What is an ISO 19001 Audit Checklist?
An ISO 9001 Audit Checklist is used to assess the effectiveness of an organization’s Quality Management System (QMS). The audit helps organizations identify and address issues, and discover potential improvements they can make with their QMS to ensure best practice processes are in place as preparation for a third-party ISO 9001:2015 certification audit.
Types of ISO 9001 Audit
An ISO Audit is an official assessment sanctioned by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to determine if a company fulfills set criteria, usually for developing a product or rendering a service. An ISO certification gives merit to companies and protects consumers by ensuring that international safety, reliability, and quality standards are met. An ISO 9001 audit is conducted in two methods:
Internal Audit
This type of audit is conducted by an assigned member of the organization to compare existing QMS with industry regulations and relevant standards such as industry, internal, and ISO 9001. Performing internal ISO 9001 audits helps organizations prepare for the actual certification audit by identifying and resolving signs of non-conformance, checking progress against goals and objectives, evaluating conformance to regulation and legislation, discovering areas for improvement, and conducting a management review to ensure that QMS processes meet requirements for certification.
External Audit
This type of audit is performed prior to obtaining ISO certification. An external auditor will do the assessment and will verify and ensure that the organization’s documentation meets the requirements of the ISO 9001 standard. At the end of the audit, the auditor will recommend whether you’ll be granted a certification or require corrective actions before you can be accredited. Should an organization be granted certification, after the three-year period, they would have to renew their certification by going through the same external audit.
ISO 9001: 2008 vs 2015 comparison
ISO 9001:2015 intends to focus on the PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act) management method; therefore, the updated version of any ISO 9001 template is structured according to PDCA. The purpose of this change was to guard against complacency and give momentum to continuous improvements in quality management systems.
Refer to the table below in order to spot the main differences between the ISO 9001:2008 and ISO 9001:2015 structures:
ISO 9001:2008 Structure |
ISO 9001:2015 Structure |
| 0. Introduction | 0. Introduction |
| 1. Scope | 1. Scope |
| 2. Normative Reference | 2. Normative Reference |
| 3. Terms and Definitions | 3. Terms and Definitions |
| 4. Quality Management Systems | 4. Context of the Organization |
| 5. Management Responsibility | 5. Leadership |
| 6. Resource Management | 6. Planning |
| 7. Product Realization | 7. Support |
| 8. Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement | 8. Operation |
| – | 9. Performance Evaluation |
| – | 10. Improvement |
Furthermore, ISO 9001:2015 focuses on risk-based thinking rather than preventative measures. Therefore, the most recent ISO 9001 checklist reflects this by focusing on analyzing situations that are specific to your organization and deciding individual actions based on that risk analysis.
How to Prepare the Checklist
Preparing an audit checklist doesn’t need to be difficult; you can either create it from scratch or use a template. Below is an example of what a typical ISO 9001 audit checklist might look like, along with some example questions that can be considered to properly assess compliance with ISO 9001 standards:
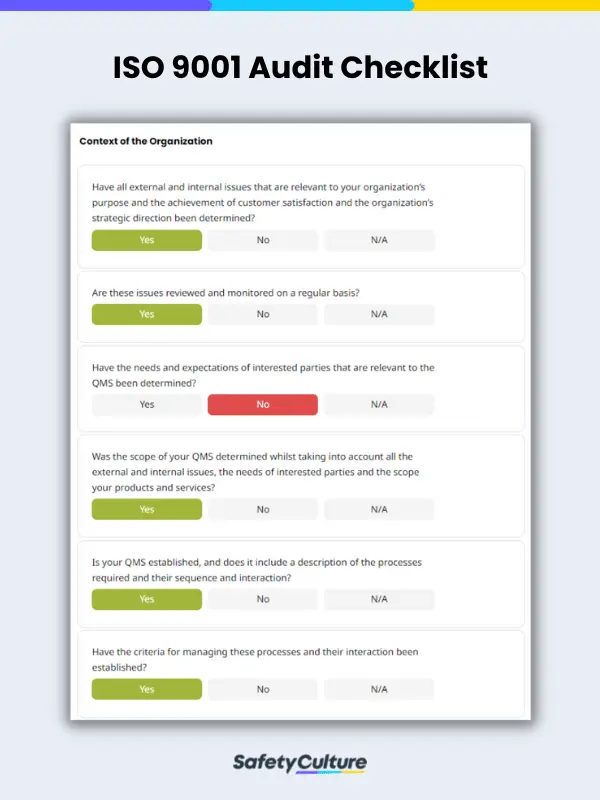
Clause 4: Context of the Organization
- Understanding the organization and its context
- Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties
- Determining the scope of the QMS
- The Quality Management System and its processes
Example questions:
- Have all external and internal issues that are relevant to your organization’s purpose and the achievement of customer satisfaction and the organization’s strategic direction been determined?
- Are these issues reviewed and monitored on a regular basis?
- Have the needs and expectations of interested parties that are relevant to the QMS been determined?
- Was the scope of your QMS determined whilst taking into account all the external and internal issues, the needs of interested parties and the scope your products and services?
- Is your QMS established, and does it include a description of the processes required and their sequence and interaction?
- Have the criteria for managing these processes and their interaction been established?
- Have all responsibilities, methods, measurements and related performance indicators, needed to ensure the effective operation and control, been established?
Clause 5: Leadership
- Leadership and commitmentQuality policy
- Organizational roles, responsibilities, and authorities
Example questions:
- Has top management taken accountability for the effectiveness of the QMS?
- Have the policy and objectives for the QMS, which are compatible with the strategic direction of the organization, been established and communicated?
- Have the objectives been established at relevant departmental and individual levels with the business?
- Have the requirements for the QMS been integrated into the business processes and have management promoted awareness of the process approach?
