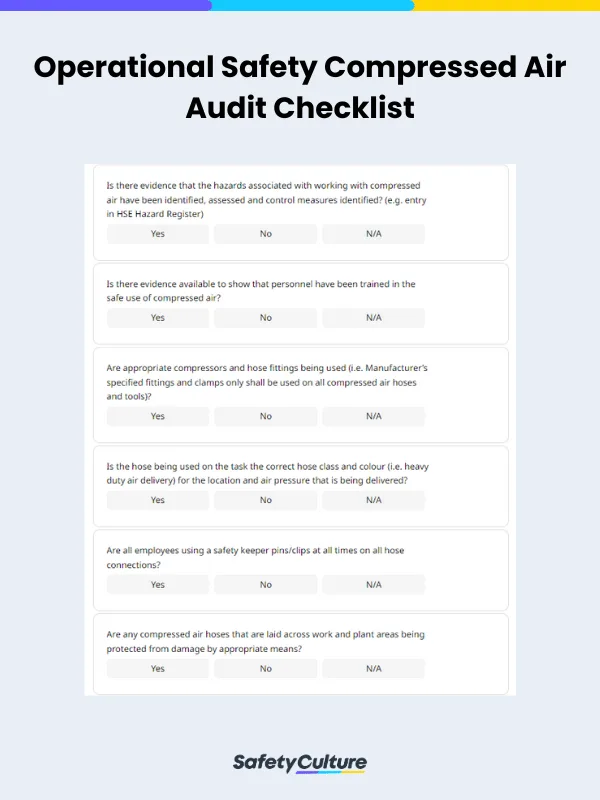
Published 26 Sept 2025
Article by
6 min read
What is a Compressed Air Audit Checklist?
A compressed air audit checklist is a document or tool that can help you perform regular checks on equipment and systems that require the use of compressed air. If your facility relies on a compressed air system, it is crucial to perform regular audits to ensure its efficiency and safety. A compressed air audit checklist can help you identify potential issues and areas to focus on.
Importance of Conducting Compressed Air Audits
Compressed air is a type of energy used to operate different machines, equipment, and other manufacturing and construction processes. It is often used in situations where electrical energy is impractical or dangerous to use as a direct source. However, while it is somewhat safer as an energy source, compressed air systems still need to be maintained and audited regularly. Doing so is essential to ensure safe and efficient operation. Neglecting regular maintenance and inspections can lead to equipment failures, which can result in accidents, injuries, and property damage.
Some of the key maintenance tasks for compressed air systems that a checklist can help with include:
Regular inspections of pipes, fittings, and hoses for signs of wear or damage
Checking and replacing air filters as needed
Draining moisture from the air compressor tank
Lubricating moving parts as required
Regularly testing safety valves and pressure relief devices
With a checklist, you can also better provide training to workers on the safe use of compressed air tools and equipment, as well as following established safety procedures for working with compressed air systems. A checklist can also help with listing down the areas where there may be issues in maintenance and complying with industry standards.
How to Create a Compressed Air Audit Checklist and What to Include in it
It is crucial to perform regular audits on systems and equipment reliant on compressed air to ensure their efficiency and safety. A compressed air audit checklist can help you identify potential issues and areas to focus on.
Here are the steps to creating your own comprehensive compressed air audit checklist:
1. Identify the Scope of the Audit
Before getting to your checklist, you must first begin by defining the scope of the audit. Determine what components of your compressed air systems need to be assessed, such as the compressor, dryer, receiver, filters, piping, and end-use equipment. Afterward, decide on the level of detail and data you need to collect—this will be the basis of your checklist.
Most common compressed air audit checklists will contain sections that will prompt you to do the following:
Check for current air leaks and identify their source and assess previous records for any history of leaks and other issues
Verify that air treatment equipment is installed and functioning correctly, then replace it if necessary
Measure and monitor pressure, flow rates, and dew point
Ensure that employees have been trained on how to safely use compressed air
Assess the effectiveness of energy-saving measures and other equipment meant to support the system
Identify equipment maintenance needs and schedule repairs accordingly
Inspect piping, fittings, and valves for damage and wear
2. Review Equipment Data
Collect data on the compressed air equipment, including compressor specifications, usage, maintenance records, and air quality data. Additionally, make sure to review your equipment’s installation, operation, and maintenance manuals to ensure compliance with the manufacturer’s guidelines.
