Published 26 Sept 2025
Article by
5 min read
What is a COSHH Assessment Template?
A COSHH assessment template is a structured tool helps businesses evaluate and manage the risks associated with hazardous substances in the workplace. COSHH stands for Control of Substances Hazardous to Health. This template enables users to identify hazardous substances present in their operations, evaluate the risks associated with them, and establish control measures to manage these risks.
What is a COSHH Assessment?
A COSHH (Control of Substances Hazardous to Health) Assessment, or COSHH Risk Assessment, is a health and safety evaluation process and document often used with COSHH registers. It aims to identify and evaluate hazards and risks from hazardous substances used in the workplace or produced during operational processes and devise control measures to reduce or eliminate identified risks.
The UK’s Health and Safety Executive (HSE) requires a COSHH assessment as a standard safety measure to protect employees from harmful substances and avoid adverse health effects.
Why Perform COSSH Risk Assessments?
Exposure to chemical substances is a common occupational hazard. An HSE report found 6,000 self-reported cases of skin disease from 2015 to 2018 due to hazardous substance exposure. Skin disease from chemical exposure has profound detrimental effects on workers’ daily activities, ability to work, and self-image. Occupations most affected include metalworkers, machine operators, and other industrial workers dealing with hazardous substances.
Benefits of Using a Template for COSHH Assessments
COSHH assessments help identify risks from hazardous substances but can be time-consuming without the right expertise. A COSHH assessment template can simplify the process.
Save time – With a template, you don’t have to spend hours creating a new file from scratch, as it already covers the necessary information for a COSHH assessment.
Improve accuracy – Reduces the risk of overlooking crucial information or sections in the assessment. Throughout this document, prompts or questions help you identify all potential hazards, ensuring that all sections are completed as required.
Ensure consistency – The standardized format of these templates creates a structure for COSHH assessments, making them more systematic and organized.
What to Include in a COSHH Risk Assessment Template
An efficient COSHH assessment should document these 5 essential elements:
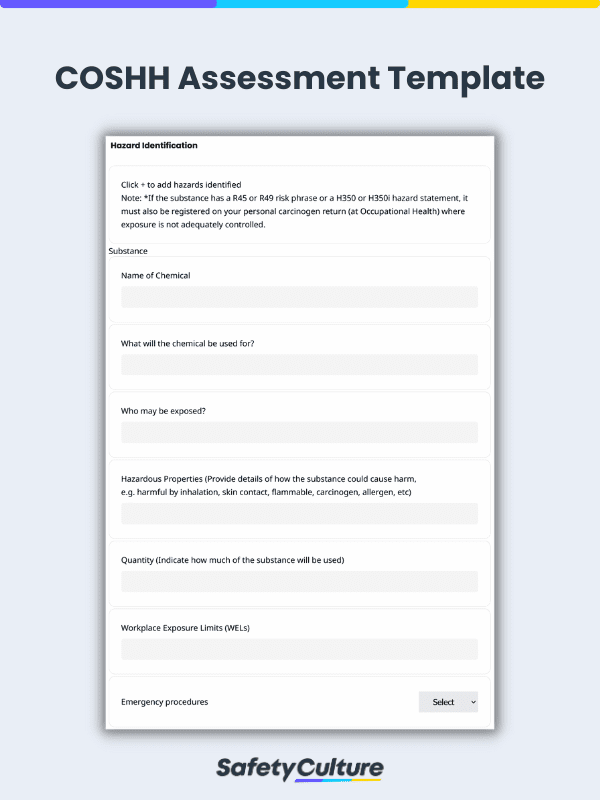
COSHH Assessment Template | SafetyCulture
Detailed listing of hazardous substances present in the workplace
Workplace Exposure Limits (WELs) and health risks
Control measures to be implemented (PPE, First Aid Measures)
Information on proper storage, handling, and disposal of chemicals
Authorization by employer or supervisor
How to Use This Template
Using a COSHH assessment template is easy once you have your template ready. Below is a step-by-step guide:
1. Identify existing hazardous substances.
Begin the COSHH assessment by identifying all hazardous substances— chemicals,dust, fumes, and biological agents. Even small amounts can be harmful, so thorough identification is essential.
2. Assess the risks.
Consider factors such as exposure, toxicity, and likelihood of harm for each substance. Assess not just the overall work, but also specific tasks and activities, as these influence risk levels.
