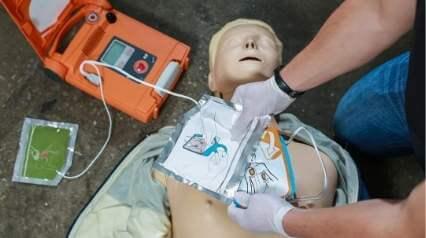
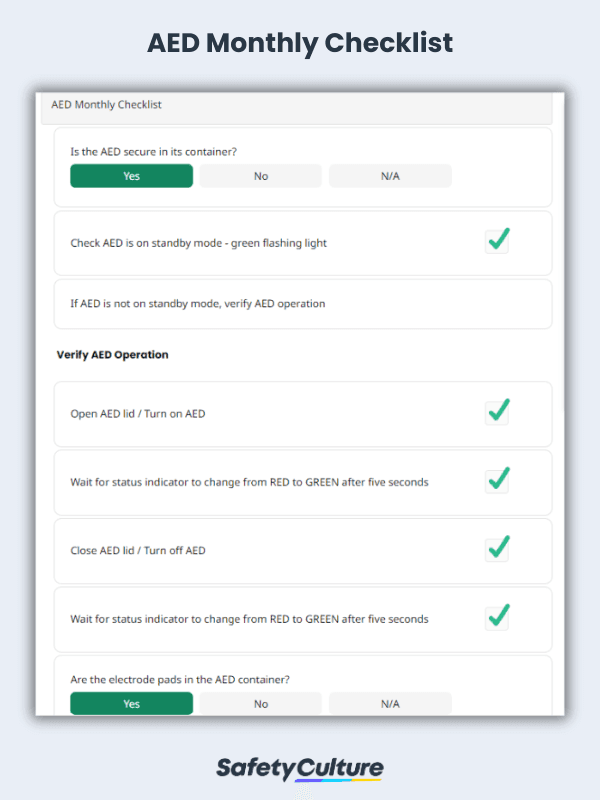
What is an AED Checklist?
An AED checklist is an essential tool for anyone using an AED (automated external defibrillator). AEDs are portable medical devices used to treat those experiencing cardiac arrests. Since every minute without treatment decreases their chances of survival, it’s critical to ensure through routine maintenance that AEDs are always ready-to-use.
AED checklists can also be used to guide persons delivering emergency assistance. This is especially important for AEDs placed in areas that lack on-site trained medical personnel. In addition, even those with AED training may forget how or be unable to operate it due to shock.
Who Uses Automated External Defibrillator and Why?
AEDs are mainly used by those working in EMS (emergency medical services), a coordinated system of emergency medical care. While it may be the first responders who operate the AED, the overall well-being of the patient is in the hands of many others as well. These include dispatch, EMT (emergency medical technicians), ER doctors, and the patient’s personal physician, nurse, or caregiver. Outside of EMS, AED units are also found in schools, offices, and shopping malls for the public to access.
Common Issues
Though AEDs are known for simplicity, ease-of-use, and sophistication, these life-saving devices may fail due to improper maintenance. According to the Sudden Cardiac Arrest Foundation, 45% of AED incidents linked to fatalities were caused by insufficient battery charge and 23.7% of AED failures were caused by problems with pads and connectors.
Other common issues with AEDs are electrodes drying out, damaged cables, faulty circuit boards, malfunctioning resistors, and software bugs. While a majority of the issues are manufacturing-related, some can be solved by regularly inspecting, using, and caring for AEDs.
How to Maintain It
To avoid experiencing a manufacturing-related issue, it’s recommended to buy only FDA-approved AEDs. Popular AED brands with FDA approval are ZOLL, Philips, Defibtech, Physio-Control, and Cardiac Science. Though each AED brand has specific maintenance and troubleshooting procedures, here are some general tips on how to maintain AEDs:
Keep Them Fully Charged
As mentioned previously, failing to keep AEDs fully charged can lead to devastating consequences. New batteries must be installed at least every 4 years. However, if a battery needs replacement in the midst of an emergency, it’s critical to only replace it during a CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) interval.
Test, Practice, and Train
Most AEDs have self-testing capabilities and will alert users if they encounter a problem. This can either be through an audio alarm (machine starts beeping) or a visual one (light flashing). That’s why it’s important to always have someone near the device so that these notifications aren’t missed. Users can also test AEDs and themselves by having practice runs frequently.
To get the most benefit from AEDs, users should consider starting AED training.
Use a Checklist
Whether one is a home user, a first responder, or a future Good Samaritan, using an AED checklist to prepare for emergencies is crucial. According to the Defibrillator Working Group of the FDA, evidence suggests that error in operator use and errors in defibrillator care and maintenance account for a high proportion of defibrillator failures. Using an AED checklist helps ensure that such errors are minimized and defibrillator failures are avoided. To illustrate this, here’s a sample of a pre-use AED checklist:
Check to see if the person if breathing and has a pulse.
If the person is not breathing and has no pulse, call 911.
Secure the electrode pads’ cable connector to the AED.
Press electrode pads firmly, especially in the center.
Why Use a Digital Checklist?
Unlike paper checklists, digital AED checklists allow first responders to remotely transmit data to hospital emergency departments, enabling them to prepare in advance for a patient’s arrival. Aside from being a convenient method for sending a patient’s contact details, vital signs, and ECGs to the next point of care, a digital AED checklist may also be modified to request for a doctor’s interpretation, feedback, or approval.