Everything You Need to Know About PPE Safety
Understand the importance of PPE safety, its basic types, examples, and tips for proper use

Published 17 Sept 2025
Article by
9 min read
What is PPE?
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) refers to protective clothing for the eyes, head, ears, hands, respiratory system, body, and feet. It is utilized to protect individuals from the risks of injury and infection while minimizing exposure to chemical, biological, and physical hazards. PPE serves as the final line of defense when engineering and administrative controls are insufficient in reducing or eliminating risks.
What is PPE Safety?
PPE safety is the practice of ensuring a safe, working environment for employees and visitors through the use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Safety is paramount to all businesses across industries, from those present in daily life such as manufacturing to niche ones such as embalming and death care. Using PPEs, paired with inspections such as workplace and restaurant inspections, assessments like health and safety risk assessments, and analysis such as gap analysis —is essential to protect employees from risks and hazards.
Why is it Important?
According to the hierarchy of controls by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), PPE (sometimes also referred to as PPE equipment)—is recommended to be the last level of defense to prevent occupational injuries, illnesses, and fatalities, but some businesses combined it with other control measures to ensure a safe and healthy environment for their workers. Here are some benefits of using PPEs:
prevent unnecessary injury in the workplace;
protect employees from excessive chemical exposure;
prevent the spread of germs and infectious diseases including COVID-19;
help businesses comply with regulatory requirements(e.g., The Personal Protective Equipment at Work Regulations 1992 that’s recently been extended to limb workers ); and
improve employee productivity and efficiency.
The 4 Basic Types of PPE and Their Examples
However, even the strictest controls will not necessarily eliminate all the risks associated with most job tasks and this is where the need for PPE must be evaluated. A hazard assessment can help identify which specialized PPE will be required. There are numerous types of workplace safety equipment available depending on the hazard exposure and work conditions. The following are basic PPE that can help protect employees:
Face and Eye Protection
Face and Eye Protection includes safety goggles and face shields and should be used for tasks that can cause eye damage or loss of vision, sprays of toxic liquids, splashes, and burns.
Safety Tips:
Check if safety glasses comply with the ANSI Z87.1 eye protection standard.
Ensure that there are no cracks or deformities on the lenses.
Ensure the strap is in good working condition and is firmly sealed to the cheek and forehead.
Clean and disinfect after use.
Respiratory Protection
PPE includes full-face respirators, self-contained breathing apparatus, gas masks, N95 respirators, and surgical masks are used for a task that can cause inhalation of harmful materials to enter the body. This includes harmful gas, chemicals, large-particle droplets, sprays, splashes, or splatter that may contain viruses and bacteria such as COVID-19, viral infections, and more.
Safety Tips:
Ensure that the equipment is fit-tested and the employee has undergone proper training before wearing one.
Carefully read the instructions to determine if it is designed to help protect against the hazards you may face.
Change filters on half-mask or full-mask respirators frequently.
Replace disposable respirators with every use.
Surgical masks are not to be shared with anyone.
Avoid touching the surgical mask after wearing it.
Change surgical mask timely and should be disposed of after use.
Replace the mask immediately if it is damaged or soiled.
Skin and Body Protection
Skin and Body Protection PPE includes the following categories to protect employees from physical hazards:
Head Protection
Head Protection includes hard hats and headgears and should be required for tasks that can cause any force or object falling to the head.
Safety Tips:
Ensure that there are no dents or deformities on the shell and connections are tightened inside.
Do not store in direct sunlight as extreme heat can cause damage.
Choose appropriate cleaning agents as it can weaken the shells of hard hats and may eliminate electrical resistance.
Always replace a hard hat if it was used for any kind of impact, even if the damage is unnoticeable.
Body Protection
Body Protection PPE includes safety vests and suits that can be used for tasks that can cause body injuries from extreme temperatures, flames and sparks, toxic chemicals, insect bites and radiation.
