good idea to help gather alternative viewpoints. - Accurate Computation of RPN
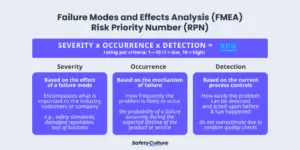
FMEA RPN Risk Analysis
The RPN is used to prioritize the potential failures that require additional quality planning. It is the product of the numerical severity, occurrence, and detection ratings. Determine the RPN accurately by following the guide below:
As a rule of thumb, FMEA teams should focus their improvement efforts on potential failures at the top 20% of the highest RPNs. These high-risk failure modes should be addressed through effective and executable action plans.
- Regular Monitoring of Corrective Actions
Companies usually fail to mitigate the adverse effects of failures because they neglect following up on corrective actions and their effectiveness. FMEA teams should review high-risk failure modes with the management and update FMEAs with subsequent tests and linkages to control plans.
FMEA Report Example
Here’s a practical example and implementation of the FMEA method:
| FMEA Step | FMEA Example |
| Process Step/Input – Utilize a process map to identify all the steps and key inputs on the process being analyzed | Pouring a concrete foundation for a building |
| Potential Failure Mode – For each process step and key input, list all of the different things that could go wrong, AKA: Failure modes | The cured concrete doesn’t support the weight of the structure placed on top of it |
| Potential Failure Effects – Anticipate the impact of the failure on the output of the process | The structure could collapse |
| Severity Ranking – Assign a severity ranking to each effect that has been identified. This can range from 1 (low impact with almost no effect) to 10 (high impact with catastrophic results). Set criteria for each ranking from 1-10. | 10 Very High – This could result in catastrophic failure, injury, and damaged public opinion with little to no warning |
| Potential Causes – Determine the root cause of each failure mode. Utilize root cause analysis tools such as 5 why and fishbone diagrams as well as employee experience |
|
| Current Controls – For each potential cause, list the current control measures in place to prevent failures. These are things like procedures, tests, inspections, and other mechanisms |
|
| Occurrence Ranking – Assign a probability to the likelihood or frequency of the failure mode occurring. This can range from 10 (very likely) to 1 (very unlikely). Have a set objective criteria for each rank between 1 and 10. | 5 – There have been occasions of this happening but it is not very frequent. |
| Detection Ranking – This represents the likelihood of a failure mode being detected if it were to occur. A detection ranking of 10 is bad, it means there’s almost no chance it will be detected. A rank of 1 means it is almost certain. Define criteria for each number between 1 and 10 with the likelihood of detection getting less as the number goes up. | 3 – There is a high likelihood that this failure mode will be prevented or, worst case scenario, it will be detected prior to setting the structure. |
| Risk Priority Number – This is the relative risk ranking. It is calculated by multiplying a failure modes severity x occurrence x detection. The mode with the highest RPN should be addressed first and so on down. | 150 – This falls at the low end of the priority ranking because, although the outcome is severe, the likelihood is low. |
| Action Plan – Develop an action plan to reduce failure modes RPN. Include who is responsible, what will be done, and when it will be done by | It has been determined that the current detection and prevention methods are adequate to prevent the concrete from failing. The general foreman is to ensure all quality procedures are followed and all installation procedures are adhered to.
However, out of an abundance of caution, we will have a second engineer review the mix designs and steel plans to ensure the structure will be adequately supported |
| Recalculate RPN – Recalculate a failure modes RPN once action has been taken to reduce it to ensure they had a positive effect. | 90 – The ranking has come down due to a lower occurrence score. |