What is Data Management?
Data management is a complex process of collecting, storing, and analyzing data to help make informed decisions. It involves various tools and techniques to ensure that data is obtained, stored, and utilized in a secure and efficient manner. With the help of data management strategies, organizations can effectively use data for their business needs.
Benefits
Effective data management offers several advantages to organizations. For one, it enhances their decision-making process. A robust data system allows them to access and analyze data quickly and accurately so that they make informed decisions based on facts and evidence.
Another benefit of data management is improved efficiency. By having access to accurate and up-to-date data, organizations can streamline their processes and reduce the amount of time and resources needed to complete tasks. This can help organizations save money and increase their productivity.
Lastly, data management also helps organizations protect their data. By establishing a sound and secure system, they can safeguard their data from unauthorized access and ensure that data is not compromised.
Components of Data Management
Data management consists of the following functions:
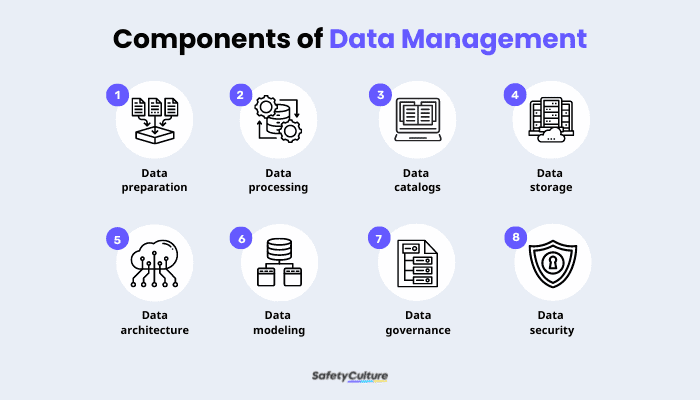
- Data preparation – cleaning and organizing raw data into a readable format for further analysis
- Data processing – loading information from multiple sources using data integration techniques, after which they are filtered and combined to be ready for use
- Data catalogs – handling the metadata of existing datasets, including their location, quality, and history of changes
- Data storage – documenting and keeping data in a repository for future use
- Data architecture – managing how data flows around the organization from its source to its destination
- Data modeling – mapping out the flow of data from a business process or organizational activity, such as customer information and product data
- Data governance – establishing rules and standards to maximize the value of data within the organization
- Data security – safeguarding digital assets and information from theft, corruption, unauthorized access, and other security threats
Types
The methods and approaches in data management can be classified into the following types:
Database Management
Database management is considered the most common type of data management. It involves the storage, retrieval, and manipulation of data stored in a database. Meanwhile, database management systems (DBMS) are used to store and manage large batches of data, making them ideal for business applications.
Data Warehousing
Data warehousing is the process of collecting and consolidating data from multiple sources in a single repository. It sorts through all the data types that businesses have gathered and stores them in a secure location for further analysis.
This type of data management is often used to assess large volumes of data as well as create reports and dashboards.
Data Mining
Data mining is the process of obtaining useful information from large datasets. This process allows organizations to identify recurring patterns and trends in data based on the information their users or customers provide.
This type of data management is typically used to gauge customer interest in a specific product or service, detect fraud, and filter spam.
Data Visualization
Data visualization refers to creating visual representations of data, such as charts and graphs, to make it easier to understand and interpret. Using graphical elements, companies can spot anything amiss in their processes.
Presenting data in a visual manner is also great for communicating information to non-technical users in a way they can easily digest and understand.
Other Specialized Types
Data management also comes in specialized types, such as:
- Text mining – the process of extracting meaningful information from text documents
- Natural language processing – the process of understanding and interpreting natural language, such as spoken or written language
- Machine learning – the process of using algorithms to learn from data and make predictions
Must-Haves of a Data Management Plan
A data management plan or strategy is essential for any organization that wants to ensure that its data is secure, organized, and accessible. When creating one for your organization, here are a few things to plan out for:
- How data is collected, stored, and used (considering the needs of the organization and the goals of the data management system)
- How data is protected from unauthorized access and backed up in case of a disaster
- How data is shared with other departments within the organization, as well as with external partners
- How data is used to make decisions (e.g., which products to develop or which marketing campaigns to launch)
Challenges
With managing data comes various challenges that can put organizations at risk. Here are the most common ones to watch out for and prepare:
- Data security – Security breaches and cyber attacks pose a serious threat to the data resources of an organization. For this reason, companies must establish measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Data accuracy – As the volume of data being captured increases, there’s a higher chance for oversight as inaccuracies slip through the system, especially when there is little to no monitoring. The challenge for organizations now is to ensure that they have the right processes to ensure that their data is reliable and up-to-date.
- Data utilization – The amount and diversity of data collected and stored in this age continue to rise, given the technological innovations. But because of its sheer volume, organizations might fail to maximize the value of this resource if they don’t know what data they have, where it’s stored, and how to leverage them.
- Process efficiency – Processing large volumes of data can be a time-consuming process. And while organizations try to find the right resources to manage their data efficiently, they must also balance their efforts with the need for accuracy and security.
- Compliance – Data and privacy regulations are constantly changing as technology keeps evolving. Thus, the challenge for organizations is to keep pace with these changes, starting with understanding which data they can and cannot use.
Best Practices
Because of the setbacks mentioned in the previous section, it’s important to establish a set of standards and procedures to ensure the accuracy and integrity of data. Listed below are the best practices for managing data systems:
- Properly secure data using strong passwords, encryption, and two-factor authentication methods.
- Establish a system to monitor data usage and detect unauthorized access to data.
- Implement a policy for the appropriate and legitimate use of organizational data.
- Create backups of your records regularly and store them in a secure location.
- Regularly review and update data according to the specific needs of the organization and existing privacy laws.
Digitize the way you Work
Empower your team with SafetyCulture to perform checks, train staff, report issues, automate tasks, and visualize data with our digital platform.
Get Started for FreeFAQs about Data Management
Data management is beneficial for businesses that rely on data to make decisions, such as those in the finance, healthcare, and retail industries. It can also aid organizations that need to comply with data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
The six principles of data management are as follows:
- Avoid the re-collection of existing information.
- Manage the lifecycle of datasets carefully.
- Develop a solid data policy.
- Clearly define who the owner of the data is.
- Provide the right metadata for all datasets.
When measuring how your data management system is working, it’s important to look into the following Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Completeness – Capture missing or inaccurate information from existing data.
- Consistency – Check the uniformity of your data and spot inconsistencies that could result in errors.
- Uniqueness – Measure the number of duplicate records in your repository.
Data management plans are used to handle datasets efficiently, meet business requirements, and provide ways to leverage data for business growth. An effective plan is comprised of the following items:
- Datasets to be processed (including a brief description)
- Guidelines for documenting, storing, and organizing data
- Specifications for accessing and sharing data
- Procedures for archiving data




