Factor of Safety Definition
The higher the number of FoS, the safer the product or structure is. An FoS of 1 indicates that a structure or component will fail immediately when the design load is reached and will not be capable of supporting any extra load. Structures or components with FoS less than one are not acceptable. If the consequences of failure are severe, such as loss of life or physical injury, a higher FoS will be required either by design or by law.
The higher the number of FoS, the safer the product or structure is. An FoS of 1 indicates that a structure or component will fail immediately when the design load is reached and will not be capable of supporting any extra load. Structures or components with FoS less than one are not acceptable. If the consequences of failure are severe, such as loss of life or physical injury, a higher FoS will be required either by design or by law.
Simply put, structures or devices must be able to bear more weight than they would under normal use to be safer. FoS indicates by what factor the design is safe.
Typical Overall Factors of Safety
Below is a table of typical FoS of equipment, provided by Engineering ToolBox:
| Equipment | Factor of Safety
– FOS – |
| Aircraft components | 1.5 – 2.5 |
| Boilers | 3.5 – 6 |
| Bolts | 8.5 |
| Cast-iron wheels | 20 |
| Engine components | 6 – 8 |
| Heavy duty shafting | 10 – 12 |
| Lifting equipment – hooks | 8 – 9 |
| Pressure vessels | 3.5 – 6 (specified in the design code) |
| Turbine components – static | 6 – 8 |
| Turbine components – rotating | 2 – 3 |
| Spring, large heavy-duty | 4.5 |
| Structural steel work in buildings | 4 – 6 |
| Structural steel work in bridges | 5 – 7 |
| Wire ropes | 8 – 9 |
General Recommendations
| Applications | Factor of Safety
– FOS – |
| For use with highly reliable materials where loading and environmental conditions are not severe and where weight is an important consideration | 1.3 – 1.5 |
| For use with reliable materials where loading and environmental conditions are not severe | 1.5 – 2 |
| For use with ordinary materials where loading and environmental conditions are not severe | 2 – 2.5 |
| For use with less tried and for brittle materials where loading and environmental conditions are not severe | 2.5 – 3 |
| For use with materials where properties are not reliable and where loading and environmental conditions are not severe, or where reliable materials are used under difficult and environmental conditions | 3 – 4 |
Calculation
All of the calculations basically measure the same thing—how much additional stress beyond the designed load that a structure can withstand. A simple calculation for safety factor is:
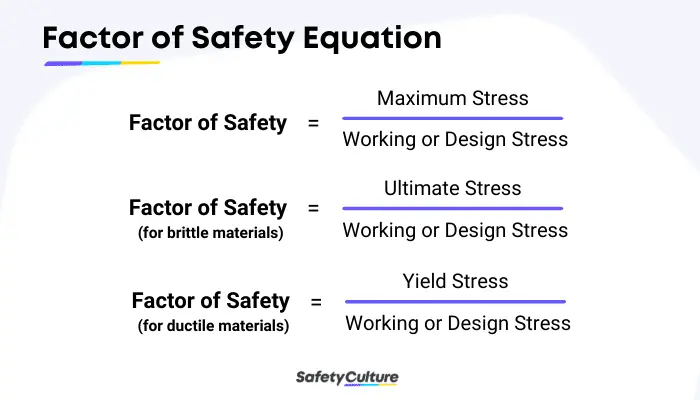
Many Factor of Safety calculators are available online for calculating FoS values when the maximum stress and allowable stress values are known.
Importance of Safety Factor
Factor of Safety varies according to the situation. Systems are intentionally designed to be way stronger than they need to be for normal settings. This increases the likelihood that they will continue functioning even under extreme conditions such as emergency situations, added loads, overuse, or degradation caused by wear and tear. Moreover, below are more reasons why using FoS in design is important:
- Maintains the structure’s functionality for the future while providing additional safety for current use
- Prevents damage to property, workers, and machines
- Provides protection for unforeseeable risks that may occur while using a product or service
- Reduces the chances that a product may fail
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
Explore nowSelection of Factors of Safety
According to A Textbook of Machine Design by R.S.Khurmi and J.K.Gupta, the selection of the appropriate Factor of Safety to be used in the design of any mechanical system is based on a variety of considerations, including the following:
- Material—ductile or brittle; ductile materials use yield strength; brittle materials use ultimate strength.
- Yield strength—determines the FoS until the beginning of deformation.
- Ultimate strength—determines the FoS until failure.
- Process of manufacturing
- Type of stress
- General service conditions
- Shape of the parts
Examples
The following are two instances of how the Factor of Safety is used:
Pressure Vessels
Boilers and pressure vessels, as well as nuclear power plant systems, are subject to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) International Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code safety guidelines, which control the design, manufacturing, and inspection of boilers and pressure vessels during the construction process. By their very nature, pressure vessels are potentially hazardous. It necessitates the addition of safety factors to protect against failure—uncertainty in design, materials used, manufacture, inspection, and operation.
Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS)
Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS) and other fall protection equipment must be built with a high safety factor. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standard 1915.159 outlines the criteria for connectors and anchorage to be capable of sustaining a minimum tensile load of 3,000 to 5,000 pounds (22.24 Kn) per employee, and a requirement of a complete personal fall arrest system which maintains a safety factor of at least 2. If the equipment is going to be used in tough circumstances, it may require an even higher safety factor.
Digitize the way you Work
Empower your team with SafetyCulture to perform checks, train staff, report issues, and automate tasks with our digital platform.
Get Started for FreeSafetyCulture for Factor of Safety
The Factor of Safety exists as a safety measure that is designed to make a product, a system, or a structure safe. SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) can help manufacturers, engineers, and inspectors conduct external and internal inspections of equipment and assess their safety factor to determine their capacity to withstand maximum allowable stress. With SafetyCulture, you can:
- Perform more convenient inspections using a mobile device.
- Capture issues found during inspections such as system failures. Immediately assign actions for urgent issues or any failure of equipment and receive real-time status updates.
- Share inspection reports through the app with other qualified personnel to do safety inspections.
- Customize safety checklist templates according to the requirements of the system or equipment, such as in pressure vessels, and meet the standards specified in industry codes.
- Provide guidance and mobile training to workers that they can bring anywhere as reference for proper use, inspection, and storage of equipment. Audit uncertainty failure and quality control of material during manufacturing, construction, or assembly.
- Manage assets from anywhere to ensure the safety of your workers at all times.
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.