3. Implement controls.
Using the results of the risk assessment, the team can develop and implement controls to manage or eliminate the identified risks, such as but not limited to:
Changing work practices or procedures
Modifying the physical environment
4. Review and revise.
COSHH assessments aren’t one-off tasks—they must be regularly reviewed and updated, especially when new substances or procedures are introduced.
COSHH Assessment Example
Now that you know how to use a template for COSHH assessments, it’s time to put that knowledge into practice. The COSHH form example below shows how a hazardous substance can be identified, controlled, and evaluated in a systematic manner:
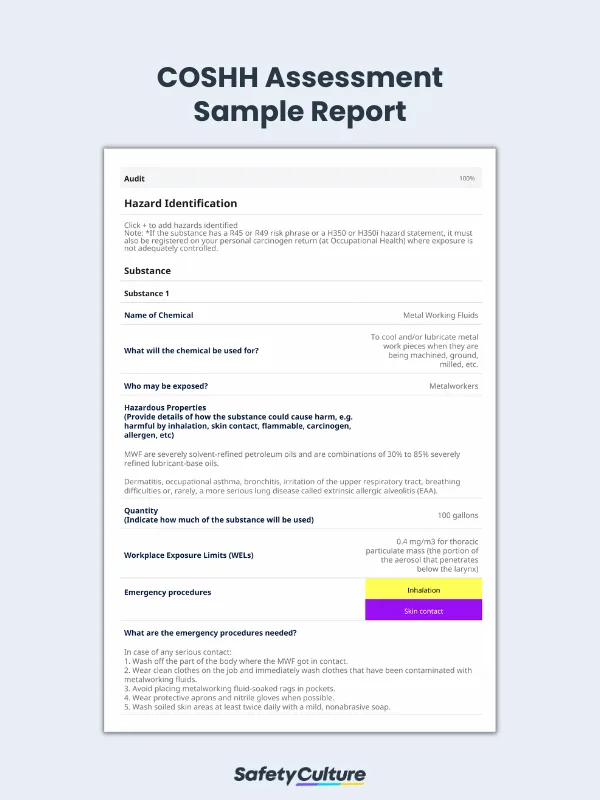
Step 1: Hazard Identification | |
Chemical name | Metalworking fluids (MWFs) |
What will the chemical be used for? | To cool and/or lubricate metalwork pieces when they are being machined, ground, milled, etc. |
Who may be exposed? | Metalworkers |
Hazardous properties (How could the substance cause harm? E.g., inhalation, skin contact, flammability, carcinogen, allergen) | MWFs are severely solvent-refined petroleum oils and are combinations of 30% to 85% severely refined lubricant-base oils. Dermatitis, occupational asthma, bronchitis, irritation of the upper respiratory tract, breathing difficulties, or, rarely, a more serious lung disease called extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA). |
Quantity (How much of the substance will be used?) | 100 gallons |
Workplace Exposure Limits (WELs) | 0.4 mg/m3 for thoracic particulate mass (the portion of the aerosol that penetrates below the larynx) |
Emergency procedures for: | Inhalation, skin contact |
What are emergency procedures needed? | In case of any serious contact: Wash off the part of the body where the MWF got in contact. Wear clean clothes on the job and immediately wash clothes that have been contaminated with metalworking fluids. Avoid placing metalworking fluid-soaked rags in pockets. Wear protective aprons and nitrile gloves when possible. Wash soiled skin areas at least twice daily with a mild, nonabrasive soap. |
Step 2: Methods of Prevention or Control of Exposure | |
Engineering controls required | Total containment, Fume cupboard, Local exhaust ventilation |
Access control | Restricted to competent personnel |
Special procedures | SOP, Code of Practice, local rules, etc. |
Approved PPE | Gloves, Eye protection, Laboratory coat |
Disposal Procedures | All containers submitted for disposal must be clearly labeled with the complete chemical name(s) of all waste in the container or product name if an MSDS is either submitted or available to EHS. A correctly completed EHS waste tag will fill this requirement. All containers must be in good condition without leaks, the outside of the container must be free from contamination, and lids or covers must be securely in place. Original containers should be used whenever possible. |
Are chemicals with risk phrases R50-R59 or hazard statements H400 – H413 (environmental hazards) involved? | Yes |
Training Requirements | To be planned next week. |
Handling and Storage Requirements | Needs to be coordinated with the responsible team. |
Step 3: Assessment of Risk Using Controls Detailed Above | |
Are the hazards/risks suitably controlled, using the control measures detailed above? | Yes |
For a full view of this example, check this sample COSHH assessment report in PDF format.
Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.