What is Hazardous Waste Disposal?
Hazardous waste disposal is the process of properly removing and disposing of hazardous substances from a property or after its use. Proper handling of hazardous waste is needed to ensure that the potential hazards are properly addressed.
The federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), which was approved by Congress in 1976, governs the disposal of hazardous wastes. It was the first federal law to address hazardous waste regulations. It was made to make sure that the production, transportation, treatment, storage, and disposal of hazardous wastes are done in a way that is safe for people and the environment.
Understanding Hazardous Waste
Definition
Hazardous wastes are any type of materials which may cause or have the potential to cause harm or serious health and environmental problems if improperly treated, managed, or disposed of. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines hazardous materials as those that can be used to create explosives, poison gas, or radioactive materials. In order for a waste to be classified as hazardous, it must possess at least one of the following characteristics: combustible, corrosive, infectious, allergenic, poisonous, or cancer-causing. Hazardous waste includes many different materials, but some of the most common include: batteries, lead, gasoline, oil, paint, and mercury.
Generators
Hazardous waste is generated from many sources. A generator pertains to any entity that generates or produces hazardous wastes. EPA established three categories of generators in its regulations:
- Very Small Quantity Generators (VSQGs) –these are generators who produce less than 100 kg of hazardous waste or 1 kg of acutely hazardous waste each month.
- Small Quantity Generators (SQGs) –these are generators who produce more than 100 kg, but less than 1,000 kg of hazardous waste each month.
- Large Quantity Generators (LQGs) –these are generators who produce 1,000 kg or more each month of hazardous waste or more than one kg each month of acutely hazardous waste.
See list of acutely hazardous wastes here.
Generators are typically well-informed about the risks of hazardous waste and know that they will need the services of a waste management business to manage their waste. However, some are unaware that hazardous waste is regulated under RCRA’s Subtitle C. The EPA has devised a comprehensive program to assure the safe management of hazardous waste from its generation until its final disposal—the “cradle-to-grave” system.
Cradle-to-Grave System
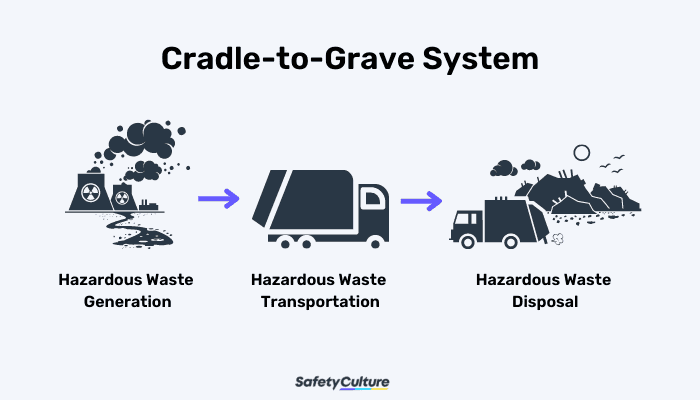
Cradle-to-grave means that a generator is responsible for its waste from the time it is made until it is disposed of. It is always the generator’s responsibility, even if the waste is transported away from their facility. Hiring a waste disposal company to transport and dispose of the waste does not free the generator from this responsibility. The cradle-to-grave system reminds generators to comply with the regulations in handling hazardous waste. Compliance will minimize the generator’s likelihood of having liabilities and fines.
EPA Identification Process
EPA has the authority in the identification and classification of whether a waste is hazardous. It has developed a regulatory process on identifying which substances are hazardous. This process consists of a series of questions for easier understanding and efficiency in identifying if waste is subject to RCRA Subtitle C Regulations.
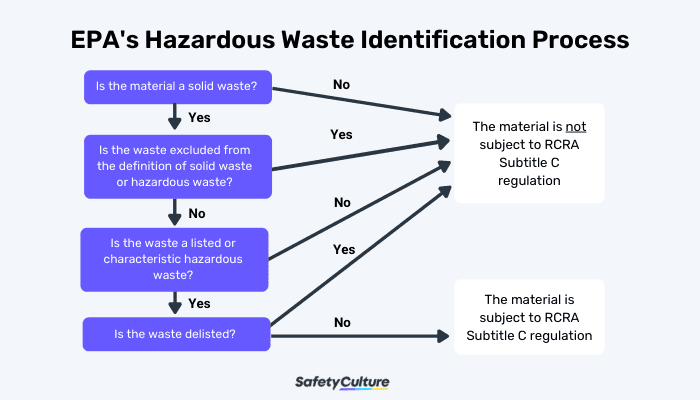
- Q: Is the material a “solid waste”?