- Have customer requirements and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements been determined, met and communicated throughout the organization?
- Have the risks and opportunities that are relevant to the QMS been established?
- Has the organization established and communicated the responsibilities and authorities for the effective operation of the QMS?
Clause 6: Planning
- Actions to address risks and opportunities
- Quality objectives
- Planning of changes
Example questions:
- Have the risks and opportunities that need to be addressed to give assurance that the QMS can achieve its intended result(s) been established?
- Has the organization planned actions to address these risks and opportunities and integrated them into the system processes?
- Is there a defined process for the determining the need for changes to the QMS and managing their implementation?
Clause 7: Support
- Resources (general, people, infrastructures, environment for the operation of processes, monitoring and measuring resources, and organization knowledge)
- Competence
- Awareness
- Communication
- Documented information
Example questions:
- Has the organization determined and provided the resources needed for the establishment, implementation, maintenance and continual improvement of the QMS (including people, environmental and infrastructure requirements)?
- Is monitoring or measuring is used for evidence of conformity of products and services to specified requirements?
- Has the organization determined the resources needed to ensure valid and reliable monitoring and measuring of results?
- Has the organization determined the knowledge necessary for the operation of its processes and the achievement of conformity of products and services and implemented a lessons learned process?
- Has the organization ensured that those persons who can affect the performance of the QMS are competent on the basis of appropriate education, training, or experience or taken action to ensure that those persons can acquire the necessary competence?
- Has the documented information required by the standard and necessary for the effective implementation and operation of the QMS been established?
Clause 8: Operation
- Operational planning and control
- Determination of requirements for products and services (market needs and interactions with customers)
- Design and development of goods and services
- Control of externally provided goods and services
- Production of goods and provision of services
- Release of goods and services
- Control of nonconforming process outputs, products, and services
Example questions:
- Is there a defined process for the provision of products and services that meet the requirements defined by the customer?
- Are there any changes planned?Are they carried out in a controlled way and actions taken to mitigate any adverse effects?
- Are any outsourced processes managed and controlled?
Is there a defined process for reviewing and communicating with customers in relation to information relating to products and services, enquiries, contracts or order handling? - Is this review conducted prior to the organization’s commitment to supply products and services?
- Do you design and develop products or services?
- Are these processes established and implemented in line with the requirements of the standard?
- Do you ensure that externally provided processes, products, and services conform to specified requirements?
- Do you have criteria for the evaluation, selection, monitoring of performance and re-evaluation of external providers?
- Is the provision of products and services carried out in controlled conditions which include: the availability of documented information that defines the characteristics of the products and services? the availability of documented information that defines the activities to be performed and the results to be achieved? monitoring and measurement activities at appropriate stages to verify that criteria for control of processes and process outputs, and acceptance criteria for products and services, have been met? the people carrying out the tasks are competent?
- Do you have effective methods of ensuring traceability during the operation process?
- Is property belonging to customers or external providers used in the provision of the product or service?
- Is this controlled effectively?
- Is there a requirement for post-delivery activities associated with the products and services such as warranty, maintenance services, recycling or final disposal?
- Are these defined and managed?
- Are any nonconforming process outputs managed so as to prevent their unintended use?
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
- Monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation
- Internal audit
- Management review
- ISO 9001 Clause 10: Improvement
- Continual improvement
- Nonconformity and corrective action
Example questions:
- Has the organisation determined what needs to be monitored and measured and the methods for monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation, to ensure valid results?
- Has it established when the results from monitoring and measurement shall be analyzed and evaluated?
- Have methods of monitoring customer perceptions of the provision of products and services been established?
- Has it determined the need or opportunities for improvements within the QMS and how these will be fed into management reviews?
- Has the organisation established a process for an internal audit of the QMS?
- Has an approach to perform management reviews been established and implemented?
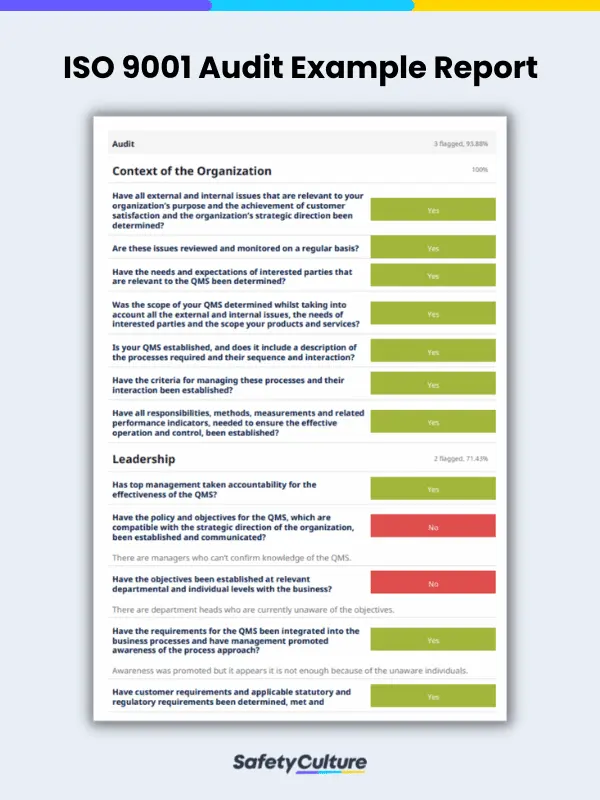
ISO 9001 Audit Checklist Example PDF
Here is an example of an ISO 9001 PDF in the context of a QMS gap analysis. This upgrade in ISO 9001 form ensures that potential risks can be identified and acted on accordingly, long before preventative measures become apparent.
This internal audit checklist PDF for ISO 9001 lets users visualize the report of an already answered audit for an organization’s QMS.