Near Miss Reporting: A Safety Guide
Learn about the essentials of near miss reporting in this comprehensive guide. Understand the importance of addressing near miss incidents and the best practices for establishing a successful near miss program.

Published 13 Oct 2025
Article by
7 min read
What is a Near Miss?
A near miss is an incident that did not result in injury or property damage, but had the potential to if it had not been addressed in a timely manner. Though the worst possible outcomes of a near miss are not realized, affected employees should still report it as an unsafe event.
How Does a Near Miss Differ From an Incident and Accident?
Near miss vs. incident
A near miss is an unplanned event that could have caused injury, illness, or damage but did not, often narrowly avoided by luck or quick action. An incident, on the other hand, is any unplanned event that results in or could result in harm, including near misses and events that actually cause injury or damage.
For example, if the outcome of an unsafe event is fully realized and not prevented by a last-minute decision, then the unsafe event is considered an incident. This is still the case even if the incident did not result in injury or property damage.
Near miss vs. accident
An accident is an unsafe event that results in injury or property damage. Though the OSHA definition of incident is similar to that of an accident, other safety organizations consider incident and accident to be two separate entities. An incident becomes an accident once it causes harm or results in damage to the immediate environment, which is usually why accidents are more widely reported than incidents.
For example, dropping a tool from scaffolding without hitting anyone is a near miss. However, if the tool had struck a worker and caused injury, it would count as an accident.
Importance of Reporting Near Misses
Reporting near misses is crucial to prevent accidents by addressing underlying hazards. It is a common misconception that incidents, which include near misses, are nonconsequential since they do not cause or lead to harm or damage. However,a research study on construction worksites revealed that for one fatal injury, there were 10 minor injuries, 29 property damage incidents, and 600 non-injury incidents.
While OSHA does not legally require companies to report near misses unless they result in injury or property damage, it is important for businesses to encourage near miss reporting. Timely reporting helps mitigate risks and prevent accidents by raising awareness about the hazards employees face to ensure a safer working environment for all stakeholders involved.
Streamline Incident Management
Respond to incidents as they occur. Quickly log, track, and resolve incidents to minimize operational downtime.
Examples in the Workplace
Though near miss reporting is crucial in the construction industry, corporate environments also benefit from setting up a near miss program. Below is a near miss example in the workplace:
An employee rushing to get to the cafeteria during his lunch break fails to see a large cable on the floor and trips over it. However, he notices that a table is nearby and uses it to stop himself from falling face-first onto the concrete floor.
If the employee decides to report the near miss:
After the near miss, the employee tries to remove the large cable from the floor but is unable to.
He submits a near miss report to the office manager, who is in charge of ensuring that employees have a safe space to work in.
Upon receiving the near miss report, the office manager recognizes that the large cable is a safety hazard.
She immediately enlists the help of other staff members to remove the large cable, and by the time the employee returns from his lunch break, the large cable is no longer on the floor, but is propped up on a bench. It causes no further incidents.
If the employee chooses not to report the near miss:
After the near miss, the employee continues speeding towards the cafeteria. He has his lunch and goes back to work, having forgotten about the near miss.
A week passes by with the large cable still on the floor, and another incident occurs. This time, the employee involved did not notice the table nearby and fell face-first onto the concrete floor.
She takes the day off and goes to the emergency room to receive treatment for her injuries. Once there, the doctors inform her that she needs a week to recover. She ends up taking a leave of absence until the following week.
Steps for Setting Up a Successful Near Miss Program
A near miss program can be considered successful if it is integrated into or functions as the organization’s health and safety program. Isolating the near miss program from the wider organizational culture and other relevant policies may cause it to lose its effectiveness. To avoid implementing a faulty near miss program that becomes obsolete after a few months, follow the steps below:
Step #1: Ask For Employee Input
This can be done through formal one-on-one interviews or informally via an online survey. In both cases, the health and safety team should ask questions such as:
