What is Quality Risk Management?
Quality risk management is a systematic, risk-based approach to quality management. The process is composed of the assessment, control, communication, and review of quality risks. It is especially critical in the pharmaceutical industry, where product quality can greatly affect consumer health and safety.
Quality Risk Management Principles
According to the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), quality risk management has two primary principles, which are:
- Quality risk evaluation should be based on scientific knowledge, such as data and research, and ultimately work towards the protection of consumers.
- The higher the risk level, the stronger a QRM process should be. The level of effort, formality, and documentation should be equal to the risk level.
These principles can be seen in the examples provided below by the European Commission in its Good Distribution Practice (GDP) Guidelines for Medicinal Products:
- Temperature and environment control: Temperature mapping should be repeated according to the results of a risk assessment.
- Equipment: Equipment should be calibrated at defined intervals based on a risk and reliability assessment.
- Qualification and Validation: The scope and extent of key equipment qualification and/or key process validation must be determined using a documented risk assessment approach.
- Operation – Principles: All means available must be used to minimize the risk of falsified medicinal products entering the supply chain.
- Returned Medicinal Products: Returned products must be handled according to a documented, risk-based process.
- Transportation: Risk assessment of delivery routes should be used to determine where temperature controls are required.
Why Quality Risk Management is Important?
Quality risk management is important because it can facilitate better and more informed decisions. With QRM, decision-making has the following qualities:
- Decisions are data-driven instead of subjective.
- The potential impact on the lives of consumers is prioritized.
Another benefit is that companies can use risk level as the basis for prioritization, leading to a more efficient use of resources. Moreover, it helps build a culture of trust and transparency among companies and regulatory authorities.
Quality risk management is also a requirement of GDP, an internationally recognized set of standards for ensuring the quality of medicines throughout the supply chain. While GDP is primarily enforced in Europe, there has been an increase in its use in the United States and other countries.
Quality Risk Management Process
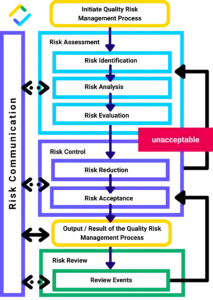
Solid arrow – Required, Broken arrow – Optional; If risk control is unacceptable or ineffective, perform risk assessment again.
The following steps are based on ICH Q9, a guideline developed by the organization to standardize quality risk management:
Step 1: Before Starting
Form a cross-functional team and choose a leader. Example QRM team:
|
|
Each member of this team will be responsible for coordinating quality risk management across various functions and departments in the company.
Step 2: Risk Assessment
- Define the problem: Ask “What might go wrong?”
- Risk identification: Identify hazards related to the problem.
- Risk analysis: Estimate risk associated with identified hazards. For each estimated risk, define the likelihood of occurrence and the severity of consequences.
- Risk evaluation: Based on risk analysis, evaluate each risk using a 3×3 risk matrix, 4×4 risk matrix, or 5×5 risk matrix based on your needs.
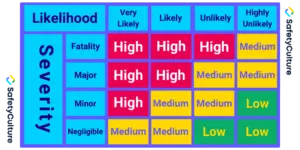
To quantify the expression of risk, assign a numeric value to each likelihood and severity category. The formula for calculating the risk level based on these values is up to you.
- Set rules for defining the overall risk level: For example, if more than half of the risks are high, then the overall risk level is high.
The output of the risk assessment will either be a numeric value or qualitative description expressing the overall level of risk posed by the problem.
Step 3: Risk Control Selection
The key focus of this step is choosing between risk reduction and risk acceptance. Answer and discuss the guide questions below with other QRM team members before making a decision:
- Is the risk above an acceptable level?
- What can be done to reduce or eliminate the risk?
- What is the appropriate balance among benefits, risks, and resources?
- Are new risks introduced as a result of initial risk being controlled?
Also keep in mind that the amount of effort used for risk control should be equal to the significance of the risk/s. If needed, refer to the output of the risk assessment in Step 2 or conduct a cost-benefit analysis to help determine the appropriate risk control.
Step 4: Risk Control Implementation
- Risk reduction is the set of actions taken to minimize the likelihood of occurrence and the severity of consequences. It may also include improving the detectability of hazards (i.e. making hazard identification easier) and risks (i.e. catching risks before they cause further damage).
- Risk acceptance is a decision to accept risk since it cannot be eliminated. This form of risk control is typically only chosen when mitigating the risk is out of the QRM team’s control. Another case where it may be the best option is when risk reduction has already been applied and the remaining risk is at an acceptable level.
Step 5: Risk Review & Risk Communication
Once risk control has been implemented, establish a system for monitoring its effectiveness. Quality risk management should be continuously reviewed, especially when:
- there is new research, experience, knowledge, or data on specific risks;
- there are events that may have an impact on the original decision/s; and
- factors influencing the overall risk level have changed.
