Mastering EHS Standards for Effective Implementation
Stay ahead with this in-depth look at EHS standards across sectors, and explore compliance requirements, industry applications, and best practices in workplace safety and environmental protection.

Published 3 Jul 2025
Article by
7 min read
What areEHS Standards?
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) standards are formal guidelines and regulatory frameworks that ensure organizations minimize their adverse impacts on the environment, safeguard the health and well-being of their workforce, and prevent hazards and potential accidents in the workplace. Established by governmental bodies and international organizations, these cover a wide range of areas, from ergonomics to emergency response planning. By adhering to these standards, companies demonstrate their commitment to risk mitigation, employee welfare, and sustainable practices.
Importance
Historical events primarily shaped the development of formal EHS standards. While its roots can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution, disasters such as the Seveso chemical accident (1976) and the Bhopal Gas Tragedy (1984) underscored the need for a systematic approach to EHS compliance. Here are some specifics:
Improves risk mitigation – These guidelines serve as a roadmap for identifying hazards and implementing controls, helping companies prevent workplace injuries, fatalities, and environmental damage.
Boosts employee morale and productivity – Workers who feel valued and protected are more confident in accomplishing their tasks and engaged in safety initiatives proposed by top leadership.
Increases cost savings – Effective EHS programs minimize costs associated with accidents, downtime, compensation claims, and regulatory fines. Sustainability practices also enhance efficiency by reducing waste and energy consumption.
Enhances legal compliance – Adherence to Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) standards and environmental regulations is a legal requirement in most countries. Non-compliance may result in severe penalties, including lawsuits, imprisonment, and even the cessation of business permits.
Advances the company’s reputation – Companies committed to sustainability goals (e.g., reducing carbon footprint , responsibly managing waste, etc.) are more attractive to the environmentally-conscious public. Aside from improving public perception, this fosters trust among stakeholders.
Ensure Health & Safety Compliance with Ease
Stay ahead of regulations and maintain a safe workplace with a digitized compliance tool.
Core Components
EHS standards are built on a foundation of three essential pillars. While distinct, each component is interconnected with others, creating a safe, healthy, and responsible work environment.
Environmental Protection
Focused on reducing the environmental impact of business operations, this includes managing air and water emissions, proper waste disposal, chemical handling, energy efficiency, and adherence to environmental regulations. Here are a few EHS ISO standards and similar regulations from certain countries:
ISO 14001 or the Environmental Management System
Clean Air Act by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) by the European Parliament and Council
Health Management
Central to an organization’s operational success, this includes monitoring occupational exposure to harmful substances, promoting mental and physical well-being, preventing work-related illnesses, and maintaining hygiene standards. Here are some examples under this component:
ISO 145001 or the Occupational Health and Safety Management System
Work Health and Safety (WHS) Act of 2011 by Safe Work Australia
Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) and the Control of Asbestos at Work Regulations by the UK’s Health and Safety Executive (HSE)
Control of Vibration at Work Regulations 2005 under the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 in the United Kingdom (UK)
Workplace Safety
Crucial in eliminating and controlling workplace hazards, this component includes hazard identification, risk assessments, training, Personal Protective Equipment ( PPE ) usage, and emergency preparedness, to name a few. These are the most relevant standards in this component:
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards by the US Department of Labor
Canada Labor Code – Part II by the Labor Program of Canada
Integrating these three pillars creates a robust and proactive EHS management system that boosts employee morale, fosters a culture of responsibility, and builds long-lasting operational resilience.
Create your own EHS audit checklist
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
Process of Implementing EHS Standards
Implementing EHS standards isn’t just about ticking regulatory boxes. It should be about building a safer, healthier, and more environmentally responsible workplace. This is the step-by-step approach that ensures that organizations lay a solid foundation:
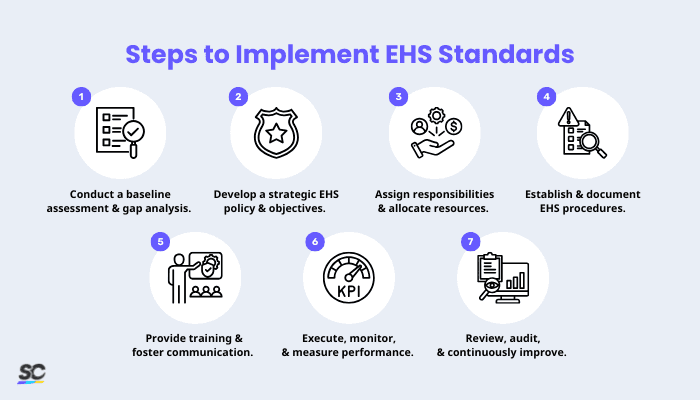
Steps to Implement EHS Standards
Step 1: Conduct a baseline assessment and gap analysis.
