Risk Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide
Everything you need to know about risk analysis: its components, types, and methods, as well as examples and steps on how to perform risk analysis

Published 17 Sept 2025
Article by
7 min read
Key Takeaways
Risk analysis is a multi-step process used to mitigate the impact of risks on business operations and minimize vulnerability to unexpected events. It includes risk assessment, management, and communication.
Two primary methods of risk analysis are qualitative (based on perceived severity and likelihood) and quantitative (based on specific data), each suited for different types of risk evaluation and decision-making.
Common approaches include risk-benefit analysis, needs assessment, business impact analysis, failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), and root cause analysis, helping leaders identify gaps, prepare for disruptions, and improve business reliability.
What is Risk Analysis?
Risk analysis is a multi-step process aimed at mitigating the impact of risks on business operations. Leaders from different industries use risk analysis to ensure that all aspects of the business are protected from potential threats. Performing regular risk analysis also minimizes the vulnerability of the business to unexpected events.
Difference Between Risk Assessment and Risk Analysis
Risk assessment is just one component of risk analysis. The other components of risk analysis are risk management and risk communication. Risk management is the proactive control and evaluation of risks while risk communication is the exchange of information involving risks. Unlike risk analysis, risk assessment is primarily focused on safety and hazard identification.
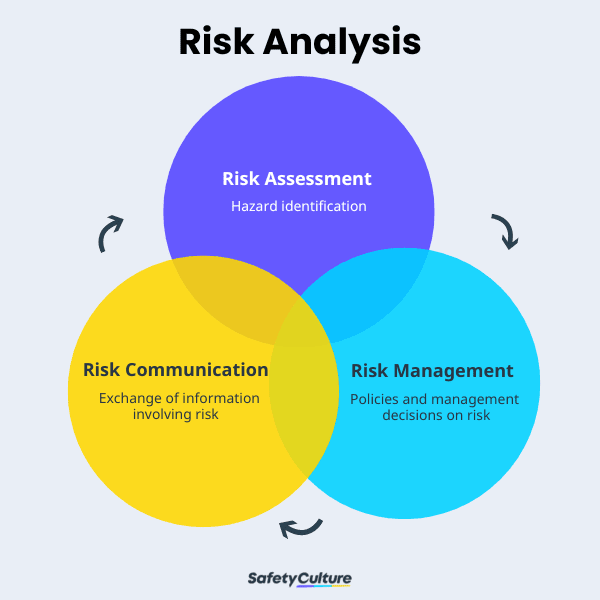
Risk Analysis Framework
Risk Analysis Methods
There are two primary risk analysis methods: qualitative and quantitative.
Easier and more convenient.
Rates risks based on perceived severity and likelihood.
Calculates risk using available data.
Qualitative analysis tools include all root cause analysis (RCA) tools except failure mode and effects analysis, needs assessment, and risk matrix. Common quantitative types include the 3×3, 4×4, and 5×5 risk matrix.
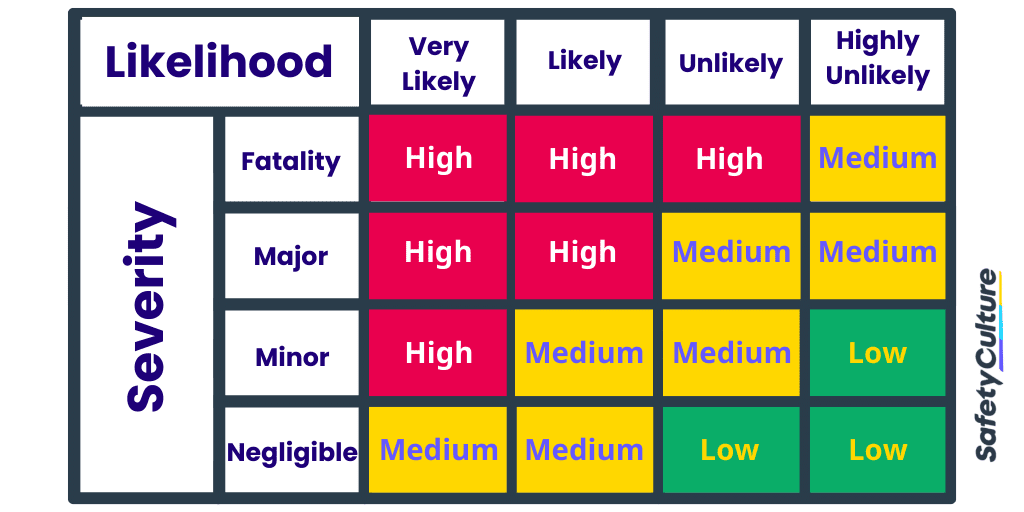
Risk Assessment Matrix | SafetyCulture
Quantitative risk analysis includes types such as business impact analysis (BIA), failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), and risk benefit analysis. The main distinction between qualitative and quantitative risk analysis lies in the type of risk assessed: qualitative analysis yields projected risk (estimates of how risks may manifest), while quantitative analysis focuses on statistical risk (specific and verified data), often used for calculating insurance premiums.
Mitigate Health and Safety Risks
Proactively assess, identify, and track potential hazards before they become issues to reduce workplace incidents and injuries.
Types of Risk Analysis
As risk analysis covers a wide range of topics, there are many approaches to analyzing risks or types of risk analysis. These include, but are not limited to, the following:
Risk Benefit & Cost Benefit Analysis A risk-benefit analysis looks at the advantages and disadvantages of an action, helping to determine how likely it is to succeed or fail, such as stakeholder analysis . On the other hand, a cost-benefit analysis adds up the expected costs and compares them to the expected benefits. Both methods help leaders make smart choices, as taking on risky or expensive actions can result in losses.
Needs Assessment A needs assessment is a structured process that helps organizations find out what they are lacking. It identifies gaps in the business and allows leaders to understand what needs improvement. This way, they can better use their resources to reach their goals more effectively.
Business Impact Analysis A business impact analysis helps companies prepare for disruptions caused by natural disasters and other external factors. It lays the groundwork for recovery plans and guides investments in prevention and mitigation strategies.
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) A failure mode and effects analysis is a method used to find possible problems in business processes and reduce their impact on customers. By identifying these issues, FMEA helps improve the reliability of products and services while also lowering costs associated with failures.
Root Cause Analysis A root cause analysis aims to find and remove the main reasons behind problems. This approach helps prevent the same issues from happening again by addressing the weak systems that lead to them. Besides failure mode and effects analysis, other tools used for root cause analysis include:
Risk Analysis Example
Here are risk analysis examples for three major industries: construction, transport & logistics, and manufacturing.
Construction Risk Analysis Example: The owner of a construction company considers a luxury resort project proposal that could boost her company’s reputation, but hesitates due to her focus on mid-range residential buildings. She conducts a risk-benefit analysis with her team to evaluate the potential risks and benefits before making a decision.
Transport & Logistics Risk Analysis Example: The director of a multinational shipping company worries about an upcoming storm’s impact on operations and proposes setting aside recovery funds. A colleague disagrees, believing the storm will have minimal effects. To convince him and other directors, she conducts a business impact analysis and presents the results at the next board meeting.
Manufacturing Risk Analysis Example: A new manager conducts a needs assessment by surveying workers to prepare the factory for increased summer orders, ensuring successful production of sufficient units.
How to Perform Risk Analysis
For leaders who have already decided on the type of risk analysis to perform, here are steps and instructions for each type:
How to Perform Needs Assessment
Step 1: Identify requirements – What must the business deliver to succeed?
Step 2: Assess existing resources – What can be used to achieve success?
Step 3: Identify needs – What does the business lack that is critical to success?
Step 4: Develop a plan of action – What must be done to fill the gaps and succeed?
Needs Assessment Template
Use this digital template to assess your business or department’s performance and identify learning needs, providing leaders with essential tools for effective management.
How to Perform Business Impact Analysis
Step 1: Gather information on business processes, finances, and management.
Step 2: Identify Recovery Time Objective (RTO) or how long it takes to restore business processes after disruption. RTO helps determine how long the business can function without normal business processes.
Step 3: Identify Recovery Point Objective (RPO) or the acceptable loss to customers when a disruption occurs. RPO helps determine the estimated financial impact on the business.
Step 4: Develop workaround procedures of the business in the event of disruption.
Step 5: Decide business needs based on the information gathered in previous steps.
Business Impact Analysis Template
Use this digital template to evaluate the impact of potential disruptive events on key business functions. It assesses operational losses and revenue, helping leaders prioritize recovery efforts during crises.
How to Perform Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
Step 1: Identify mechanism of failure
Identify potential failure modes and causes by reviewing past failures and establishing ground rules.
Step 2: Determine RPN
Calculate the risk priority number (RPN) based on severity, occurrence, and detection to prioritize failures. Focus on the top 20% of high RPNs for improvement efforts.

