What is Electrical PPE?
Electrical PPE stands for electrical Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). It refers to a range of specialized gear and equipment designed to protect individuals who work with or around electricity from electrical hazards. Using electrical PPE is a vital part of electrical safety protocols and should always be accompanied by proper work practices and adherence to relevant safety regulations and standards.
The Importance of PPE in Electrical Safety
As per the Safety and Health Magazine, the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) found that workers in the construction and extraction industries accounted for 40%, and those in installation, maintenance, and repair work accounted for 20% of electrical fatalities caused by electrical hazards and risks.
Electrical hazards can include electric shock, burns, arc flashes (sudden releases of intense energy during electrical faults or short circuits), and arc blasts, which can occur during tasks like electrical installation, maintenance, troubleshooting, or repair. In this regard, the proper and safe use of PPE serves as a barrier between the worker and the electrical energy, preventing or minimizing the impact of potential hazards.
Aside from playing a crucial role in ensuring worker safety, here are more reasons why PPE for electrical safety must be prioritized:
- Protection Against Electrical Shock – Electrical PPEs, like insulated gloves and voltage-rated tools, are designed to withstand and insulate against the voltage levels present in electrical systems.
- Prevention of Burns and Arc Flashes – Flame-resistant clothing and arc flash suits help resist ignition, reduce the extent of burns, and provide thermal protection in case of an arc flash incident.
- Reduction of Electrical Contact Injuries – Electrical PPE, like safety shoes with non-conductive soles and insulating mats, provides insulation and prevents the flow of electric current through the worker’s body, reducing the severity of injuries in case of an electrical fault.
- Compliance with Safety Regulations – Workers and employers can ensure compliance with relevant regulations in countries and states to maintain a safe work environment.
- Risk Mitigation – Electrical PPE acts as an additional layer of protection, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries and the overall risk associated with electrical work.
Types of PPEs in Electrical Work
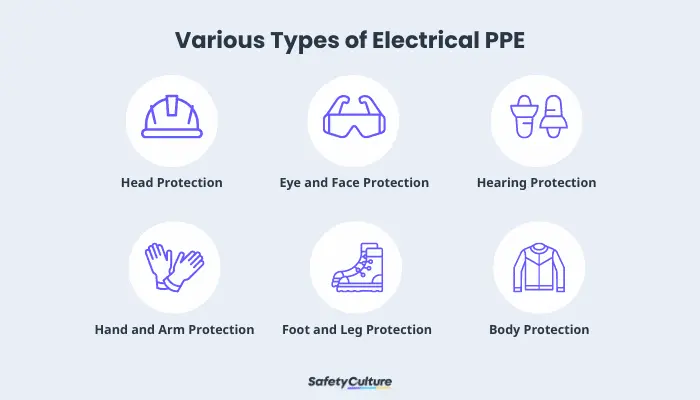
Various Types of Electrical PPE
It’s important to select the types of electrical PPEs to be used based on the specific electrical hazards and voltage levels present in the work environment. The following are some essential types of PPE for electrical work:
- Head Protection:
- Hard Hats – with electrical insulation properties to protect against falling objects, electrical shock, and impact hazards
- Eye and Face Protection:
- Safety Glasses – with side shields or goggles to protect the eyes from flying debris, sparks, and other hazards
- Face Shields – provide additional protection to the face and eyes against larger hazards, such as arc flashes or chemical splashes
- Hearing Protection:
- Earplugs – made of foam or other materials that can be worn to protect the ears from excessive noise levels when working with loud electrical equipment
- Hand and Arm Protection:
- Insulated Gloves – made of rubber or other insulating materials to protect against electric shock while working on live electrical circuits
- Rubber Lineman Gloves – provide added insulation and protection for electrical workers involved in high-voltage tasks
- Sleeves – made of insulating materials to cover the arms and provide additional protection against electrical contact
- Foot and Leg Protection:
- Safety Shoes – with non-conductive soles to protect against electrical shock and provide insulation for the feet
- Dielectric Overshoes – made of non-conductive materials that can be worn over regular footwear to provide an additional layer of electrical insulation
- Body Protection:
- Flame-Resistant Clothing – made of non-conductive materials, such as cotton, to reduce the risk of burns from arc flashes or electrical fires
- Arc Flash Suits – consist of flame-resistant jackets, pants, and hoods or face shields to protect against the thermal effects of arc flashes
Also, there are other ways to complement an organization’s efforts to protect workers. One is by covering or guarding exposed live electrical parts using Insulating Protective Equipment (IPE) enables qualified workers not wearing insulating PPE to enter the Minimum Approach Distance. However, with the limited protective capacity of IPE, it’s still best practice to wear minimum electrical PPE requirements.
