Cyber Security: Definition, Types, and Examples
Get answers to the following questions: What is cybersecurity? What are the 3 major types of cyber security? What are the 7 types of cyber security threats?

Published 26 Mar 2025
Article by
9 min read
What is Cyber Security?
Cyber security (or cybersecurity) is the practice of protecting and defending systems, networks, programs, data, and devices from malicious digital attacks. This starts with preventing unauthorized access, which could be part of coordinated cyber attacks and other digital threats against a company.
Types of Cyber Security
The 3 major types of cyber security are network security, cloud security, and physical security.
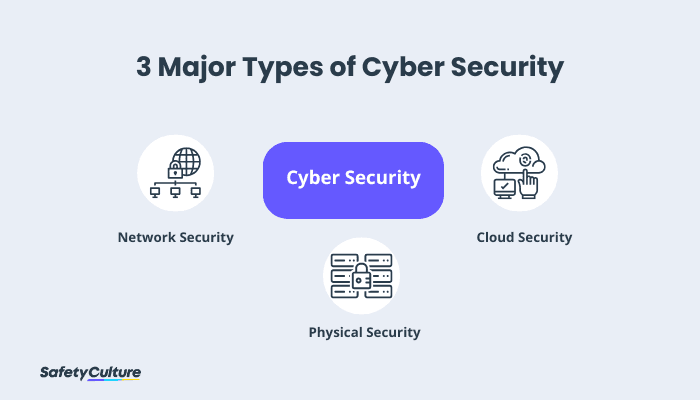
Your operating systems and network architecture make up your network security. It can include network protocols, firewalls, wireless access points, hosts, and servers. Cloud security, on the other hand, is the encryption of cloud data at rest, in motion, and in use. Meanwhile, physical security refers to the control of physical access to computers and other devices.
Other types of cyber security include:
Application security
Information security
Internet of Things (IoT) security
Mobile security:
Identity and Access Management (IAM):
Endpoint security
Why is It Important?
Neglecting cyber security can make your sensitive information vulnerable to all kinds of cyber attacks that could not only halt business operations but also damage the company’s reputation. Another reason why cybersecurity is important is that today’s customers are increasingly aware of the dangers lurking in the current digital landscape and expect their data to be governed and protected against cyber attacks.
Types of Cyber Threats and How to Prevent Them
Below are the types of cyber threats you need to look out for and tips on how to prevent them from infiltrating your digital assets:
1. Malware
Malware is cyber attack software. It’s specifically designed to help the hacker or group of hackers gain unauthorized access. Whether in manufacturing or healthcare, malware can target digital networks and critical systems. There are many different types of malware which are:
Ransomware – Prevents owners from accessing their own computer systems and files; can include threats to erase data or make data public.
Botnet software – Since it uses a small amount of processing power, botnet software can infiltrate multiple devices (forming a botnet) without being detected by most users.
Trojans – Downloaded by users because it’s disguised as legitimate software.
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) – If a Trojan is a completely fake software appearing to be legitimate, RATs instead infiltrate a system through a covertly installed backdoor.
Viruses and Worms – The difference between them is that a virus needs a host program or file, while a worm does not. Both are self-replicating and infectious.
Ways to Prevent Malware:
Install anti-virus software and, where possible, set it to automatically scan your systems and report to you if it finds anything suspicious.
Add several layers of protection to make it extremely difficult for hackers to access digital assets (e.g., change passwords frequently, require additional authentication, etc.)
2. Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS)
The goal of a DDoS is to crash the target server, website, or network by overloading it with traffic. The first effect of this attack is that users are unable to access the server, website, or network. The second effect is that the target becomes more susceptible to other cyber threats that allow the hacker to access it and go through confidential data without anyone watching.
Ways to Prevent DDoS:
Implement network security protocols such as firewalls and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). The key is to set up a system that effectively balances the load at all times.
Address loopholes or gaps in your cyber security. DDoS requires multiple sources for it to overwhelm its target and successfully blocking one of those sources can stop your server, website, or network from overloading and crashing.
3. Social Engineering
Social engineering is the use of manipulation and deceit to gain unauthorized access to systems and information. Unlike other types of cyber threats which look for and then pass through neglected access points into your company’s system, network, or program, social engineering exploits the human factor of cyber security.
Ways to Prevent Social Engineering:
A key defense against social engineering is to train employees to be emotionally intelligent and perceptive. Those provided with the right training are more likely to recognize the subtle social cues that indicate they are being deceived or that the person they are communicating with is not being entirely truthful.
Have robust authentication procedures for access to company systems. This is to prevent human error or a situation in which an employee inadvertently gives access to a person with bad intentions because they “know” them or see them as completely harmless.
4. Phishing
The most common type of social engineering is phishing, which involves sending fake messages to people within the company. These fake messages can be quite convincing and usually aim to get the recipient to divulge private information or click on a link that allows malware to access their accounts or infect their computer system.
Ways to Prevent Phishing:
Require the use of corporate emails and spam filters.
Educate employees on what fake messages from key people in the organization can look like (e.g., hackers will try to convey a sense of urgency to get you to respond to them and typically bad formatting and incorrect grammar is a sign of a phishing attempt).
5. Man-in-the-Middle (MITM)
Man-in-the-middle attacks take place when the hacker is able to insert themselves into an information relay process, such as a device connecting to a network or a user logging into an account. Hackers in this position can read and use the data being passed and even gain further access to the device, network, and the other systems linked to them.
Ways to Prevent MITM:
Don’t connect to public Wi-Fi networks or those that don’t require login details.
Only visit websites with the HTTPS protocol (“S” stands for secure).
