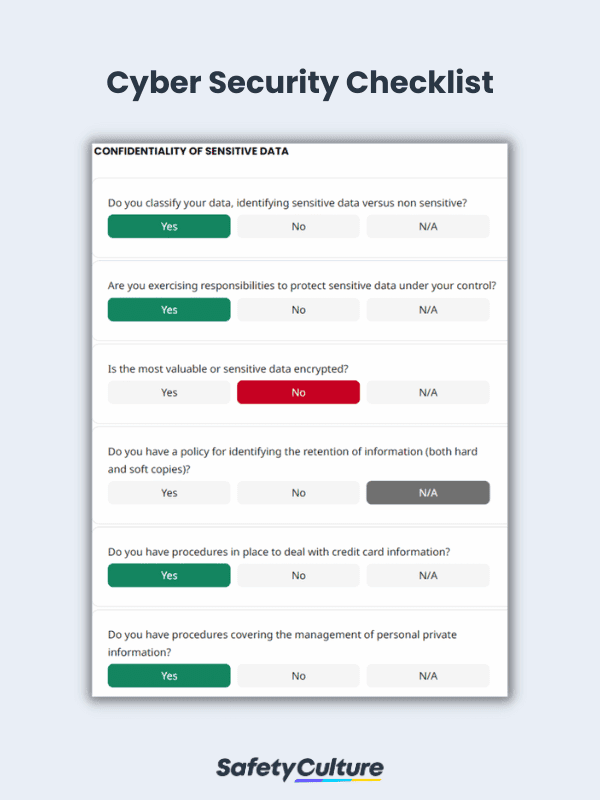
What is a Cyber Security Checklist?
A cyber security checklist is used by IT teams to record the status of cyber security controls such as policies, standards, and procedures. It helps identify and detect malicious activities such as unauthorized access and device malfunctions to prevent IT incidents in the workplace. Failure to perform regular cyber security checks can result in revenue and integrity loss, regulatory fines, or worse, business closure.
Most Common Cybersecurity Threats
As the organization progresses it becomes exposed to more threats, vulnerabilities, data breaches, and ransomware attacks that are often overlooked by employees. Non-compliance with regulatory cyber security checks often leads to costly expenses, data loss, penalties, and customer defection. Below are examples of cyber security risks that are easily spotted but often overlooked:
Outdated Operating Systems and Antivirus
The operating systems and antivirus software must be up to date and performing to their highest capacity to avoid extensive damage. Software and system updates are usually scheduled and automated. A notification is sent to each device within the organization, but employees tend to delay the update which can cause a bigger problem.
Unfollowed Password Policy
Allowing different employees to use another employee’s access is not a good practice. When data leakage or error happens it would be difficult to track down the root cause. Changing passwords regularly is a must for every employee to avoid risks and issues with access and data ownership. A complex password is recommended but sometimes neglected by employees because complex passwords are harder to remember.
Negligence in Proper Disposal of Data and Equipment
Employees’ negligence in following the Federal Trade Commission disposal rules, i.e., “proper disposal of information in consumer reports and records to protect against ‘unauthorized access to or use of the information,’” can cause penalties for your organization. Failure to regulate proper disposal procedures can lead to information leakage and unauthorized data recovery.
Lack of Cyber Security Awareness Training
Organizations should implement cyber security awareness training to keep employees up-to-date and knowledgeable on different forms of cyber security threats such as malware, phishing, cryptojacking, and more. Cyber attacks are designed to damage your computer systems and disrupt operations.
Lack of a Breach Response Plan
A breach response plan is important to every organization because it prepares the company for any cyber security incidents. It enables the company to respond immediately and implement corrective actions to mitigate the risks. Employees must be aware of “what to do after an incident” to avoid data breaches.
What should be in a Cyber Security Checklist
A comprehensive cybersecurity checklist improves your process and ensures that everything is covered. When creating the checklist, here are the key components that are commonly used :
Data Protection
- Data Encryption: Ensure that sensitive data is encrypted both at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Backups: Schedule automatic backups of critical data to secure locations, allowing for quick recovery in case of a cyber incident.
Network Security
- Firewalls: Use firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Implement IDS for real-time monitoring of network traffic to detect suspicious activities.
Access Control
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Limit access to sensitive information based on user roles, ensuring only authorized personnel can access critical data.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for critical systems to add an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
Incident Response Planning
- Develop and regularly update an incident response plan that outlines steps to take in the event of a cyber attack, including roles and responsibilities during a breach.
Documented Policies
- Acceptable Use Policy: Defines rules for using organizational IT assets, ensuring users understand their responsibilities.
- Remote Access Policy: Outlines security requirements for accessing systems remotely, including the use of VPNs.
- Data Breach Response Policy: Establishes procedures for responding to data breaches, including communication and recovery plans.
Asset Management
- Inventory of Assets: Maintain a real-time inventory of all hardware and software to identify vulnerabilities and manage risks effectively.
- Patch Management: Regularly update software to fix vulnerabilities and enhance security.
More items can be added in the list such as cybersecurity training in the organization for employees to educate them about current cyber threats, such as phishing and ransomware attacks. It’s also best to conduct continuous monitoring by regularly auditing security measures for unusual activity that indicate a breach or attempted attack.
7 Steps to Conduct a Cyber Security Risk Assessment
To help businesses improve their cyber security practices and prevent cyber-related issues from affecting daily operations, take a look at these cyber security risk assessment steps:
Step 1: Implement access restrictions
Issuing badges, IDs, or other forms of identification is the primary step of restricting non-authorized people from accessing your organization’s site. To further protect data and other confidential information, modify access levels according to the type such as employee, third-party provider, or visitor.
Step 2: Specify policies and procedures
Create a set of rules that clearly defines the organization’s policies and procedures when it comes to physically securing digital data. One of the things assigned personnel can do is to make sure that equipment and machines are not accessible to unauthorized people.
Step 3: Manage account access and password
Establish best practices for account administration and control the items employees are allowed to access. Manage passwords by enforcing strict rules on creating, regularly changing, and recording them. Also ensure that when staff is entering their account credentials, it is not visible to other people.
Step 4: Classify confidential data
Specify data that contains sensitive information and categorize them from non-sensitive ones. Encrypt the most sensitive data as a layer of protection and governance strategy. Create a standardized procedure for managing personal information and disposing of waste materials (especially confidential ones).
Step 5: Develop disaster recovery plans
Design a set of procedures that aligns all people and stakeholders in cases of disasters, emergencies, or security breaches. These procedures can include items such as a business continuity plan, a communication plan, and assigned people for different tasks.
Step 6: Promote security awareness
Although all the above-mentioned items are crucial in securing data, it’s always important to start by amplifying the knowledge of staff and promoting awareness. Provide training on a regular basis and educate them on how to practice security best practices on their own.
Step 7: Review compliance
Finally, regularly assess the organization’s compliance with all the policies and procedures in place. Utilize cyber security checklists to confirm that everyone is on the same page and identify processes that need polishing, as well as recognize areas for improvement.
The use of cyber security templates can help IT professionals conduct thorough cyber security checks in the workplace. Address overlooked items and eliminate cyber security threats in the organization.