Understanding HSE Management System
What is a health and safety management system? Learn about the HSE management system definition, its importance, key elements, standards, and practical application.

Published 10 Nov 2025
Article by
8 min read
What is an HSE Management System?
An HSE management system is a comprehensive framework used by organizations to prevent, mitigate, and eliminate disruptions and losses caused by workplace accidents. HSE stands for Health, Safety, and Environment—it helps manage risks, control hazard exposures, and respond to environmental challenges. Further, an HSE management system is key to monitoring an organization’s compliance with relevant laws and industry standards.
Importance
As a legal requirement for organizations, an HSE management system ensures that there are documented and implemented policies in place. Its specific benefits revolve around the areas of moral,legal, and financial obligations held by an organization. Employee welfare should be paramount, with employers providing them a safe workplace.
In the same way, an HSE management system also puts relevant expectations on employees to take charge of their safety in the workplace. Ultimately, following local and international laws for HSE helps prevent personal and company financial losses and mitigate risks related to workplace health and safety.
In addition to that, an HSE management system also plays a key role in promoting environmental sustainability. Companies must also minimize negative environmental impact and reduce their carbon footprint by ensuring compliance with relevant legislation on the environmental aspects of business operations.
In most cases, utilizing technology like HSE software to help ensure standard compliance is one of the best practices to consider.
What are the Key Elements of HSE Management System?
Implementing HSE management system practices entails having key elements to ensure successful implementation and regulatory compliance. That said, here are the 12 HSE management system elements.
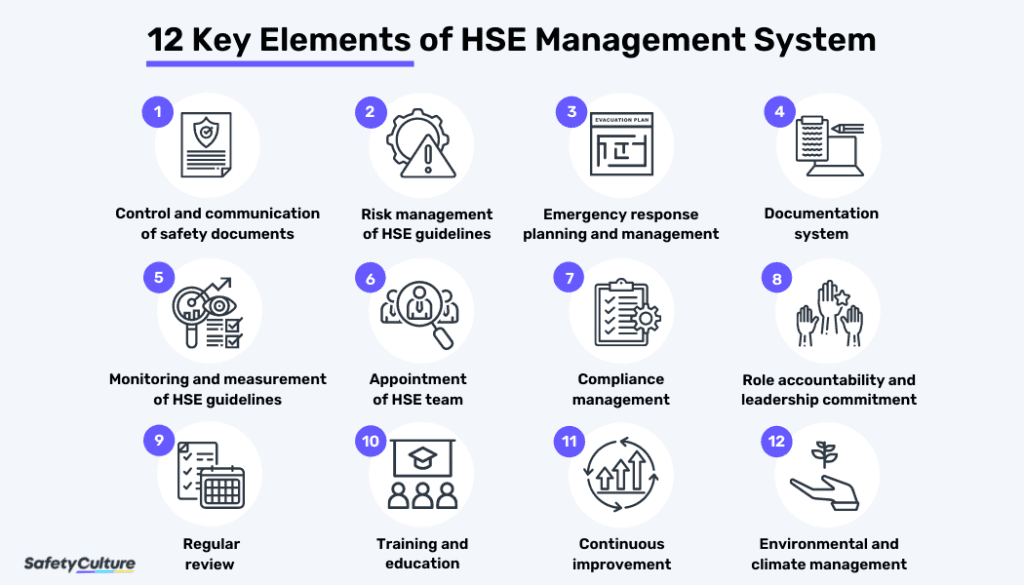
12 Key Elements of HSE Management System
1. Control and communication of safety documents
Organizations must have a reliable and streamlined system of distributing the latest protocols, safety standards, and other key documents to stakeholders. Giving easy access to such information reduces communication gaps and improves compliance status.
To give an example, there are Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines in displaying HSE posters which aim to inform employees of their rights outlined in the Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) Act. Putting up posters and other safety communication materials in places where everyone can see them often is a way to encourage awareness and compliance among employees. On the other hand, utilizing a cloud-based platform to store and access your organization’s HSE management system manual is also highly effective.
2. Risk management of HSE guidelines
A successful HSE management system focuses on risk analysis and management to promote a proactive culture of safety, rather than only addressing issues and incidents as they arise and happen.
This broad umbrella can also cover hazard identification, hazard assessment, and hazard control. To effectively identify potential HSE risks at work, knowing what kind of workplace hazards employees are exposed to lets HSE leaders and managers determine the next steps, such as change management and continuous improvement.
Create your own Hazard Identification checklist
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
3. Emergency response planning and management
Having Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) on emergency reporting, rescue operations, and medical duties helps prevent unnecessary panic during times of unprecedented events. OSHA’s guidelines on emergency preparedness and response aim to help employers train and prepare their workers and ensure they are equipped with the necessary knowledge and equipment to effectively deal with emergencies.
4. Documentation system
Nothing beats a proper administration process when it comes to maintaining a functioning HSE management system with good recordkeeping. This pertains to how every program, policy, and set of standards are documented and organized. When the time comes that the organization needs to do internal audits and regular monitoring, it’s going to be easier for HSE managers to check if there are missing details, lacking training sessions, and other key regulations.
5. Monitoring and measurement of HSE guidelines
Setting performance metrics helps organizations monitor and measure the effectiveness of safety controls and how workers take action in keeping themselves and others safe. Some examples of such metrics include Lost Time Injury Rate (LTIR), Total Case Incident Rate (TCIR), and Experience Modification Rate (EMR).
Creating standard safety inspection checklists is greatly helpful in optimizing the process and quality of HSE inspections, giving organizations relevant insights and data on how their HSE management system is doing. In most cases, this is also where incident management can be included.
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
6. Appointment of HSE team
A dedicated team of HSE leaders, managers, and members is key to a targeted, more effective implementation of an organization’s HSE management system. Their roles must focus on prevention of workplace accidents and injuries, having Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in place to measure if and how they’re helping the company achieve a safer working environment.
7. Compliance management
As non-compliance can cause serious financial liability, damage to organizational reputation, and operational disruptions, the role of HSE in the workplace also covers the financial and legal duties of an organization. While conducting internal assessments is a good move, considering a third party to determine the level of compliance may be the better decision for some.
