What Is Condition Based Maintenance?
Condition-based maintenance, also known as CMB, is a proactive maintenance technique that is performed depending on the condition of the asset. CBM doesn’t rely on a schedule-based maintenance, but on indicators that can determine if the asset is about to break down or has broken down.
How Does It Work?
The equipment maintenance supervisor or facility manager will determine a set of condition-based maintenance (CBM) indicators. In the event that these CMB indicators were met, the maintenance personnel will have to proceed with the maintenance of the equipment or machinery. The facility should have standard operating procedures (SOPs) to provide step-by-step instructions and guidelines on how the issue can be fixed for the maintenance personnel.
Create Your Own Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Template
Eliminate manual tasks and streamline your operations.
Get started for FREEWhen Do We Use It?
Condition-based maintenance is a type of maintenance under the preventive maintenance category. What sets it apart from other types of maintenance is that CBM relies on real-time data on an asset’s condition and maintenance parameter levels. CBM is recommended for equipment and machinery that is highly critical for production and costly to repair and replace.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Every maintenance strategy has its strengths and weaknesses. Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of applying condition-based maintenance:
Advantages
Lessened asset downtime
CBM is performed on a need basis. This means that there can be less time spent on repairs and maintenance and that the person can make use of the time saved to do other tasks. This is in comparison to other types of maintenance such as regularly scheduled maintenance.
Another key aspect of condition-based maintenance is that the equipment and machinery can possibly have reduced downtime if the maintenance indicators set in place were appropriate for the facility. These performance measures could alert the maintenance personnel and they’ll know what SOP to follow depending on the affected maintenance indicator.
Lastly, having reduced asset downtime means that production will run more smoothly and continuously.
Another scenario is that condition-based maintenance on minimal issues can be conducted even without shutting down the equipment, this reduces time to setting the equipment or machine back up again.
Lower possibility of asset failure
Since CMB is a proactive maintenance procedure, issues that could lead to equipment and machinery failure can be caught before they can happen. Once the maintenance measures reach a certain level, maintenance personnel will have to quickly respond by conducting a condition-based maintenance procedure to solve the problem.
Disadvantages
Unpredictable maintenance indicators
Here’s a possibility that something can happen to a machine or equipment that wasn’t part of the maintenance indicators. This could leave the maintenance personnel not knowing what to do and how to solve an issue. Furthermore, unpredictable maintenance measures can cause the maintenance team to be on standby, and some personnel will be responsible for observing the assets throughout their shifts. Additionally, there could be instances wherein multiple assets need to be repaired or maintained at the same time.
Maintenance supervisors will have to keep track of the unpredicted maintenance conducted and update the maintenance indicators accordingly to reduce stress on the staff and optimize their time on the job.
Required expertise of maintenance technicians
In connection with the previous disadvantage, condition-based maintenance will require a level of expertise for their maintenance staff depending on the equipment and machinery of the facility. This facility can also employ additional maintenance tools such as sensors and software which would need someone with the technical knowledge to operate the maintenance equipment.
Types of Condition Based Maintenance Techniques
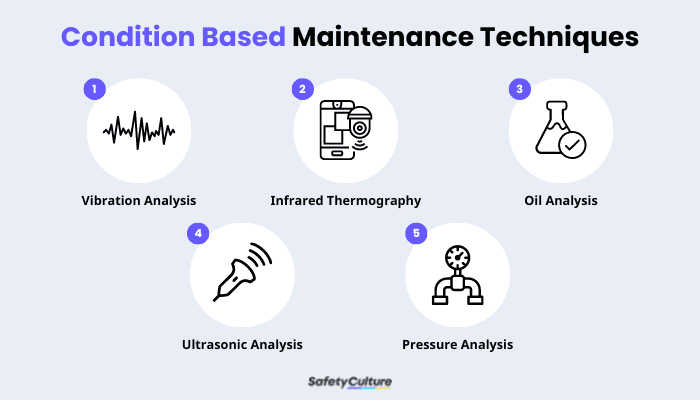
There are 5 common condition-based maintenance strategies available which are:
- Vibration analysis – this is used to monitor the vibration level of machines that are often with rotating components.
- Infrared thermography – this condition-based maintenance technique is used for identifying if there’s any abnormalities in the heat wavelength of the machine or equipment.
- Oil analysis – is the method used to analyze oil health of the machines and equipment in the facility. This includes oil contamination, viscosity, and if there’s particles present in the oil due to the mechanical wear and corrosion of an asset.
- Ultrasonic analysis – This strategy uses sound to determine if a machine needs to be maintained by detecting high-frequency sounds and then converting them to digital data. There are two categories for ultrasonic analysis, contact and non-contact. Contact is commonly used for issues such as bearing faults and lubrication problems as these emit high-frequency noise. A non-contact ultrasonic method, air surveys are used to check for leaks in a compressed gas system. These ultrasonic methods are used to detect what the infrared thermography couldn’t.
- Pressure analysis – This CBM strategy ensures that the pressure level of fluid, gas, and air moving through a pipeline or hydraulic hose are within the parameters it was set in.
Condition Based Maintenance Techniques | SafetyCulture
Examples
The strategies mentioned earlier can be too costly and advanced for certain companies, especially for smaller businesses, but there are other ways for you to be able to implement condition-based maintenance such as using checklists tools to aid you during a visual inspection. Checklists tools can also be used for auditing the other CBM techniques—vibration analysis, infrared thermography, oil, ultrasonic, and pressure analysis.
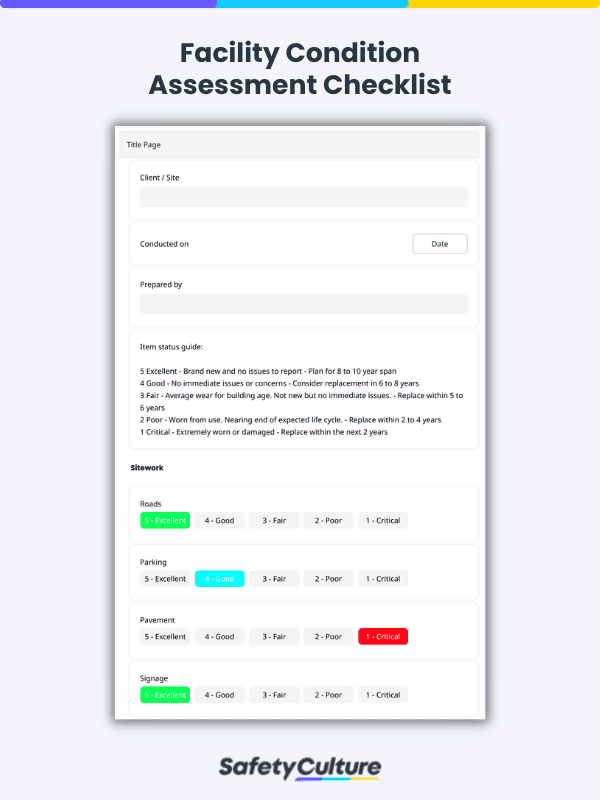
Here’s an example of a facility condition assessment template:
How SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) Can Help
SafetyCulture is a digital checklist tool that can assist maintenance personnel during a condition-based maintenance inspection and audit. With SafetyCulture, you can:
- Create and customize the condition based maintenance template to fit your facility
- take photo evidence of structures, assets, equipment, and machinery that is in need of repair and maintenance
- Assign tasks to specific maintenance personnel
- Automatically sync the inspection results on the secure cloud-based storage and share with your organization
- Generate data insights that can assist with creating corrective maintenance actions such as for unpredictable maintenance indicators