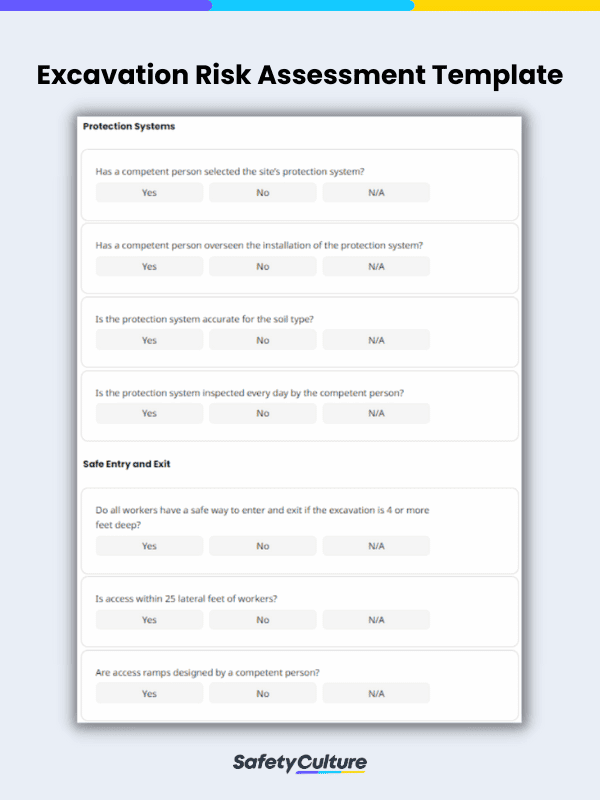
What is an Excavation Risk Assessment Template?
An excavation risk assessment template is a standardized document or form used by organizations, construction companies, or project managers to evaluate and manage the potential risks associated with excavation work. Excavation activities involve digging, trenching, or digging below the ground surface to create holes or cavities, often for construction, utility installations, or archaeological purposes. These activities can pose various safety and environmental hazards, and a risk assessment template helps identify, assess, and mitigate such risks.
Why Use Excavation Risk Assessment Templates
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) states that excavating is recognized as one of the most hazardous construction operations. In some situations, hazard potential increases, especially after rainstorms and when fissures, tension cracks, and water seepage occur.
Hence, an excavation risk assessment is performed to determine and decrease safety risks before trenching and excavating activities. This type of risk assessment should be carried out at least daily and before the start of each shift to protect workers from cave-ins. Also, this helps make sure that protective systems such as sloping, benching, shoring, shielding, and other engineering controls are properly in place and good condition.
For this, excavation risk assessment templates help offer a structured approach to identifying, evaluating, and mitigating the potential hazards involved in this job. Apart from that, here are other reasons why using these templates is a must:
Standardization of Safety Practices
By using templates for excavation risk assessments, organizations can standardize safety practices across various projects. This consistency ensures that every excavation site undergoes a thorough risk assessment, minimizing the likelihood of oversight or missed hazards.
Compliance with Regulations
Excavation work is subject to numerous safety regulations and standards. Using a template helps ensure that all legal requirements are met, reducing the risk of non-compliance, penalties, and legal liabilities.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Proper documentation is crucial in demonstrating due diligence in excavation safety practices. Hence, templates help create a detailed record of the risk assessment, which can be helpful in the event of audits, inspections, or insurance claims.
What to Include in an Excavation Risk Assessment Template
An effective excavation risk assessment template should cover a range of critical aspects to ensure the safety of personnel, prevent accidents, and comply with regulations. Generally, the following elements and sections must be included in it:
- Title Page – task/activity details, including the site name, location, date, and personnel involved
- Risk Assessment – list of identified hazards, their description, the people at risk, controls, risk rating, and recommended actions
- References – e.g., risk rating matrix and its guidelines
- Completion Page – names and signatures of the personnel who conducted the risk assessment
How to Create a Template for Excavation Risk Assessments
Creating a checklist for excavation risk assessments is a valuable tool to ensure that no crucial aspect is overlooked during the assessment process. Such checklists provide a clear structure for hazard mitigation and control of safe work.
To help you build an excavation risk assessment template, follow these steps:
Start with the title page.
Begin your checklist with a title page that includes essential project information such as the site name, location, date of assessment, and the names of individuals involved in the assessment. This provides context and accountability for the assessment process.
Create a comprehensive risk assessment section.
This is the core of your checklist and should be divided into key fields based on the critical areas of hazard assessment. These include the hazard’s description, the recommended controls to mitigate it, its risk rating, and the people who are at risk with it.
Make sure to include references.
Incorporate references in your checklist that point to relevant guidelines. This section should provide easy access to such, including risk matrix benchmarks and other categories.
Add a completion page.
End your checklist with a completion page where relevant personnel can sign, indicating their acknowledgment and commitment to implementing the risk assessment’s safety measures. This signature section verifies that all necessary safety precautions have been considered and agreed upon.
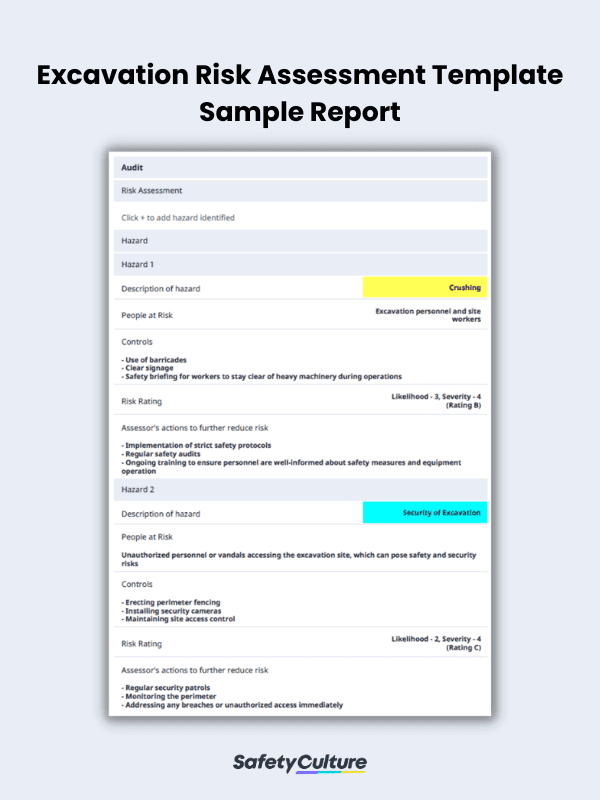
On that note, here’s a sample excavation risk assessment template exported as a report:
FAQs About Excavation Risk Assessment Templates
By documenting excavation hazards, control measures, and emergency procedures, these templates help provide a tangible record of an organization’s commitment to safety. These can serve as solid evidence of due diligence in case of legal inquiries or inspections.
Involving a safety professional when using an excavation risk assessment template is highly advisable, especially for complex projects or projects subject to specific legal requirements. They bring expertise in hazard identification, risk assessment, and safety compliance, which can enhance the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the assessment.
While training isn’t always required to use an excavation risk assessment template effectively, it can greatly enhance the quality and accuracy of the assessment. Training ensures that users understand the purpose of each section in the template, the significance of hazard identification, and how to evaluate risks appropriately.