3. Conduct Visual Inspection
Conduct a visual inspection of the equipment and the surrounding area. With your compressed air audit checklist ready, check for leaks, damage, corrosion, and wear and tear, then evaluate them and their other equipment. This ensures that safety features such as pressure relief valves and gauges are installed and functioning correctly.
4. Evaluate Air Quality
Evaluate the air quality of the compressed air system. Check for oil mist, water, and particulate contamination in its system or product, and determine if air treatment equipment such as dryers and filters are installed and functioning correctly.
5. Review Operating Procedures
Review your operating procedures and best practices with equipment operators. Evaluate any new opportunities to reduce air leaks, optimize air pressure, and minimize wasted energy. Additionally, consider implementing an energy management system to monitor and control compressed air usage.
Following this, it is important to also train your staff on the proper use of equipment and safety measures. Identify pain points in your procedures that may need to be addressed and assess if these can be solved with additional training. Ensure that your staff understands the importance of regular maintenance, cleaning, and inspection. This not only improves your operations but also helps in identifying areas where energy-saving opportunities can be utilized.
6. Determine Maintenance and Repair Needs
Based on the audit findings, determine the maintenance and repair needs of the compressed air system. Prioritize the identified issues and develop a plan for addressing them, then assign responsibilities to the right personnel and establish timelines for completion.
7. Regularly Review and Update the Checklist
Your compressed air audit checklist should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that it reflects changes in the system and the facility’s operating procedures. Make adjustments based on the results of previous audits and feedback from equipment operators and maintenance personnel.
By following these steps and including relevant items in the compressed air audit checklist, you can ensure the efficient and safe operation of your compressed air system and protect your employees in the workplace all at the same time.
Example Sample Report
Here is a sample filled-out compressed air audit checklist for your reference:
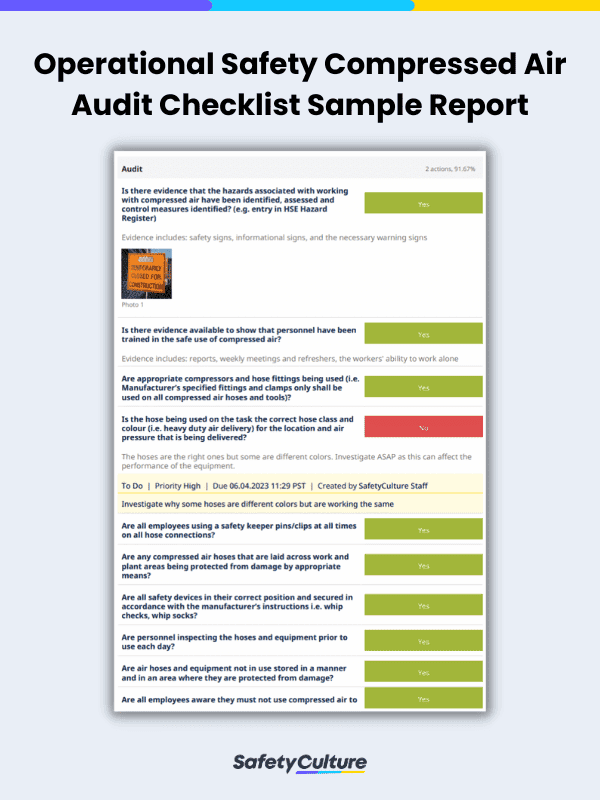
Operational Safety Compressed Air Audit Checklist Sample Report | SafetyCulture
Common Issues to Look Out For
During a compressed air audit, a number of common issues can be identified. These issues can have a significant impact on the efficiency and effectiveness of the compressed air system and can result in increased energy costs and reduced productivity.
The most well-known issue to be aware of in using a compressed air audit checklist is the presence of leaks. However, there are also other problems to look out for, such as:
Inappropriate use: While compressed air is a good alternative energy source when electrical energy is unsafe, it can also be used inappropriately for tasks that could be performed more efficiently using other methods. This can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and increased cost, as well as issues with the equipment.
Inefficient air distribution: Poorly designed or maintained piping systems in equipment that uses compressed air can lead to inefficient air distribution, resulting in pressure drops and reduced system performance. In the long run, this can cause leaks or breakages.
Lack of maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of compressed air systems. Failure to perform regular maintenance can result in increased energy consumption and reduced system lifespan, affecting the performance of the compressed air system and the safety of those operating it.
By identifying and addressing these common issues during a compressed air audit, businesses can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their compressed air systems, resulting in reduced energy costs and increased productivity.
Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.