The first step is evaluating your current EHS performance and comparing it with relevant standards and legal requirements. Identify strengths, weaknesses,compliance gaps, and risk areas to determine what needs to be changed or improved.
Utilize digital EHS checklists to speed up the process and ensure accurate and complete data gathering.
Step 2: Develop a strategic EHS policy and objectives.
Based on the insights from the initial assessment, define your organization’s overall EHS policy. Find alignment between EHS standards and procedures in the company, reflecting its commitment to legal compliance,risk reduction, worker health and safety, and environmental protection.
Step 3: Assign responsibilities and allocate resources.
Build an in-house team that includes an EHS manager, safety officers, and department heads, and ensure they have the authority, tools, and resources required to lead the implementation.
Cross-functional collaboration is key at this stage. However, ensure each team member understands their specific duties and how they can contribute to the program.
Step 4: Establish and document EHS procedures and controls.
Create clear procedures and work instructions based on the internal Safety Management System (SMS) to effectively manage environmental impacts, health risks, and safety hazards. These should outline the following:
Responsibilities
Required actions
Control measures (e.g., PPE usage, safety measures, etc.)
Emergency processes
Compliance protocols
Step 5: Provide training and foster communication.
All employees at every level of the organization should understand the new EHS policies and procedures. To build awareness and uphold competence, try implementing the following:
Encourage risk and incident reporting .
Tailor training programs based on the workers’ needs.
Conduct daily toolbox talks .
Open clear communication channels.
Step 6: Execute, monitor, and measure performance.
Roll out the system across the organization. Use monitoring tools, checklists, and inspections to ensure procedures are followed. These are also helpful in tracking and addressing potential negligence or nonconformities against EHS performance standards and the company’s objectives.
Step 7: Review, audit, and continuously improve.
Conduct regular internal audits and management reviews to assess the system’s effectiveness. Gather feedback, investigate incidents, and use data to drive Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA).
Leverage technology to collect input from employees and stakeholders. This helps managers measure progress, analyze near-misses, and identify areas for improvement.
Addressing Key Issues in Meeting EHS Standards
Executing any new EHS initiative can be a complex process for an organization. These are the top three challenges that companies often encounter, and some ways to deal with them:
Lack of employee engagement and awareness – Achieving compliance and reducing workplace risks is impossible when employees aren’t actively engaged in the company’s safety culture. Investing in comprehensive training programs addresses the “how” and the “why” behind EHS systems.
Inadequate resources and budget allocation – Many EHS managers cite budgetary restrictions as a major barrier to adopting new tech for their initiatives, which require substantial financial investment or time commitment. Aside from sharing resources and expertise, leveraging cloud-based EHS software can reduce administrative effort and costs.
Continuously evolving regulations – Keeping up with constantly changing local, national, and international EHS regulations is a growing challenge for companies, especially those operating in multiple regions or industries. On top of scheduling regular compliance reviews, using regulatory horizon scanning tools helps automate legislation monitoring.
Strengthen EHS Compliance with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries, such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Implement consistent data gathering and subsequent issue resolution by streamlining inspection, reporting, and compliance tasks. Maintain digital records of all EHS activities, making them easily shareable to all stakeholders. Comply with EHS standards by building a robust system that empowers employees at all levels to contribute to a safe and regulatory-adherent workplace.
✓ Save time and reduce costs ✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents ✓ Boost productivity and efficiency ✓ Enhance communication and collaboration ✓ Discover improvement opportunities ✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Related articles
Quality Management
Quality

Critical to Quality (CTQ): Guide to Customer-Driven Excellence
Learn the basics of Critical to Quality, its benefits, parameters, and specific applications in this comprehensive guide.
Quality
Quality Management

A Guide to Understanding Management Reviews
Learn about what a management review is, its importance, its key inputs and outputs, its process, and some FAQs.
Quality
Quality Management

5 Core Tools of Quality: The Ultimate Guide
Learn how the 5 core tools of quality work together to reduce risk, improve consistency, and drive continuous operational improvement.