A Brief Guide to Production Line Workers
Understand what a production line worker does, the importance of their work in maintaining product quality and operational efficiency, and the risks they face when working alone.

Published 22 May 2025
Article by
6 min read
What is a Production Line Worker?
A Production Line Worker (PLW) is an individual responsible for observing, assembling, inspecting, and packaging products during the manufacturing process to ensure they meet quality standards. They operate and maintain machinery, keep an eye on the production process to maximize efficiency, and make sure every item leaving the line is up to the mark. This role often requires someone with a sharp eye for detail, solid physical endurance, and the ability to keep up in a busy, team-focused setting.
In some situations, PLWs may be required to work alone in isolated areas. Lone working in these scenarios increases the importance of safety protocols, as immediate assistance may not be available in case of emergencies or equipment malfunctions. Employers must implement effective lone worker policies, regular check-ins, and monitoring systems to ensure the safety and well-being of PWLs when they are working independently.
When Production Line Workers Work Alone
PLWs may be required to work alone during certain tasks or situations where immediate assistance is not readily available. While most PLWs work in manufacturing, some of the other industries where they may work alone vary from food processing and production, mining operations, water and wastewater treatment facilities, and many more.
The most common instances where PLWs may work alone include the following:
Equipment Inspection and Repairs: Workers often handle tasks such as inspecting, cleaning, repairing and maintaining equipment and machines alone.
Shift Changes or Off-Hours Operations: Some workers on night shifts or off-peak hours may be the sole operator on a production line or specific equipment area.
Performing Specialized or High-Risk Tasks : Sometimes, workers handle hazardous chemicals, dangerous equipment, and more that are isolated for safety or operational reasons, which also keeps them alone.
Cleaning and Housekeeping: Workers who clean production areas or perform routine equipment upkeep often take place in quieter parts of the facility, where workers may be alone for a period of time.
Security Patrols: Specific workers may be tasked with conducting security checks or monitoring certain areas after hours, which often they do alone.
Emergency or Unplanned Downtime: In the instances where equipment fails or malfunctions, lone production line workers are the first responders.
In case PLWs are to be left alone, it’s essential to implement the right lone working policies for their needs to keep them safe. Putting solid safety measures and communication systems in place helps lone workers stay connected and supported, promoting a healthier, more positive work environment.
Importance of Keeping Production Line Workers Safe
PLWs are a vital part of production system because they directly contribute to the production of goods, ensuring quality, efficiency, and safety. The importance of keeping lone PWLs safe centers on several critical factors:
Risk Management and Accident Prevention: Prioritizing worker safety helps identify and address potential hazards—like machinery accidents, chemical exposure, or falls—helping reduce the risk of injuries and fatalities on the job.
Emergency Response and Assistance: Regular monitoring, check-ins, mobile-accessible panic buttons , and GPS tracking help ensure quick response during emergencies, which can be crucial in saving lives.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Complying with regulations such as Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) 1915.84 in the US, which mandates regular visual or verbal check-ins for lone workers, protects lone PLWs and shields employers from legal and financial consequences.
Operational Continuity and Productivity: Safeguarding lone PLWs helps efficient monitoring and rapid intervention keep production lines running smoothly and reduce costly disruptions.
Monitor and ensure lone worker safety with SafetyCulture
Ensure visibility over lone workers and manage their quality and safety with our digital solutions, built for and trusted by lone workers and leaders globally.
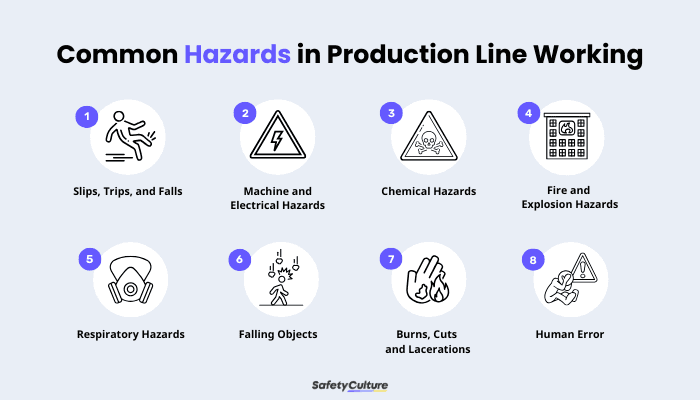
Common Hazards
Lone working in any scenario can present unique safety challenges, where risks are heightened due to isolation from immediate support. Here are some of the most common hazards PLWs face:
Slips, Trips, and Falls :Cause non-fatal injuries, such as sprains, fractures, or more serious harm, due to wet or oily surfaces, cluttered walkways, and uneven floors.
Machine and Electrical Hazards :Pose a high risk of injury for lone workers especially due to possibly unguarded or inadequately guarded moving parts, such as gears and belts.
Chemical Hazards :Exposure to different chemicals like solvents, acids, and gases can cause skin irritation, respiratory problems, and other serious health issues
Fire and Explosion Hazards: Exposure to flammable gases, vapors, or dust can lead to fires or explosions, causing serious injury or damage.
Respiratory Hazards :Causes respiratory issues, lung damage, or even cancer through prolonged exposure to substances such as hazardous dust, fumes, and vapors.
Falling Objects: Cause head injuries or other trauma when objects or equipment fall from heights.
Burns, Cuts, and Lacerations: Increase the risk of burns and cuts when handling hot surfaces, chemicals, or sharp tools.
Human Error: Lead to mistakes and increase the likelihood of accidents due to stress, fatigue, or rushing to meet production targets.
Role of Technology in Safe Production Lines
Various technologies today exist to help keep lone workers in any industry safe. One of which is SafetyCulture, which can help lone PLWs through its mobile-first operations platform that equips them with digital tools to enhance safety, quality, and productivity on the floor. By giving employers immediate visibility of their PLWs anytime and anywhere, and by connecting lone workers to them through their mobile devices, safety is ensured every step of the way.
Other key ways it benefits production line workers include:
Standardizing Procedures: Convert work instructions and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) into digital formats to help reduce production errors and ensure consistent adherence to best practices by all team members.
Real-Time Issue Reporting: Document inspection findings with photo annotations to enable immediate identification and resolution of safety or quality issues before they escalate.
Schedule Maintenance and Alerts: Keep equipment and other manufacturing assets in good shape, minimize their downtime, and avoid issues from faulty machines by setting up automatic maintenance reminders.
Training and Upskilling: Boost skills and stay up to date on procedures with mobile-friendly, bite-sized training courses that fit into the workday without causing disruptions.
Safety Monitoring: Implementing lone worker safety devices and digital monitoring platforms improves hazard detection, communication, and incident reporting.
Monitor Your Lone Production Line Workers with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across the manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality industries. It is designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Stay connected with your team and manage lone worker risks through location sharing and discreet panic alerts that can escalate to emergency services. Foster a culture of safety and transparency by enabling constant communication with lone workers, allowing them to perform tasks with configurable durations and check-ins.
✓ Save time and reduce costs ✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents ✓ Manage compliance with safety standards ✓ Enhance communication and collaboration ✓ Monitor worker condition ✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Related articles
Safety
Safety Management

Transforming Workplaces with AI Safety Inspection
Learn about AI safety inspection and its role in smarter audits, automated insights, and proactive risk management.
Food Safety
Safety

Cold Holding: The Ultimate Guide
Learn about cold holding methods for food safety and how it reduces contamination risks across operations.
Food Safety
Safety

A Comprehensive Guide to Natasha’s Law Training
Learn about the process of Natasha’s Law training and how it helps food businesses efficiently meet allergen labeling requirements.