Predictive Maintenance
Learn the difference between predictive and preventive maintenance, examples of predictive maintenance, its benefits, how it works, and how to best use it when given limited resources

Published 31 Jul 2025
Article by
7 min read
What is Predictive Maintenance?
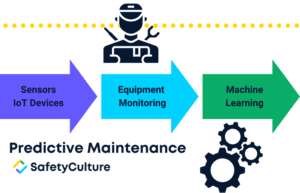
Predictive maintenance is a strategic approach to optimizing equipment usability. Using data collected from IoT devices such as sensors, machine learning, and real-time equipment monitoring, predictive maintenance determines exactly when it’s the best time to perform equipment maintenance. With this capability, maintenance managers save both time and resources.
What is the Difference Between Predictive and Preventive Maintenance?
Preventive maintenance involves doing whatever is required, regardless of the cost or strain on resources, to avoid equipment failure. Predictive maintenance, on the other hand, is focused on taking minimal action while still ensuring that equipment can be used for longer periods of time.
Another difference between predictive and preventive maintenance is that the latter requires frequent inspections, as these form the basis of when maintenance should be performed. With predictive maintenance, equipment conditions can be monitored remotely through the use of sensors and other IoT (Internet of Things) devices (e.g., smart meters, environmental monitoring IoT devices, etc.). There are also differences in how maintenance is documented for both.
What are Examples of Predictive Maintenance?
Data is at the heart of predictive maintenance. While the following are not straightforward examples of predictive maintenance, they do show how real organizations apply and use data to make more informed decisions and take action where it’s needed.
Example 1: BOS Solutions, a liquid solids separation organization in the oil and gas industry, used its data to predict equipment lifespan. This resulted in less defective or deteriorating equipment being used by workers, which led to a decrease in equipment-related injuries.

Example 2: National Grid UK , a natural gas and electricity transmission company, used their data to spot areas of poor performance, potentially risky areas, and areas of good performance.