Safety Tips:
Ensure that they are clean and free from cuts and burns.
Always get a good fit to ensure full body protection.
Ensure bodysuit is when working with high-temperature hazards.
Hands Protection
Hands Protection PPE includes safety gloves and should be used for tasks that can cause hand and skin burns, absorption of harmful substances, cuts, fractures or amputations.
Safety Tips:
Ensure hand protection fits perfectly with no spaces and is free from cuts, burns, and chemical residue.
Always replace them if any sign of contamination was observed.
Use rubber gloves when working with heat and electricity to reduce the risk of burn or electrical shock.
Foot Protection
PPE includes knee pads and safety boots and should be used for tasks that can cause serious foot and leg injuries from falling or rolling objects, hot substances,electrical hazards, and slippery surfaces.
Safety Tips:
Ensure boots have slip-resistant soles that can protect against compression and impact.
Ensure the sole plate is in good condition to prevent punctures.
Fall Protection
PPE includes safety harnesses and lanyards and should be strictly used for tasks that can cause falling from heights and serious injury or death.
Safety Tips:
Ensure that the straps are free from tears, deformities, and burn marks.
Check the buckles if connected securely and tightly.
Dispose of the equipment if used after a falling incident.
Hearing Protection
PPE includes ear muffs and plugs and should be used for tasks that can cause hearing problems and loss of hearing.
Safety Tips:
Ensure the equipment fit the ear canal perfectly.
It is recommended to use formable earplugs to fit different sizes of ear canals.
Use protectors that reduce noise exposure to an acceptable level to have room for communication.
Ensure earplugs are clean and in good condition.
Learn more about hearing protection.
Other examples of PPE include:
safety glasses or goggles
safety shoes
high-visibility clothing or vests
heat-resistant gloves
anti-vibration gloves
oil-resistant gloves for lubrication tasks
welding PPE such as helmets and and flame-resistant clothing
chemical-resistant suits or aprons
safety harnesses and lanyards
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
Toolbox Talk for PPE
Workplace safety should begin with a hazard assessment. Once the hazards and risks have been identified, a plan can be put forward to prioritize and reduce the risk of injury. Useful systems and tools to perform hazard assessments include performing a risk assessment and a Job Safety Analysis (JSA).
The hierarchy of controls is a proven safety approach that helps protect employees. If elimination, substitution, engineering, and administrative controls are not enough to eliminate the risk, it is vital to choose the appropriate PPE carefully. Ensure employees are properly trained to use the safety equipment and be able to detect and report any damages before commencing work.
A toolbox talk about PPE is recommended to discuss the different kinds of PPE that can be used to minimize the likelihood and mitigate the effects of hazards. A toolbox talk template can help in assessing the sufficiency and availability of safety equipment for all employees.
PPE Safety Requirements
Safety Officers play a crucial role in maintaining workplace safety by ensuring proper use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). This includes assessing worksites for PPE requirements, providing well-fitted equipment, and training employees on safety standards.
Learn more about PPE Safety Requirements.
PPE Safety Examples
These examples of PPE safety are based on a free PPE checklist provided by SafetyCulture for anyone to download and use for free.