8. Role accountability and leadership commitment
The roles and responsibilities along with the goals and objectives of the management and the workers must be clearly defined so that everyone can have a clear understanding of their individual roles and accountability. This can be done by writing up policies that are outlined in SOPs and written agreements.
Likewise, employers also have the jurisdiction to consider including the workers’ HSE duties in their job descriptions and enforce disciplinary actions as needed.
9. Regular review
Schedule and arrange regular meetings that are designed to tackle and review current HSE policies so that there are opportunities for the management and employees to collaborate in further improving the overall system. Most importantly, highlight the effectiveness of the safety communication plan and see if there are aspects that would need additional attention. Such instances can also require conducting Root Cause Analysis (RCA),Job Hazard Analysis (JHA), and the like, so it’s best to regularly touch base with stakeholders for effective execution.
10. Training and education
Carrying out an HSE management system training aims to keep HSE teams and workers informed, well-prepared, and skilled at addressing emergency situations, accidents, and other HSE hazards. Some examples of training programs include fire safety, first aid, and evacuation plan.
11. Continuous improvement
Certain incidents and issues may still arise, so it’s important to continue doing internal checks on policies and schedules. Conducting HSE management system audits is one way to do so, reviewing areas for improvement and recommending necessary amendments in existing policies and processes to reduce potential risks and improve overall mitigation.
12. Environmental and climate management
Organizations also have the responsibility of minimizing their negative impact on the environment. Likewise, initiatives must also be in place to maximize their positive contribution by using renewable energy, reducing carbon emissions, and preventing pollution caused by business operations. A successful HSE management system should include clear policies to guide workers, safety personnel, and other stakeholders. In addition, another framework that includes an environmental element, is QHSE.
International Standards for HSE
To better guide organizations in ensuring regulatory compliance for their HSE management system framework, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) established two major standards. Take a look at what each of these covers.
ISO 45001 – The 45001:2018, known as the world’s international standard for Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) management system, replaced the British standard OHSAS 18001 . It aims to protect workers and visitors against work-related accidents, illnesses, and injuries.
ISO 14000 – The 14001:2015 is the international standard responsible for the Environmental Management System (EMS) of organizations. It outlines specific guidelines to help organizations focus on how they can reduce negative impact and responsibly respond to ever-changing environmental conditions, while maintaining balance in quality operations.
Industry Examples
Here are examples of how HSE management systems are implemented in different industries:
Energy sector
According to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), an HSE management system example relevant to this sector is the High-Level Framework for Process Safety Management by the Energy Institute. It comprises 4 pillars such as process safety leadership, risk identification and assessment, risk management, and review and improvement. The main goals are to prevent fatal accidents and dangerous substances exposure, among others.
Construction sector
In the UK, the National Examination Board in Occupational Safety and Health (NEBOSH) issues the Health and Safety Management for Construction (UK) certification mostly for site managers, site workers, and health and safety advisors. This aims to strengthen an organization’s HSE management system by ensuring compliance with The Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 (CDM 2015).
Chemical sector
Chemical Industries Association’s Responsible Care framework is also a good example of an HSE management system. At its heart, ensuring effective management of health, safety, and environment along with product stewardship is a key driver of the Responsible Care initiative. The framework has various factors, including process safety, chemicals management, and resource efficiency, to name a few.
Optimize Your HSE Management System Using SafetyCulture
Why use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Efficiently manage and streamline health and safety processes across the organization, including incident management, safety audits and inspections, risk assessment, waste management, and more, using a comprehensive EHS software solution.
✓ Save time and reduce costs ✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents ✓ Boost productivity and efficiency ✓ Enhance communication and collaboration ✓ Discover improvement opportunities ✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Related articles
Food Safety
Safety

A Comprehensive Guide to Natasha’s Law Training
Learn about the process of Natasha’s Law training and how it helps food businesses efficiently meet allergen labeling requirements.
Construction Safety
Safety

A Complete Guide to Scaffolding Safety Training
Learn everything about scaffolding safety training, from topics to best practices, to uphold construction and maintenance safety.
Construction Safety
Safety

A Simple Guide to Oil and Gas Production
Learn about the oil and gas production process and the equipment and modern technologies used to improve field productivity.