By dividing its data into separate categories, the company was able to dive deeper into areas of non-conformance. Within these areas, they identified high-risk issues requiring immediate action. As a result, proactive behavior within the company increased and quality improved.
Predictive Maintenance Benefits
As seen in the examples in the previous section, using data to guide actions and decisions can deliver significant benefits. Given the impact that data driven insights can have on business performance, maintenance managers should strongly consider adopting predictive maintenance as a proactive maintenance strategy.
While other maintenance approaches such as preventive,corrective,planned, and condition-based maintenance are still widely used and will not become obsolete anytime soon, organizations that begin integrating predictive maintenance into their processes can gain a significant advantage.
By using real time data, sensors, and analytics to detect issues before they become critical failures, predictive maintenance allows organizations to shift from reactive problem solving to proactive optimization.
Below are the top five benefits of predictive maintenance:
Streamlined maintenance costs
Predictive maintenance helps organizations reduce unnecessary inspections and repairs. Companies implementing predictive strategies have reported maintenance cost reductions of up to 25 to 30 percent.
Maximized equipment lifespan
Early detection of wear and potential failures allows equipment to be repaired before severe damage occurs, which can extend asset life by up to 20 to 25 percent .
Increased equipment uptime
Predictive maintenance significantly reduces unplanned downtime, with many organizations experiencing 30 to 50 percent fewer unexpected outages.
Reduced unexpected failures
Continuous monitoring and predictive analytics help detect anomalies early, allowing teams to address issues before they escalate into critical failures.
Improved equipment reliability
By identifying patterns and potential risks in operational data, predictive maintenance improves overall reliability and performance, leading to more consistent and efficient operations.
Achieve operational excellence
Cultivate a culture of excellence with our digital solutions that enhance efficiency, agility, and continuous improvement across all operations.
How Does Predictive Maintenance Work?
While applying predictive maintenance leads to concrete results, as stated in the section above, some maintenance managers may find it intimidating or overly complicated. To help clarify how predictive maintenance works, here is a simple outline of the process in 4 steps:
Step 1: Sensors collect real-time data on equipment conditions
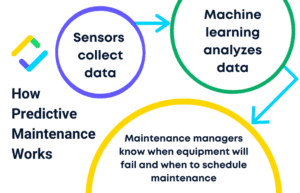
Step 2: Data from sensors is processed by a predictive algorithm
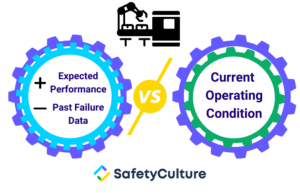
Expected performance – For example, after 3 years in operation, equipment should still be producing at a rate of 1.5 units per minute Past failure data – For example, before equipment failed, it produced only 0.3 units per minute and showed the following deterioration signs
Step 3: Powered by machine learning, the predictive algorithm generates predictions on when equipment will fail
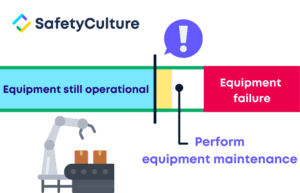
Step 4: Based on these predictions, maintenance managers schedule maintenance to occur right before equipment failure or at the time recommended by the algorithm
How to Get Started with Predictive Maintenance
Though how predictive maintenance works has been explained in general terms in the previous section, maintenance managers may still have difficulty seeing how they can apply a predictive maintenance strategy to their existing maintenance workflow.
This brief guide gives maintenance managers options on how to use predictive maintenance without the technical resources:
1.Choose Equipment to Monitor
While predictive maintenance has many benefits, it cannot be applied to each equipment in operation since it generates large amounts of data from daily equipment monitoring. To conserve organizational resources, maintenance managers must start by only selecting a few pieces of equipment to monitor. The equipment chosen should:
Have high maintenance costs
Be prone to equipment failure
Conditions causing or leading up to failure can be monitored by sensors
2. Choose a Prediction Method
Though using a predictive algorithm is the known prediction method for predictive maintenance, it requires maintenance managers to do either of the following: a ) Develop a predictive algorithm on their own b ) Hire a data scientist to develop a predictive algorithm c ) Purchase specialized software for predictive analytics
This is why predictive maintenance usually has a high barrier to entry. However, another option available to maintenance managers is to conduct their own predictive analysis. Depending on the conditions maintenance managers want to monitor and their own preferences, a simple predictive analysis may evaluate a number of variables or factors which will help predict when equipment is most likely to fail.
For example, a basic predictive analysis would be taking a certain number of equipment performance issues in a week as a sign that equipment is about to fail.
3. Connect Sensors to Database
If maintenance managers have decided to purchase predictive analytics software, it can also act as a database storing the equipment monitoring data collected by sensors.For those who have not purchased predictive analytics software, an alternative digital solution is a predictive maintenance tool like SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor). SafetyCulture can be connected to different types of sensors, such as temperature, humidity, air particulate, gas, and air pressure.
Simplify maintenance scheduling for your business with SafetyCulture
Streamline your operations with usage-based maintenance using our intuitive management software.
4. Connect Sensors to Equipment
Once maintenance managers have connected the sensors to their chosen database, they can proceed with installing sensors to the equipment.
After verifying that sensors are monitoring the correct equipment conditions and sending the data to the database in real-time, maintenance managers should set up alerts that will notify them when equipment conditions have reached a certain point.
5. Schedule Maintenance
When maintenance managers receive alerts from sensors, they can do either of the following: a ) Immediately schedule maintenance or send a maintenance technician on the way b ) For those using a predictive algorithm as their prediction method, they can schedule maintenance at the time recommended by the algorithm c ) For those relying on their own predictive analysis as their prediction method, they can evaluate this information against other factors and then decide when to schedule maintenance
SafetyCulture as a Predictive Maintenance Tool
Why SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) is a digital operations platform that assists maintenance teams in following or implementing standards, and monitoring maintenance tasks. Using SafetyCulture, maintenance managers can assign maintenance tasks and other repair jobs to service technicians.
Service technicians are able to document maintenance work completion. And, maintenance workers are able to perform investigations with the assistance of a digital checklist.
Quickly capture issues, such as equipment malfunction and failures. With SafetyCulture, the entire team can be empowered to work together and solve problems quicker.
Use SafetyCulture sensors orother sensor brandsfor continuous monitoring of humidity, air pressure, temperature, air quality, gas concentrations, and other environmental conditions. Set thresholds to alert teams when data moves outside of the set range.
Easily perform maintenance checks using mobile or tablet device
Assign and schedule maintenance tasks
Robust scheduling and notification features
Free plan available with up to 10 users
30-day free trial of premium plan available
Article by
SafetyCulture Content Team
SafetyCulture Content Contributor, SafetyCulture
View author profileIn this article
- What is Predictive Maintenance?
- What is the Difference Between Predictive and Preventive Maintenance?
- What are Examples of Predictive Maintenance?
- Predictive Maintenance Benefits
- How Does Predictive Maintenance Work?
- How to Get Started with Predictive Maintenance
- SafetyCulture as a Predictive Maintenance Tool
Related articles
Facility Management
Maintenance

A Guide to Retail Facility Management
Improve store performance with effective retail facility management, and learn its key components, challenges, and top solutions for success.
Equipment Maintenance
Maintenance

Autonomous Vehicle Maintenance for Safety and Asset Performance
Discover how autonomous vehicle maintenance supports safety, reliability, and asset performance through preventative workflows.
Maintenance
Equipment Maintenance

Understanding Mechanical Integrity and Its Importance
Understand the meaning of mechanical integrity, its fundamental components, and how to develop a mechanical integrity plan for the team.