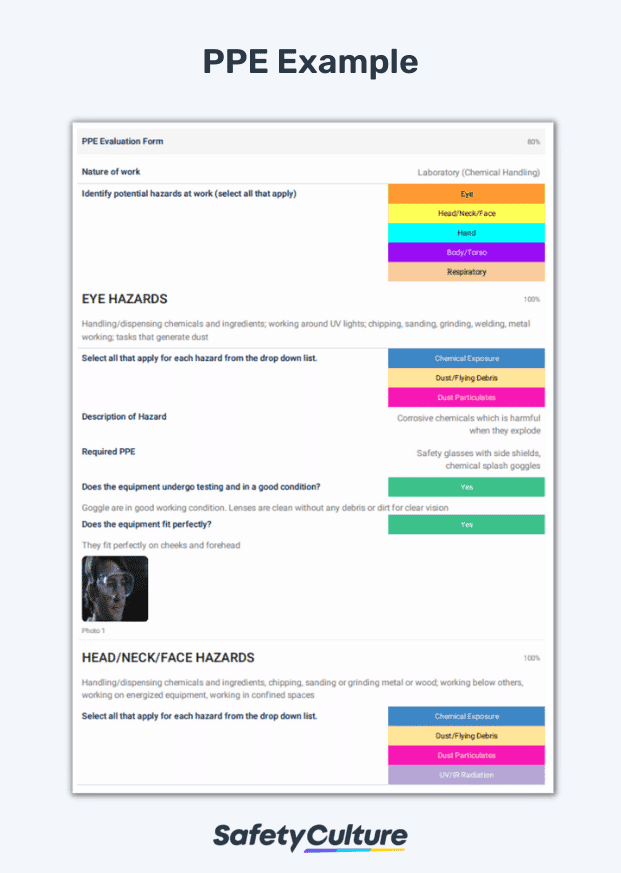
Nature of work :Laboratory (Chemical Handling)
Potential hazards at work:
Eye hazards – Handling/dispensing chemicals and ingredients; working around UV lights; chipping, sanding, grinding,welding, metal working; tasks that generate dust
Risk/s – Chemical exposure, dust particulates, flying debris
Description of hazard – Corrosive chemicals which are harmful when they explode PPE required – Safety glasses with side shields, chemical splash goggles
Does equipment undergo testing and in a good condition? Goggles are in good working condition. Lenses are clean without any dirt or debris
Does the equipment fit perfectly? They fit perfectly on cheeks and forehead.
Head/Neck/Face hazards – Handling/dispensing chemicals and ingredients, chipping, sanding or grinding metal or wood; working on energized equipment, working in confined spaces
Risk/s – Chemical exposure, dust particulates, flying debris, UV/IR radiation
Description of hazard – Dispensing chemicals and spills
PPE required – Full face shields
Does equipment undergo testing and in a good condition? Face shields have no dents and marks.
Respiratory hazards – Handling/using highly hazardous chemicals; tasks that generate dust and/or fumes; cutting, brazing on certain metals (stainless steel)
Risk/s – Chemical exposure, dust particulates, flying debris
Description of hazard – Exposure to dangerous vapors
PPE required – Respirators
Does the equipment fit perfectly? It fits perfectly. Straps are tight.
To give you a better idea, we’ve created a PPE checklist sample pdf report below:
PPE Safety Training
To make sure that PPEs are properly used and fully serve their functions, it’s important that your workers understand their proper use, maintenance, and disposal of PPE to protect themselves and the people around them. One of the most effective and efficient ways to do this is through hand-crafted courses that allow employees to do their PPE safety training even on mobile. SafetyCulture Training includes highly recommended premade courses that will cover the different types of PPE and demonstrate when and how to use them properly.
Unlock a Safer, More Efficient Workplace with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture helps businesses across industries improve their EHS practices and operational efficiency. See how we can help you:
✓ Streamline EHS compliance and reduce risks ✓ Enhance incident prevention and management ✓ Boost operational efficiency and productivity ✓ Strengthen communication on safety protocols ✓ Leverage data-driven insights for continuous EHS improvement
FAQs about PPE and PPE Safety
Related articles
Food Safety
Safety

Cold Holding: The Ultimate Guide
Learn about cold holding methods for food safety and how it reduces contamination risks across operations.
Food Safety
Safety

A Comprehensive Guide to Natasha’s Law Training
Learn about the process of Natasha’s Law training and how it helps food businesses efficiently meet allergen labeling requirements.
Construction Safety
Safety

A Complete Guide to Scaffolding Safety Training
Learn everything about scaffolding safety training, from topics to best practices, to uphold construction and maintenance safety.