Meanwhile, risk communication involves sharing information on the entire process with stakeholders who are not part of the QRM team. It also includes documenting the QRM team’s thought process at each step and the results they were able to achieve after completing a step.
Create Your Own Quality Risk Management Template
Eliminate manual tasks and streamline your operations.
Get started for FREEQuality Risk Management Tools
While following the steps of the quality risk management process above is sufficient for starting with QRM, certain industries or companies may need the help of recognized tools to fully deploy their strategy. Below are 3 quality risk management tools, their descriptions, and templates to help get you started:
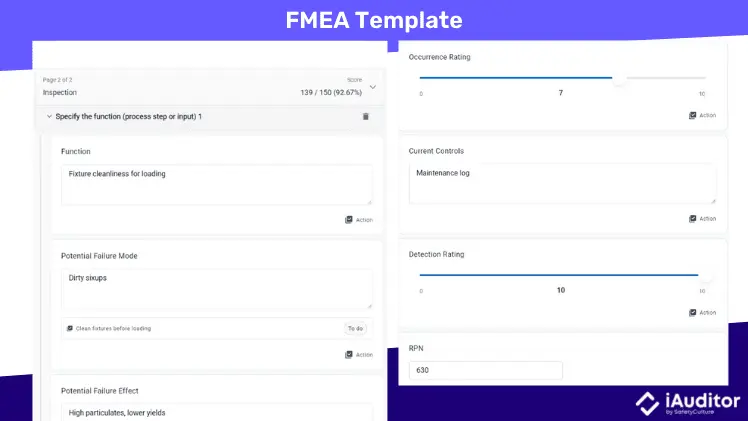
FMEA
Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a systematic method of anticipating potential failures in a process, product, or design and mitigating the negative impact of those failures on consumers. Key elements of this tool are mechanism of failure, risk priority number (RPN), and follow-up corrective actions.
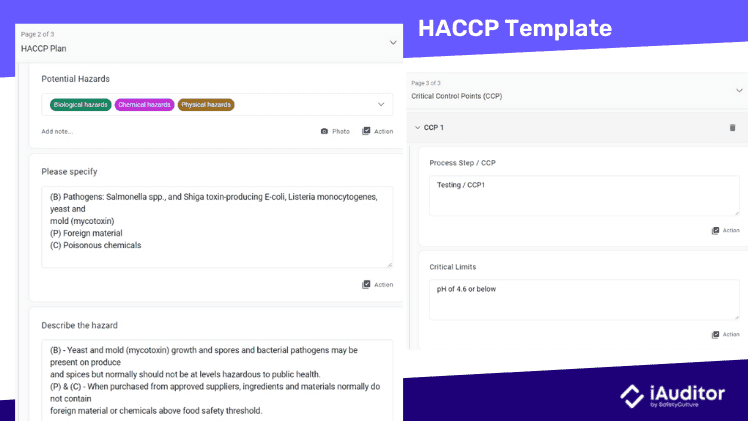
HACCP
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a monitoring system for identifying and controlling hazards. First, a hazard analysis is performed on each step in the production process. If there is an opportunity to prevent, mitigate, or eliminate a hazard, the step is considered a critical control point.
HAZOP
Hazard Operability Analysis (HAZOP) is a risk management technique used to determine functional flaws in manufacturing systems. Similar to FMEA, it involves exploring different scenarios where a process, design, or procedure could deviate from its intended function.
Effectively Manage Quality Risks Through QRM Training
One thing you can control is the way you address and mitigate risks involved in quality management. Hence, you must standardize these processes in your organization by providing regular QRM training to employees.
With the help of SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor)’s Training, leaders, supervisors, and facilitators can create and deploy training programs targeted to the needs of the business. They can also monitor course completion progress and make necessary follow-ups to ensure no one misses training requirements for compliance.
Through easy-to-grasp training courses and modules created using the platform, employees can take charge of their knowledge and skill development to help manage quality risks and minimize their negative impact on the organization.
A Mobile App for Managing Quality Risks
SafetyCulture provides thousands of free templates (such as the FMEA, HACCP, and HAZOP templates above) which quality managers can use to complete checks, conduct inspections, perform audits, and more.
Create and implement your entire QRM program using the SafetyCulture app. Here’s how:
- Use the Templates feature to start identifying and assessing risks.
- Use the Inspections feature to ensure that risk control measures are being followed.
- Use the Issues feature to empower your workers to raise urgent problems immediately.
- Use the Actions feature to assign tasks to your other QRM team members.
- Use the Training feature to empower your teams to do their work more effectively and aligned with your organization’s best practices.
- Use the Assets feature to manage your organization’s equipment, machinery, tools, and other tangible assets that are valuable to ensuring quality and safe processes.