A Brief Guide to Heat Illness Prevention
Understand heat illness prevention, its importance, and some examples of heat illness prevention plans.

Published 13 Mar 2025
Article by
4 min read
What is Heat Illness Prevention?
Heat illness prevention pertains to setting proactive measures in helping people avoid contracting illnesses caused by excessive heat exposure and heat exhaustion. Workers, especially those in the construction industry, can’t avoid working in the heat or any condition and place with high temperatures. Hence, heat illness prevention is key to help keep them healthy and safe when they’re at work.
Why is it Important to Prevent Heat Illness from Developing in the Workplace?
Heat is one of the top causes of weather-related fatalities in the United States. In relation to that, the Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) also states that almost 3 out of 4 fatalities caused by heat illness occur during the first week of work, which means many employees aren’t well-adjusted to their working conditions properly.
In the workplace, employees highly exposed to heat (whether indoors or outdoors) must receive proper assistance from their employers in ensuring they have a safe place to work. This can be done by having a well-ventilated work area when they’re indoors (falling under an organization’s Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning or HVAC system) and setting guidelines or protocols for strict implementation when working outdoors or on the field.
Here are a few of the major benefits of having proactive measures in place:
Increased employee productivity and efficiency
Reduced medical and emergency services costs
Improved culture of safety in the workplace
How Can You Prevent Heat Illness at Work?
While there are available first aid treatments for heat illnesses, it’s still best for organizations to put prevention as the first and foremost strategy.
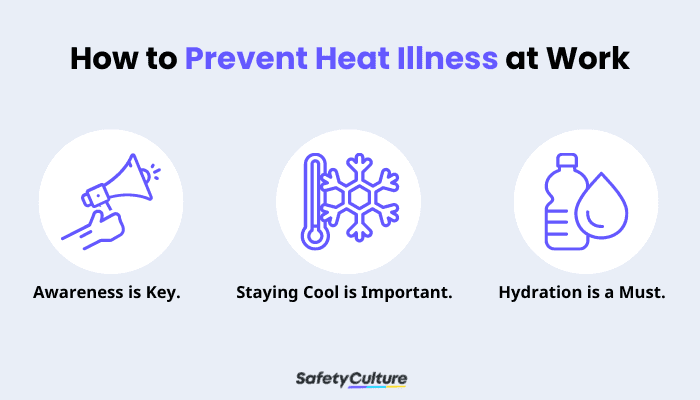
Having that said, what are 3 ways to prevent heat illness? Take a look at each of them in detail, as stated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Awareness is Key.
Know the warning signs , such as light-headedness, mild nausea, sleepiness, and profuse sweating.
Proactively monitor workers at high risk, such as those who overexert during work and/or are vulnerable to physical illnesses.
Stay updated on any heat-related alerts and safety tips in your area.
Staying Cool is Important.
Wear appropriate clothing that is lightweight and loose-fitting to help you beat the heat. Also, there are Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) available called personal cooling systems used to protect against heat exposure.
Let your body adjust to working in the heat to acclimatize properly and avoid putting your body under heat stress .
Don’t forget to wear broad-spectrum sunscreen to avoid sunburns which can cause dehydration and weaken your body’s ability to cool down.
Stay cool indoors by being in an air-conditioned or properly-ventilated place.
Schedule outdoor activities accordingly to avoid working under extremely high temperatures.
Avoid hot and heavy meals as these may also influence your body temperature to rise.
Hydration is a Must.
Drink more fluids without waiting to get thirsty before you do so.
Stay away from sugary or alcoholic beverages to avoid losing more body fluid.
Make sure to replace the salt and minerals you have lost from excessive sweating by taking salt tablets or drinking sports beverages.
Digitize the way you Work
Empower your team with SafetyCulture to perform checks, train staff, report issues, and automate tasks with our digital platform.
Heat Illness Prevention Planning
A heat illness prevention plan is a collection of guidelines created by an organization’s management to provide leaders, managers, and employees with the necessary training and tools to help them prevent illnesses caused by working in the heat.
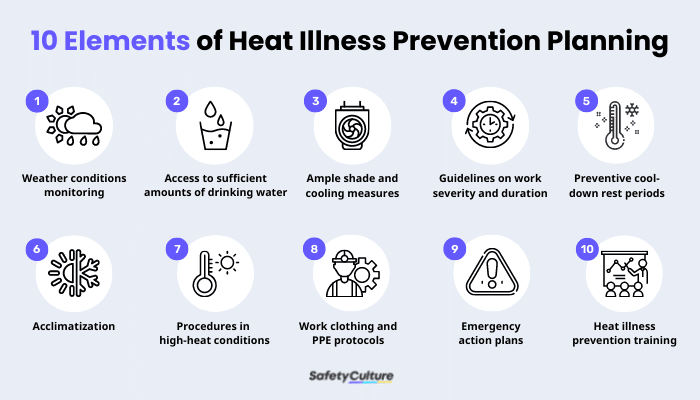
According to the California Department of Industrial Relations (DIR), your heat illness prevention plan should include 10 elements:
Weather conditions monitoring
Access to sufficient amounts of drinking water
Ample shade and cooling measures
Guidelines on work severity and duration
Preventive cool-down rest periods
Acclimatization
Procedures in high-heat conditions
Work clothing and PPE protocols
Emergency action plans
Heat illness prevention training
Moreover, the recommended OSHA Heat Illness Prevention Program under the OSH Act puts the responsibility on employers to provide workplaces free from known safety and health hazards, including those related to working in the heat. In detail, employers are highly encouraged to follow these steps toward a holistic program:
Create a heat illness prevention policy .
Enforce protocols for training workers, especially those working in the summer .
Be educated about heat illness first aid (use first aid inspection app as needed.)
Ensure proper education by sharing resources and related materials.
Using SafetyCulture (iAuditor) in Protecting Workers From Heat Illnesses
SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor)
Powerful mobile solutions such as SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) help organizations implement a comprehensive heat illness prevention program through various proactive ways. Maximizing the following smart features, build a culture of safety among your employees via iAuditor:
Leverage smart sensors for temperature and weather monitoring and connect them to the iAuditor app for a comprehensive heat control plan.
Raise and send real-time alerts for any heat stress-related issues encountered on the field, workstation, and workplace.
Use a heat exposure checklist or heat illness prevention plan template during toolbox talks to make sure you’re not missing out on important details when it comes to heat safety.
Create and assign corrective actions to address issues raised during inspections or audits.
Make use of inspection analytics and performance to gain insights relevant to designing steps and efforts for c ontinuous improvement of safety guidelines and protocols, among others.
Build and deploy engaging mobile Training courses related to working in the heat and heat illness prevention so that everyone across the board is well-educated and equipped toward a healthy and safe workplace.
Disseminate crucial guidelines on how to reduce heat stress using heat illness prevention posters, training resources, or any related educational materials via Heads Up .
Connect with lone employees working in the heat using SHEQSY by SafetyCulture for real-time monitoring.
Related articles
Safety
Safety Management

Transforming Workplaces with AI Safety Inspection
Learn about AI safety inspection and its role in smarter audits, automated insights, and proactive risk management.
Food Safety
Safety

Cold Holding: The Ultimate Guide
Learn about cold holding methods for food safety and how it reduces contamination risks across operations.
Food Safety
Safety

A Comprehensive Guide to Natasha’s Law Training
Learn about the process of Natasha’s Law training and how it helps food businesses efficiently meet allergen labeling requirements.