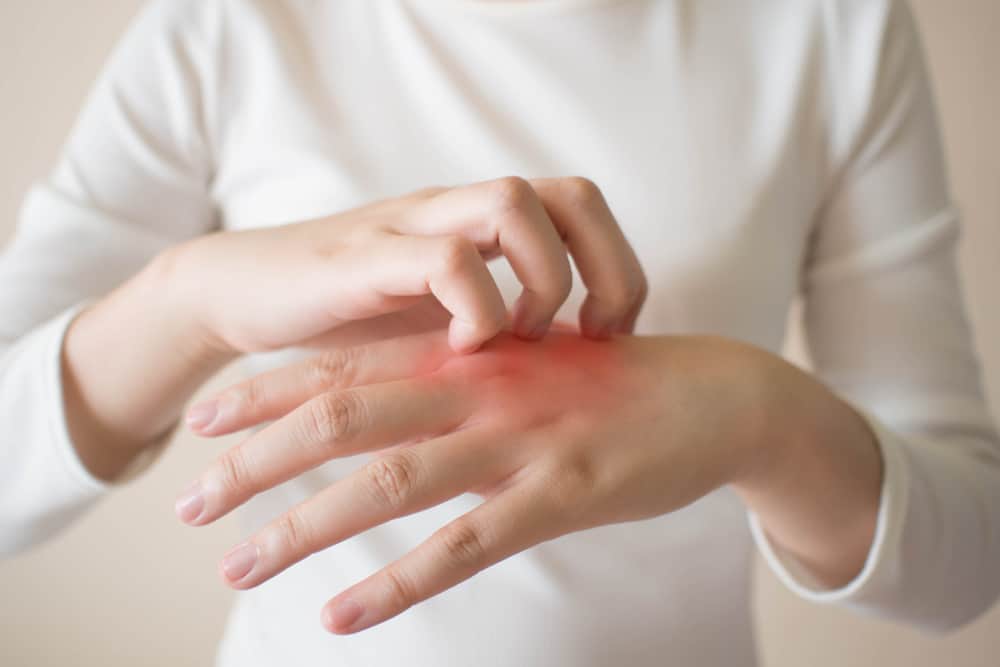
Occupational Dermatitis Explained: Symptoms, Triggers, and How to Prevent It
Occupational dermatitis is the most common workplace skin injury, and it can be a major frustration for workers who can’t perform their jobs at 100%. Fortunately, understanding its causes and prevention can help keep it under control.

Published 21 Mar 2025
Article by
4 min read
What is Occupational Dermatitis?
Occupational contact dermatitis occurs when skin contact has been made with an irritating substance. This condition is common in industries such as hospitality and construction, or any field that involves frequent exposure to irritants. Dermatitis simply refers to skin inflammation, which can lead to redness, itching, swelling, or even blistering. Left unchecked, it can seriously impact your team’s comfort and performance.
Significance in the Workplace
In hands-on jobs,workplace safety should be of the utmost importance. Work-related dermatitis affects an estimated 6.7% to 10.6% of workers, often resulting in missed work and decreased job satisfaction. While it can be cured temporarily, it can also always come back as long as allergens and the specific causes of the occupational dermatitis are present in the workplace. So, finding the source of the irritation—and implementing proper allergen management —is key to preventing occupational dermatitis symptoms from recurring. But unlike typical allergies, occupational dermatitis is a work-related condition that primarily affects the skin.
Two Types of Occupational Dermatitis
There are two main types of occupational contact dermatitis: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. It’s important to familiarize your employees with the two to avoid confusion in the workplace.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type, making up about 80% of all occupational dermatitis cases. It’s also the more straightforward one—when your skin comes into contact with an irritating substance, it reacts. Chemical irritants penetrate the skin barrier, leading to irritation.
Allergic contact dermatitis, on the other hand, is rarer and more complex. It’s not just a surface reaction; it involves your immune system. Your skin goes through a sensitization period that can last weeks or even months. Once sensitized, even a tiny amount of the allergen can trigger a strong reaction.
Causes and Risks Per Industry
According to the Health Sciences Authority (HSA), occupational dermatitis is actually the most common work-related disease in parts of Northern Europe, including Ireland. Some examples of triggers include, but are not limited to:
Hospitality and Food Service:
Soaps and detergents
Citrus fruits and acidic foods
Cleaning chemicals (e.g., bleach, disinfectants)
Latex gloves
Construction and Manufacturing:
Solvents and adhesives
Paints and varnishes
Concrete and sawdust
Metalworking fluids and cutting oils
Agriculture and Landscaping:
Pesticides and herbicides
Insecticides
Constant sun and UV exposure
Occupational dermatitis, just like eczema, can also occur from overly dry skin or frequent handwashing, by stripping away your skin’s natural oils and protection. This can lead to irritation and the cracking of skin.
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
Relevant Safety Legislations
Working with a skin condition isn’t just uncomfortable—it can be a major distraction. That’s why safety regulations set clear standards to protect workers. Employees must complete a pre-employment health questionnaire before starting a job, ensuring any existing conditions are documented.
Employers, on the other hand, are responsible for identifying tasks that may cause dermatitis and conducting risk assessments to evaluate potential hazards. Ongoing health surveillance is also essential, ensuring employees remain healthy and fit for work.
In the US, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates that employers assess risks and provide appropriate training and protective equipment. OSHA also enforces regulatory standards across all industries to ensure proper protection against dermal exposure.
In other countries, such as Canada, the Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) serves as the standard for workplace hazard management. Its safety data sheets provide workers with essential information on hazardous materials and proper handling procedures.
How to Mitigate Occupational Dermatitis Risks
To effectively prevent skin issues at work, it’s important to take a well-rounded approach that focuses on the health and safety of employees. Here are some key steps you can take to promote a safer work environment and reduce the risk of occupational dermatitis:
Conduct regular safety inspections and assessments to identify the root cause of skin irritation.
Eliminate hazards where possible or seek non-hazardous alternatives to replace skin irritants.
Provide the correct Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) such as gloves, masks, or protective clothing to minimize skin exposure.
Ensure proper waste disposal to prevent unnecessary contact with harmful substances.
Maintain hygiene and handwashing stations , especially in high-risk areas—but be mindful that excessive handwashing can also contribute to occupational hand dermatitis.
Act quickly when symptoms appear to prevent worsening conditions and ensure worker safety.
While occupational dermatitis may not always be avoidable, taking these precautions can help reduce risks and keep workers safe.
Prevent Occupational Dermatitis and Manage its Risks with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Efficiently manage and streamline health and safety processes across the organization, including incident management, safety audits and inspections, risk assessment, waste management, and more, using a comprehensive EHS software solution.
✓ Save time and reduce costs ✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents ✓ Boost productivity and efficiency ✓ Enhance communication and collaboration ✓ Discover improvement opportunities ✓ Make data-driven business decision
Related articles
Health
Medical Assessment
Achieving Zero Blood Culture Contamination
Learn what blood culture contamination is, why it occurs, and proven strategies to prevent false-positive results.
Health
Medical Assessment

A Guide to Celebrating Medical Laboratory Professionals Week
Find out what Medical Laboratory Professionals week is, its history, and different ways companies can celebrate it.
Health
Medical Assessment

A Guide to Efficient Veterinary Practice Management
Learn what veterinary practice management is, why it’s important, and its key aspects.