Considerations in Selecting the Right Electrical PPE
When selecting the right electrical PPE, it is important to consider several factors to ensure proper protection and safety for workers. Some key considerations include the following:
- Identify potential risks such as electric shock, arc flashes, arc blasts, burns, and exposure to flying debris or chemicals to determine the most appropriate types of PPE needed.
- Determine the voltage levels involved in the electrical work since different voltage levels require different levels of insulation and protection. Ensure that the selected PPE is rated for the voltage levels present to provide adequate protection.
- Familiarize yourself with the relevant safety standards and regulations specific to electrical work in your region. Ensure that the selected PPE meets or exceeds these standards to ensure compliance and maximum safety.
- Review the specifications and features of the PPE options available. Choose those that provide the necessary protection while being practical for the tasks performed.
- Consider the size and fit options available for different PPE items and choose accordingly to ensure optimal protection and comfort.
- Assess the specific tasks to be performed and the PPE requirements for each because some tasks may require additional or specialized PPE.
- Choose reputable suppliers that provide reliable and high-quality electrical PPE. Ensure that the PPE meets recognized safety standards and has undergone proper testing and certification.
Best Practices for Using Electrical PPE
When using electrical PPE, it’s crucial to follow best practices to ensure maximum effectiveness, safety, and ability to reduce the risk of electrical injuries by considering these key practices:
- Provide comprehensive training to workers on the correct selection, use, care, and maintenance of electrical PPE. Ensure they understand the specific hazards, limitations, and procedures for using each type of PPE.
- Conduct regular inspections of all electrical PPE to identify any signs of damage, wear, or deterioration. Inspect for cuts, tears, fraying, or other defects that may compromise the protective qualities and replace any damaged or defective PPE immediately.
- Select the right type of PPE based on the specific hazards present and the voltage levels involved in the work environment. Follow safety regulations and guidelines to ensure compliance and proper protection.
- Use multiple layers of PPE when necessary. For example, wearing safety glasses with a face shield or combining insulated gloves with rubber sleeves provides enhanced protection against electrical hazards.
- Follow proper procedures for donning (putting on) and doffing (taking off) PPE to minimize contamination and maintain hygiene.
- Regularly clean and maintain electrical PPE according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Use mild detergent and water to clean non-electrical components, and follow specific procedures for cleaning and inspecting insulated components.
- Store electrical PPE in a clean, dry, and easily accessible location to ensure its longevity and availability when needed. Keep PPE away from sunlight, extreme temperatures, chemicals, or other factors that could degrade its quality.
- Encourage workers to report any issues or concerns regarding the effectiveness or comfort of PPE. Use their feedback to improve the selection and use of PPE and promote a culture of safety.
Create Your Own Electrical PPE Inspection Checklist
Eliminate manual tasks and streamline your operations.
Get started for FREEIndustry Examples of How Electrical PPEs are Used
The following examples illustrate how various industries implement specific electrical PPE measures to protect workers from the hazards associated with their respective work environments.
Electrical
Electricians working on electrical panels or circuits wear insulated gloves, safety glasses, arc flash suits, and face shields to protect against electric shock and arc flashes. Also, they can use voltage-rated tools like insulated screwdrivers and pliers to safely work on live electrical equipment.
Oil and Gas
Electricians working on electrical systems in oil refineries wear arc flash suits and face shields when working on high-voltage equipment or during electrical testing procedures. Also, insulated grounding cables and mats are used to establish a safe work zone and prevent electrical contact with the ground during maintenance or repairs.
Mining
Miners working on electrical systems in mines wear insulated footwear, such as rubber boots, and insulating mats are used to provide protection against electrical contact through the feet. Also, voltage detectors and lockout/tagout devices are utilized to ensure the proper de-energization of equipment during maintenance or repairs.
Machinery
Maintenance technicians working on electrical machinery can use insulating blankets or barriers when working on electrical panels or control cabinets to prevent accidental contact with energized components. For their electrical PPE, arc flash suits and face shields are worn during tasks involving high-voltage equipment or troubleshooting electrical faults.
Automotive
To create an electrically safe work area when working on automotive electrical systems, insulating mats or rubber mats can be used by mechanics. Furthermore, voltage testers and multimeters are employed to check for the presence of electrical voltage before starting any work.
Construction
During tasks like panel upgrades or working on high-voltage electrical distribution systems, electricians and construction workers wear PPEs such as arch flash suits and face shields when installing or repairing electrical systems in buildings or construction sites. Also, insulated ladders and scaffolding are used to prevent electrical contact for a safe working platform.
Manufacturing
Workers involved in manufacturing processes that require using electrical equipment wear PPEs like safety glasses, insulated gloves, and flame-resistant clothing for safety. Also, insulating mats or rubber mats are used in areas where electrical equipment is present as protection against electrical shock. In some cases, Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) devices and procedures are followed to ensure the isolation and de-energization of equipment during maintenance or repairs.