6. Password Attack
A password attack is basically any attempt to obtain someone’s password without their consent. The following are the various methods and tools that hackers use to get passwords:
Physically spying on someone as they enter their password
Guessing using publicly available information (such as those on social media accounts, like birthdays, initials, favorite fictional characters and foods, etc.)
Keyloggers (records the person’s keyboard strokes) and other spyware
Password databases (i.e., websites) with weak security
Hacking tools and password generation programs
Other types of cyber threats (e.g., social engineering, phishing, MITM attacks)
Ways to Prevent Password Attack:
Never use the same password or variations of a password for multiple accounts.
Use unique (i.e., password is only for one account) and strong passwords (containing numbers, special characters, uppercase and lowercase letters) that are unrelated to your interests or at least those shown on your public social media accounts.
7. SQL Injection
A Structured Query Language (SQL) injection is adding malicious code to a server using SQL. This piece of code can be added via website search box and can force the server to release sensitive information that the hacker can access and even modify.
Ways to Prevent SQL Injection:
Since SQL injection is a very technical type of cyber attack, you will need the help of your webmaster or an IT specialist in resolving SQL vulnerabilities.
The most common ways to prevent SQL injection are to use input validation, parameterized queries or prepared statements, and web application firewalls.
Cyber Security Examples
Examples of cyber security measures include:
People: There is a process for effectively cutting off access to facilities and information systems when an employee/contractor terminates employment.
Physical Security: Personal Computers (PCs) are inaccessible to unauthorized users (e.g., located away from public areas).
Account and Password Management: Passwords are secure, not easy to guess, regularly changed and employees don’t use temporary or default passwords.
Confidentiality of Sensitive Data: Disposal procedures identify appropriate technologies and methods for making hardware and electronic media unusable and inaccessible (such as electronically wiping drives).
Disaster Recovery: There is a process for creating retrievable back-up and archival copies of critical information.
Security Awareness: The company’s awareness and education plan teaches proper methods for managing credit card data ( PCI standards ) and personal private information (e.g., social security numbers, names, addresses, phone numbers).
Compliance: Management regularly reviews lists of individuals with physical access to sensitive facilities or electronic access to information systems. A Security Technical Implementation Guide checklist would be useful to ensure and enhance security in an organization’s system and its products.
Download Free Cyber Security Checklist | SafetyCulture
Create Your Own Cyber Security Checklist
Cyber Security Training
An essential component of protecting the company from cyber attacks and other malicious digital threats is providing cyber security training to employees using Training. Cybersecurity courses in Training are fun, short, and easy to remember. Promote cyber security awareness in your organization with the following:
Cyber Security – This course is ideal for those who need an introduction to the basics of cyber security, such as safely using emails, password safety, and safe internet use.
Cyber Security Awareness – This is a more advanced cyber security course for those who are already familiar with the basics and want to know more about the different types of cyber threats out there, such as injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
Cybersecurity & Insider Threats – This specialized cyber security course highlights a common myth about cyber attacks, which is that they are only done by outsiders. In this course, employees will be trained on how to spot the signs of an insider threat, such as suspicious online activity and high-volume data transfers.
How Can SafetyCulture Help Boost Cyber Security
SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) is a digital, multi-functional platform for teams and enterprises that want to protect and govern their data, devices, systems, networks, and programs from unauthorized access and other cyber security threats. With SafetyCulture, you can do the following:
Conduct Information Technology (IT) and cyber security risk assessments .
Prepare for ISO 27001 certification and streamline your Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Perform network security audits as part of your cybersecurity initiative.
Ensure that software patches (aka bug fixes) are working as intended.
Maintain servers and computers regularly to prevent crashes from compromising your cyber security efforts.
Get started with SafetyCulture for free or download any of our free cyber security checklists.
Free Cyber Security Checklists
Cyber Security Checklist
This cyber security checklist will help you record the status of cyber security controls within your organization. Protect your workplace from cyber attacks by doing the following:
Check if staff ID wearing is enforced.
Assess the physical security of computers and other devices.
Review the strength of passwords.
Manage access to disposed information.
Promote a culture of cyber security through awareness and education.
Article by
SafetyCulture Content Team
SafetyCulture Content Contributor, SafetyCulture
View author profileRelated articles
Information Technology
Security

A Guide to Global Data Privacy Day
Learn more about Data Privacy Day and the activities to celebrate it to ensure a more privacy-centric and efficient workplace.
Security
Information Technology

A Guide to Ensuring Cybersecurity for Manufacturing Organizations
A deep dive into what cybersecurity for manufacturing is, its importance, and the different ways for teams to enhance their cybersecurity framework.
Security
Information Technology

Phishing Attacks: How to Spot Them and Mitigate Them
A close look at what a phishing attack is, why it’s dangerous for companies, and the different ways teams can combat these attacks.