FMEA: RPN Risk Analysis | SafetyCulture
Leaders should focus their improvement efforts on potential failures at the top 20% of the highest RPNs. These high-risk failure modes must be addressed through effective action plans.
Step 3: Follow-up on actions
Continuously review and update action plans addressing high-risk failure modes after implementation.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Template
Use this digital template to pinpoint issues in processes or products by detailing the potential failure effect, cause, and current controls. Include severity, occurrence, and detection ratings, then record the RPN and sign off.
How to Perform Root Cause Analysis
Step 1: Define the problem
Identify observable consequences of an unidentified risk or root cause.
Step 2: Select a tool
Use methods like:
5 Whys : Ask “why” five times; simple but may oversimplify issues.
8D : Eight disciplines for long-term solutions; requires extensive training.
DMAIC : Comprehensive yet easier than 8D, especially if the analysis is simplified.
Step 3: Implement actions
Develop and execute specific actions addressing the root causes identified.
Root Cause Analysis Template
Use this digital template to examine a recurring problem’s impact on productivity. Identify reasons for the issue, rate their likelihood as root causes, select a root cause category, and propose a prevention strategy.
SafetyCulture Platform for Teams
Why use SafetyCulture?
Minimize your business’ vulnerability to unexpected events and potential threats with a digital tool like SafetyCulture.
✓ Simplify processes with digital checklists✓ Receive professional reports and share instantly✓ Use for teams of any size
Streamline your organization’s operations and workflow with our digital checklist. It empowers you to:
Maintain safety and compliance standards with customizable templates
Increase your team’s engagement and accountability including contractors and stakeholders
Create powerful workflows by integrating your existing software
Gain greater visibility and transparency with real-time reporting
Access unlimited storage and data security for your reports
Take advantage of our comprehensive features to optimize your operations and enhance workplace safety today.
FAQs about Risk Analysis
Article by
SafetyCulture Content Team
SafetyCulture Content Contributor, SafetyCulture
View author profileRelated articles
Environmental Safety
Safety

Oil Drum Storage: Safety Guide and Best Practices
Learn the practices for safe oil drum storage, its importance, and the regulations for compliance.
Environmental Safety
Safety

Flood Risk Management
Read this guide to flood risk management, its importance, and the key components and strategies for this process.
Environmental Safety
Safety

A Comprehensive Guide to Stormwater Pollution Prevention Best Management Practices (SWPPP BMP)
Learn about the types of best management practices for SWPP and the steps to effectively implement them in prevention plans.