What are your thoughts on near miss reporting?
What would stop you from reporting a near miss?
What would encourage you to report a near miss?
What do you think should be included in our near miss program?
What would be your ideal form of participation in the near miss program?
Step #2: Perform Hazard Identification
This gives the health and safety team a general idea of what could possibly lead to a near miss. It also serves as training for conducting root cause analysis later in the implementation of the near miss program.
There are many types of hazards, and some industries deal with specific types, which is why it is important to cover all bases. Using a checklist can help provide a structured outline to keep track of the kinds of hazards to consider.
Create your own hazard identification checklist
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
Step #3: Conduct a Risk Assessment
In contrast to hazard identification, risk assessment focuses more on the possible consequences of a near miss, rather than possible causes. This step is crucial in spotting SIF potential even before a near miss occurs.
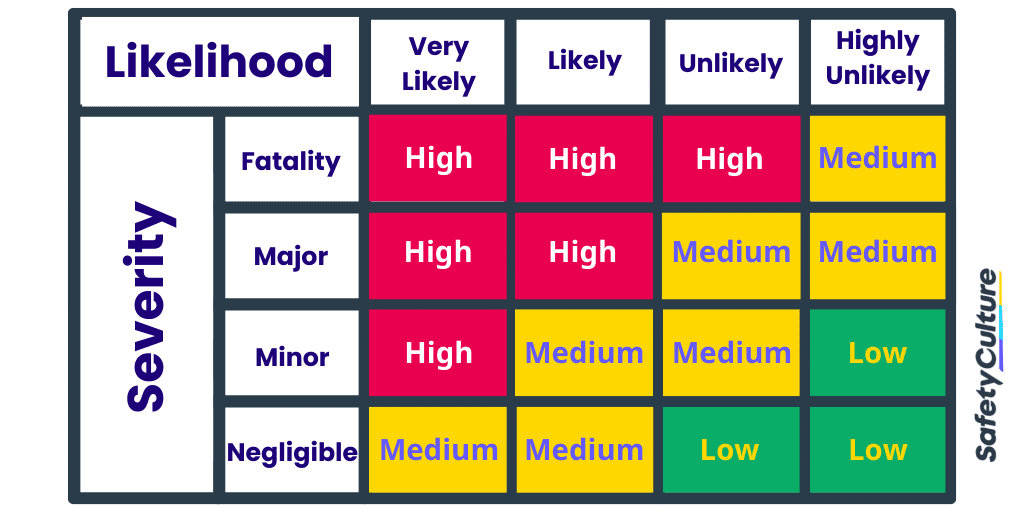
Risk Assessment Risk Matrix
By performing risk assessment before implementing the near miss program, the health and safety team gain a better understanding of the risks they should prioritize and prepare employees for.
Step #4: Create a Clear Implementation Plan
For any new policy, project, or program, the implementation phase either makes or breaks its success. Before jumping in though, it’s good to have a plan. When creating a plan for the implementation of the near miss program, the health and safety team must include representatives or leaders from different teams in the organization. This provides great insight on possible blockers to implementation and raises the credibility of the near miss program in the eyes of employees.
Tips for Successful Implementation
Once the plan for implementation has been finalized, the health and safety team can proceed with the implementation itself. While the specific steps for implementing a successful near miss program differ for each organization, here are a few basic tips that could help.
Tip #1: Conduct Regular Toolbox Talks
Though a near miss reporting toolbox talk should be held before implementation, regular toolbox talks after implementation may be necessary for effective safety discussions. Additionally, the health and safety team can use the feedback given by employees during these toolbox talks to improve the near miss program and its implementation.
Tip #2: Encourage Consistent Near Miss Reporting
Whenever a near miss occurs or is reported, it is critical to not place the blame solely on the employee, as the root cause of a near miss is more likely to be a flaw in the organization’s systems or processes. Another way to encourage near miss reporting is to emphasize how it benefits employees by giving real-life examples of how it prevented an injury or saved a life.
Tip #3: Provide Near Miss Reporting Forms
Save employees’ time spent on making near miss reports from scratch by providing near miss reporting forms that are easy to understand and fill out. A near miss reporting form should contain the following:
Date, time, and location of the near miss
Other details including the hazards involved
Person affected by the near miss and witnesses
Establish A Successful Near Miss Program with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard. Efficiently manage and streamline health and safety processes across the organization, including incident management, safety audits and inspections, risk assessment, waste management, and more, using a comprehensive manufacturing software solution.
Save time and reduce costs
Stay on top of risks and incidents
Boost productivity and efficiency
Enhance communication and collaboration
Discover improvement opportunities
Make data-driven business decisions
FAQs About Near Miss Reporting
Article by
SafetyCulture Content Team
SafetyCulture Content Contributor, SafetyCulture
View author profileIn this article
- What is a Near Miss?
- How Does a Near Miss Differ From an Incident and Accident?
- Importance of Reporting Near Misses
- Examples in the Workplace
- Steps for Setting Up a Successful Near Miss Program
- Tips for Successful Implementation
- Establish A Successful Near Miss Program with SafetyCulture
- FAQs About Near Miss Reporting
Related articles
Environmental Safety
Safety

Stormwater Pollution Prevention Best Management Practices
Learn about the types of best management practices for SWPP and the steps to effectively implement them in prevention plans.
Construction Safety
Safety

Understanding Mechanical Excavation in Modern Construction
Learn about mechanical excavation and how to maintain safety across excavation projects with this guide.
Risk Assessment
Safety

Disaster Recovery Policy: The Ultimate Guide
Discover how a disaster recovery policy bolsters operational resilience and safety through clear procedures and continuous improvement.