Published 7 Jan 2026
Article by
5 min read
What is a Mining Inspection?
A mining inspection refers to the visual inspections performed by site safety officers and professional miners during safety checks. Its primary purpose is to identify hazards, risks, and non-compliance with required safety standards so the correct control measures can be applied and a safe worksite can be established.
Why Checklists are Critical for the Mining Industry
Most of us expect to go our whole lives without a safety incident. The reality is, accidents happen everyday. In fact, each day 150 workers around the world suffer from a fatal incident. The mining industry is notorious for safety incidents, given it’s one of the most dangerous industries to work in. Checklists are there to lighten the cognitive load and free up attention from tedious tasks to focus on high level problems, situations or tough judgment calls. They also serve as a catalyst for empowering the individual and enhancing team accountability.
Improve your Mining Site Safety by Deploying Training Courses
Generate bite-sized training courses for your workers to keep them safe and upskill your team effectively. These courses do not interrupt your team's workday and are available even when offline!
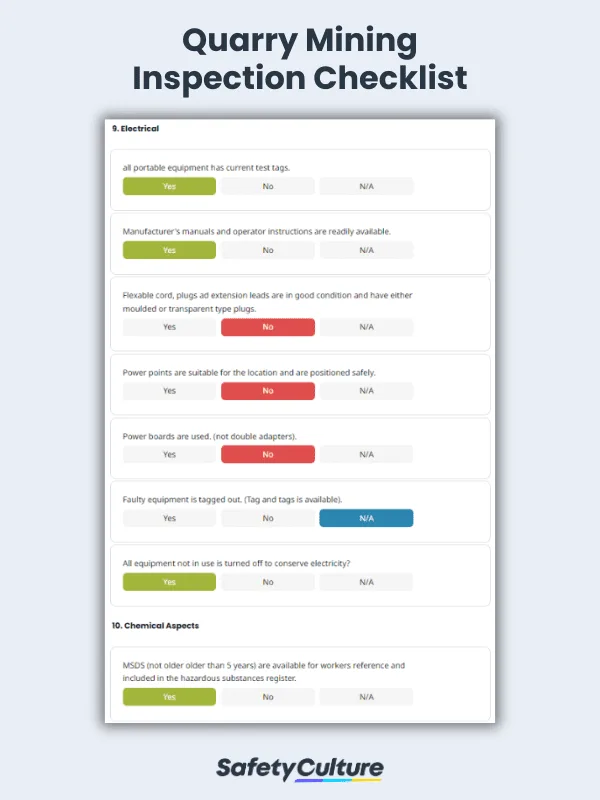
8 Key Components of a Mining Inspection Checklist
Mining operations involve a multitude of complex tasks and machinery, and ensuring safety and compliance is of utmost importance. A comprehensive mining inspection checklist plays an important role in maintaining a safe and productive mining environment. Here are eight key components that make up an effective mining inspection checklist.
Site Information – The foundation of any mining inspection begins with gathering essential site information. This includes details such as the mine’s location, ownership, contact information, and a brief description of the mining operations.
Equipment Inspection – Mining equipment is the backbone of any mining operation. A thorough inspection of equipment is essential to prevent accidents and downtime. This section of the checklist should encompass detailed equipment assessments, including maintenance records, safety features, and any potential defects.
Hazardous Materials and Chemicals – Mining often involves handling hazardous materials and chemicals. Ensuring the safe storage, handling, and disposal of these substances is crucial. The checklist should outline proper storage procedures, emergency response plans, and safety protocols when dealing with these materials.
Electrical Safety – Mines are powered by a complex electrical infrastructure. This section focuses on inspecting electrical systems, checking for exposed wires, ensuring proper grounding, and evaluating the safety of electrical equipment.
Ventilation and Air Quality – Maintaining a healthy work environment underground is vital. Inspecting ventilation systems, monitoring air quality, and ensuring proper airflow is essential for the well-being of miners. This section should cover checks for gas leaks, dust control, and adequate ventilation.
Environmental Compliance – Mining activities can have a significant impact on the environment. Compliance with environmental regulations is critical. The checklist should include items related to monitoring emissions, preventing water pollution, and preserving local ecosystems.
Emergency Response – Being prepared for emergencies is non-negotiable in mining. This section should detail the availability and condition of emergency equipment, evacuation plans, and procedures for handling accidents or disasters.
Compliance with Regulations – Mining operations are subject to various local, state, and federal mining rules and regulations . A checklist should include a comprehensive review of compliance with all relevant laws, permits, and licenses.
How to use this Checklist for Mining Inspection
Using this mining inspection checklist can be straightforward. Inspectors simply need to choose from Yes, No, or N/A answers in the checklist. If there are important notes or actions required, users are free to add them as they go through the checklist. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to run through your mining inspection with this checklist using a relevant mining software.
Add basic information about the mining site and personnel involved
Conduct an inspection on the layout and environment of the mining site.
Check whether the criterias indicated in the checklist are met
Conduct a safety inspection, whether equipment are functioning properly, PPEs are worn by staff, and if emergency procedures are clear.
Add other hazards found if necessary
Conclude the inspection in the checklist by signing off and automating report generation of the inspection.
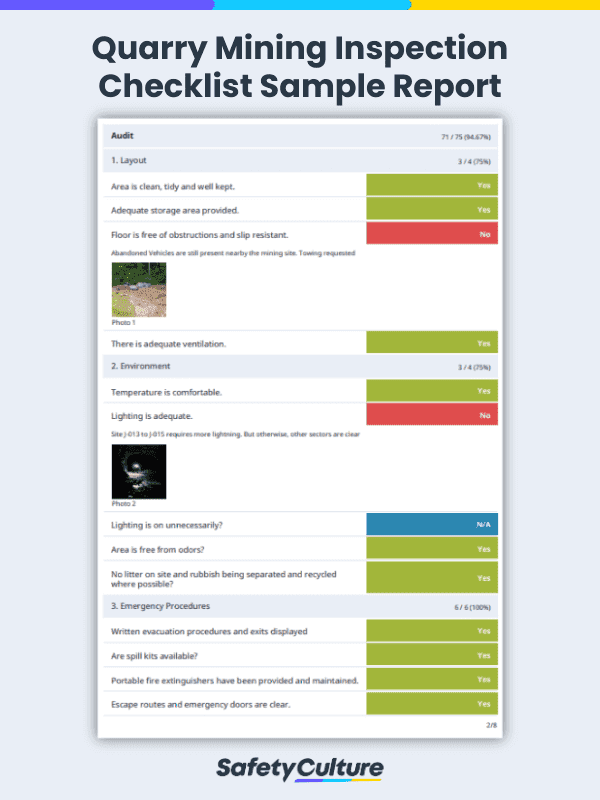
Quarry Mining Inspection Checklist Sample Report | SafetyCulture
Check Out How One of the World’s Leading Gold Producer Uses SafetyCulture For Mining Inspections
With a total of 11 mines across North, Central, and South America,Goldcorp (acquired by Newmont Mining Corporation last 2019), is a leader in gold production, with an expected 50% increase of output. The hazards are real and ever-present in the mining industry with workers exposed to a variety of risks from cave-ins to explosions, vehicle collisions and more. To ensure their safety, Goldcorp uses iAuditor for 1,000 inspections per day. Instead of taking four hours to write a report, it now takes them minutes.
“The real time hazard recognition capability across our operations wouldn’t exist if we didn’t have iAuditor. It means more people are going to go home safe,” Andrew Johnson, Goldcorp Safety Officer .
Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.