Published 26 Sept 2025
Article by
3 min read
What are Kaizen Tools?
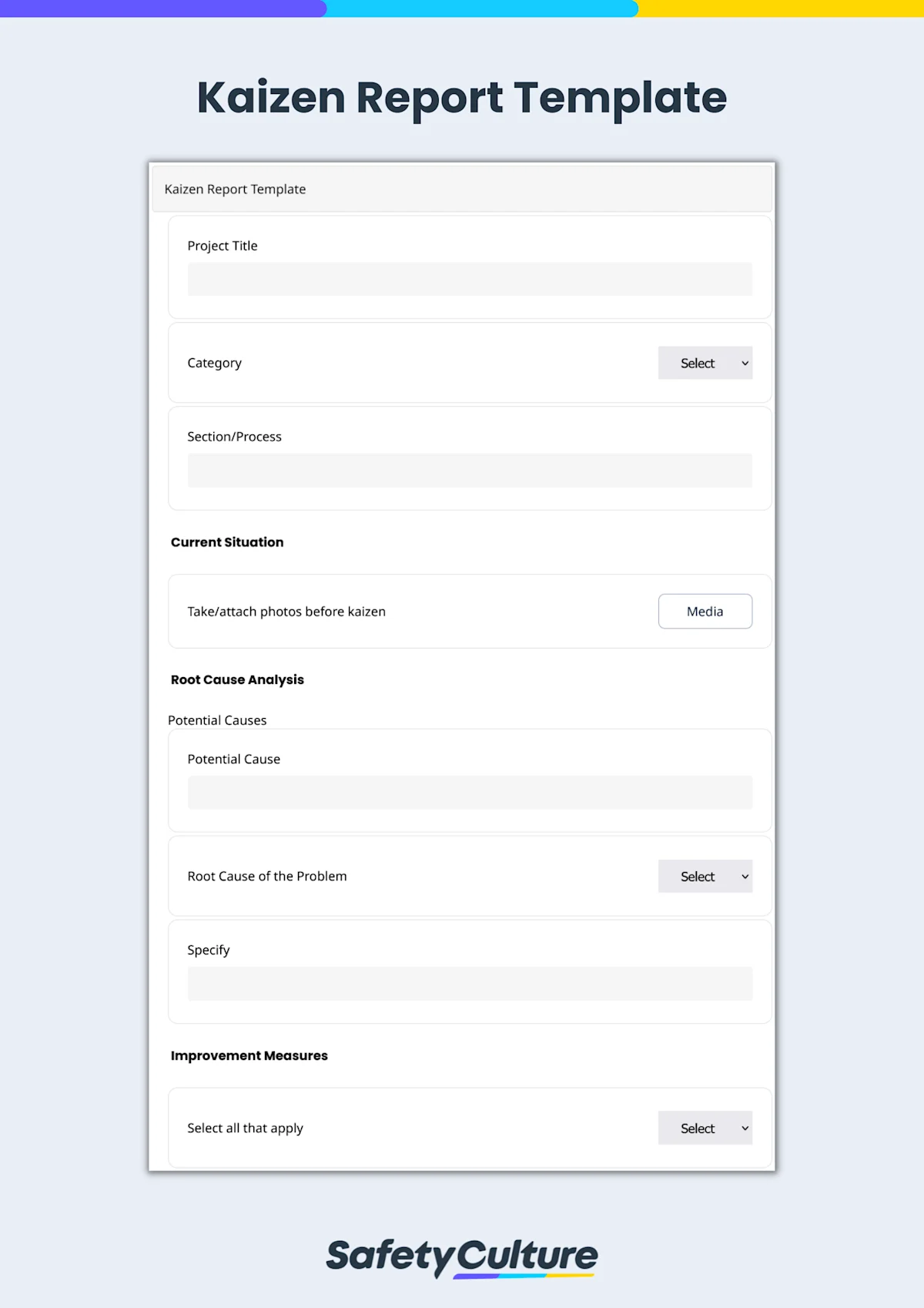
Kaizen tools are primarily used in the manufacturing industry to eliminate 8 wastes or DOWNTIME (Defects, Overproduction, Waiting, Non-utilized talent, Transportation, Inventory, Motion, and Extra-processing) and optimize business processes for global competitiveness. Kaizen tools help employees and management implement and monitor continuous improvement efforts in the workplace.
What is the Importance of Kaizen Tools?
Since kaizen means “change for the better”, the use of kaizen tools results in more efficient ways of doing tasks and more effective communication between shifts, work areas, and organization levels. Taking advantage of mobile-ready kaizen tools and templates can help cross-functional teams easily identify wastes, execute action plans, and report new changes.
What is the Kaizen Technique?
Kaizen as a business improvement technique is often practiced through a top-down approach, where the management demonstrates its commitment to operational efficiency. The kaizen technique of eliminating wastes to streamline workflows can be practically applied through a project-based format, which is often called a kaizen blitz.
What are the 5 Main Kaizen Principles?
There are actually 5 fundamental kaizen principles according to the Kaizen Institute, founded by Masaaki Imai—widely considered as the Father of Kaizen. It is unknown how the notion that there are “4 main kaizen principles”, sometimes 10 or even 15, developed, but they are probably variations or compressed/expanded versions of the 5 kaizen principles:
Principle #1: Know Your Customer
Principle #2: Let It Flow
Principle #3: Go to Gemba
Principle #4: Empower People
Principle #5: Be Transparent
Kaizen Tools: Success Factors
Continuous improvement begins with the admission that every organization has problems that provide opportunities for change. Here are 3 key factors cross-functional teams can do to successfully implement kaizen :
1. Focus on improving the process
Organizations usually fail in implementing kaizen because of reverting to a conventional approach of continuous improvement: “employees are the problem”. In implementing kaizen, apply a process-emphasis approach with kaizen tools by measuring performance, eliminating waste, and changing the process for the better. Employees and management should understand how their job fits in the process because good processes bring good results.
2. Enable people to do better
The people most knowledgeable about a task are those that perform it, so ownership of the process is raised to its highest level by involving them and showing confidence in their capabilities. Kaizen tools enable cross-functional teams to go where the real work happens and grasp the current situation because big results come from small changes everyone does on a daily basis.
3. Commit to data-driven decisions
Performance and improvements should be tangible and visible, so everyone is constantly reminded of implementing kaizen. Employees and management should practice speaking with data and managing facts.
Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.