The material must be a “solid waste” (which can be solid, liquid, or gas) to be considered a hazardous waste. The process of identifying hazardous waste begins with determining whether it should be classified as such. If the material is not a solid waste, then it is not subject to RCRA Subtitle C regulation. If it is, then the next questions will help in determining its classification as a hazardous waste.
- Q: Is the waste excluded from the definition of solid waste or hazardous waste?
If the solid waste is not excluded from the list of solid waste and hazardous waste regulations, then the material must be evaluated with the next question.
See list of wastes that are excluded from Solid Waste Regulation here.
See list of wastes that are excluded from Hazardous Waste Regulation here.
- Q: Is the waste a listed or characteristic hazardous waste?
The definition and list of listed hazardous waste and characteristic hazardous waste are found in title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) in part 261. If the material is found on the list, it must be evaluated with the next question.
- Q: Is the waste delisted?
If a solid waste is removed or “delisted” in accordance with RCRA delisting process, then the waste is not identified as “hazardous” and not subject to RCRA Subtitle C regulations.
Classifications of Hazardous Waste
As identified by EPA, waste is classified as “hazardous” if they are included in the following:

- Listed Waste –a waste is classified as hazardous if it is particularly recognized on the (1) F and K Lists or (2) P and U Lists
- Characteristic Wastes –EPA identified four main hazardous waste characteristics:
- Ignitability –this is the ability of a material to ignite a flame or spark. It is used to describe the potential for an explosive mixture of a flammable gas and air (or other gas) to explode. Examples: used oils, gasoline, and acetones.
- Corrosivity –this is the tendency of a substance to react chemically with another substance, or to rust. Example: battery acids
- Reactivity –this is the ability of the material to react with oxygen and change its state or properties and then explode. Example: Lithium-sulfur batteries
- Toxicity –this is the ability of a material to poison or harm humans, animals, or the environment when ingested or absorbed. Examples: chemical waste and medical waste.
- Mixed Wastes –refers to a waste material that contains radioactive, biological and chemical components. The RCRA and the Atomic Energy Act governs the management of mixed waste.
- Universal Waste –is a classification of waste that is regulated by a specific requirement of the EPA. Regulations addressing universal waste are found in Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) in part 273 and apply to five types of universal waste: batteries, lamps, pesticides, mercury-containing equipment, and aerosol cans.
Create Your Own Waste Audit Checklist
Eliminate manual tasks and streamline your operations.
Get started for FREESteps of Hazardous Waste Disposal
EPA has provided steps on how hazardous waste generators should comply with regulations on hazardous waste disposal:
- Identify –generators must identify each hazardous waste they generate through the identification process regulated by the EPA.
- Count –generators must get the sum of the total weight of their hazardous waste and classify themselves on what type of generator they are (VSQGs, SQGs, or LQGs).
- Notify –generators are required to notify the EPA or the authorized state agency to manage hazardous waste and inform them of their hazardous waste activities.
- Manage –generators must manage their waste in accordance with Hazardous Waste Generator Regulations.
- Transport –generators are required to fill out a Hazardous Waste Manifest when transporting hazardous waste off-site. It is designed as a tracking system for the movement of waste from a generator’s facility to the facility where it will be treated and ultimately disposed of.
Hazardous waste that will be transported off-site must also be properly packaged and labeled in accordance with Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations. - Recycle-Treat-Dispose – hazardous waste treatment and disposal is governed by the Treatment, Storage, and Disposal Facility (TSDF) regulations. Certain generators may opt to recycle their waste on-site without a permit, depending on the quantity of waste generated.
Integrate ESG principles into your operations
Drive sustainable growth and create long-term value with our ESG solutions.
Explore nowSafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) for Hazardous Waste Disposal Regulations
It’s understandable that learning the ins and outs of RCRA can be overwhelming. But if you’re a hazardous waste generator, it’s vital that you take the time to do so. It will also help you remain compliant and avoid significant fines and legal trouble. Empower your facility with the technology to support your facility’s responsibility to comply with hazardous waste regulations from cradle-to-grave with SafetyCulture.
SafetyCulture provides solutions for safety, quality, operations, and training—all-in-one, easy-to-use app that is utilized by a variety of industries for inspections, audits, and compliance checks. Generators can benefit from this app with the following features:
- Perform inspections of your hazardous waste containers to check if they are properly identified and labeled.
- Store the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) or the Safety Data Sheet acquired from other generators or created when hazardous waste is produced in a secured and easy-to-access cloud.
- Keep the Hazardous Waste Manifest in your records securely and access it anywhere (during the shipment or after the contract has ended) as part of your responsibility as a generator.
- Customize training materials based on the RCRA training module about Hazardous Waste Identification with Training.
- Review your facility’s compliance with regulations in hazardous waste removal when sorting using the Waste Audit Checklist.



