Published 2 Dec 2025
Article by
6 min read
What is a JSA Template?
A Job Safety Analysis (JSA) template or a Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) form is an essential tool for evaluating high-risk tasks by breaking them down into individual steps. This process involves identifying potential hazards associated with each step and determining preventive measures to mitigate these risks. Supervisors and employees work together in accomplishing JSA templates to ensure that both have a good understanding of the hazards and come up with safety controls.
Importance of JSA Analysis
A JSA is important because it increases job knowledge, establishes teamwork, serves as a health and safety standard and teaching aid, and supports accident investigations at work. Dangerous jobs benefit the most from a JSA because it can reduce or eliminate hazards that cause serious injuries or fatalities.
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics’ recent workplace fatality census, the following are examples of the most dangerous jobs in the US that would benefit significantly from a JSA process:
Logging workers
Fishers and hunting workers
Aircraft pilots and flight engineers
Structural iron and steelworkers
Driver/sales workers and truck drivers
Refuse and recyclable material collectors
Underground mining machine operators
These jobs require rigorous safety analyses to ensure the employees’ health and safety in the workplace. Regulatory bodies such as OSHA have outlined JHA or JSA guidelines for conducting in this document. As one of the tools used for hazard assessments, regularly performing a job safety analysis can help proactively ensure compliance with OSHA standard 1910.132:
With these in mind, complying with workplace safety standards can be helped by using a JSA checklist or template. This tool can standardize the way safety assessments are conducted, control measures are recommended, and JSA results are documented.
What to Include in a JSA Template
An effective JSA template should be able to outline and detail from basic job tasks, to identifying hazards carefully and implementing control measures., Here are some of the most important items that should be included in your JSA Template :
Job task being assessed – The supervisor or safety officer will describe the details of the job and identify the workers observed during the analysis. This should break down the job into individual steps or tasks, detailing what is done at each stage.
Potential Hazards Identification – The observer will determine the potential hazard for each task being performed. These hazards include physical, chemical, environmental, or ergonomic hazards.
Control Measures – Outline specific measures to eliminate or reduce risks, such as engineering controls, administrative changes, or personal protective equipment (PPE)
Recommendations – Recommendations on how each task can be accomplished safely will be recorded on the JSA and submitted for review and implementation.
A completed JSA template can be exported and sent to relevant stakeholders. This allows for businesses to document every inspection/audit and ensure that they stay compliant to safety regulations.
Tailoring a JSA checklist for High-Risk Jobs
Focus on High-Risk Jobs First – Start with tasks that have a history of incidents, carry potential for severe injury, or involve new, changed, or complex processes. This ensures resources target the most critical areas.
Break the Job into Clear Steps – Observe the task or consult experienced workers. List actions in sequence using concise, action-oriented words (e.g., “inspect,” “lift,” “lock out”), keeping steps between 5–15. Break down overly complex steps as needed.
Identify Hazards at Each Step – Use both standard hazard categories (physical, chemical, biological, ergonomic, psychological) and prompts like slips/trips/falls, pinch points, or exposure risks. Draw on worker input and incident records for accuracy.
Apply the Hierarchy of Controls – Follow the order: eliminate hazards, substitute safer options, add engineering controls, implement administrative controls, and use PPE as a last resort. For high-risk jobs, aim for elimination or engineering solutions where possible.
Evaluate Residual Risk – After applying controls, assess remaining risks using a matrix or scoring system. If the risk level is unacceptable, revisit control measures.
Standardize the Checklist – Create a reusable template with sections for job steps, hazards, controls, and risk ratings—especially useful for similar high-risk tasks.
Make It Visual and Accessible – Include photos or videos for clarity, and ensure the checklist is easy to access on-site—whether via mobile tools or printed copies.
Keep It Up-to-Date – Review and revise after incidents, near misses, or process changes. Treat the JSA as a living document.
Engage Workers and Use Feedback – Build the checklist with workers, not just for them, to encourage buy-in and improve hazard detection. As one practitioner put it:“Make it easy and relevant so it feels connected to the real job, not just paperwork.”
How to Conduct a Job Safety Analysis Using a Template
A JSA template is used when performing a JSA procedure and is used to generate a safety and recommendation report. These four key steps can help you get started with performing a more effective analysis:
1. Choose the right job
Start looking at a job that has a high accident frequency and severity, which results in serious injuries. Consider factors when deciding what jobs you need to conduct a JSA analysis, such as jobs that have high exposure to hazardous and harmful products
2. Break a job into steps
Don’t be too general yet not too detailed during this part of the analysis. As a rule of thumb, there should be at least 10 steps, depending on the complexity of the job. Describe each step by detailing and simplifying with verbs or action words.
It can also help to make notes about “what is done,” not “how it is done” when observing how jobs are performed during normal times and situations.
3. Identify potential hazards
When identifying hazards, the key is to ask the right questions:
Is the worker at risk of falling, slipping, and tripping ?
Is the worker exposed to extreme temperatures?
Is the worker at risk of getting caught between objects?
Is the worker exposed to explosive and combustible materials?
Is the worker at risk of electrocution?
4. Set preventive measures
Eliminate the hazards by using a different process, modifying an existing one, improving the environment, changing tools, or reorganizing work procedures. Using machine guards, enclosures, workers’ booths, or similar devices can also be done to contain certain hazards if they’re impossible to eliminate. After conducting a JSA, ensure continuous safety training and other initiatives by considering discussing safety topics regularly.
Job Safety Analysis Example
Writing a job safety analysis with the help of a free JSA template can seem challenging at first. With continuous practice, though, workers can master breaking down their job tasks, identifying hazards, and implementing controls. To guide you, below is an example of a completed Job Safety Hazard analysis:
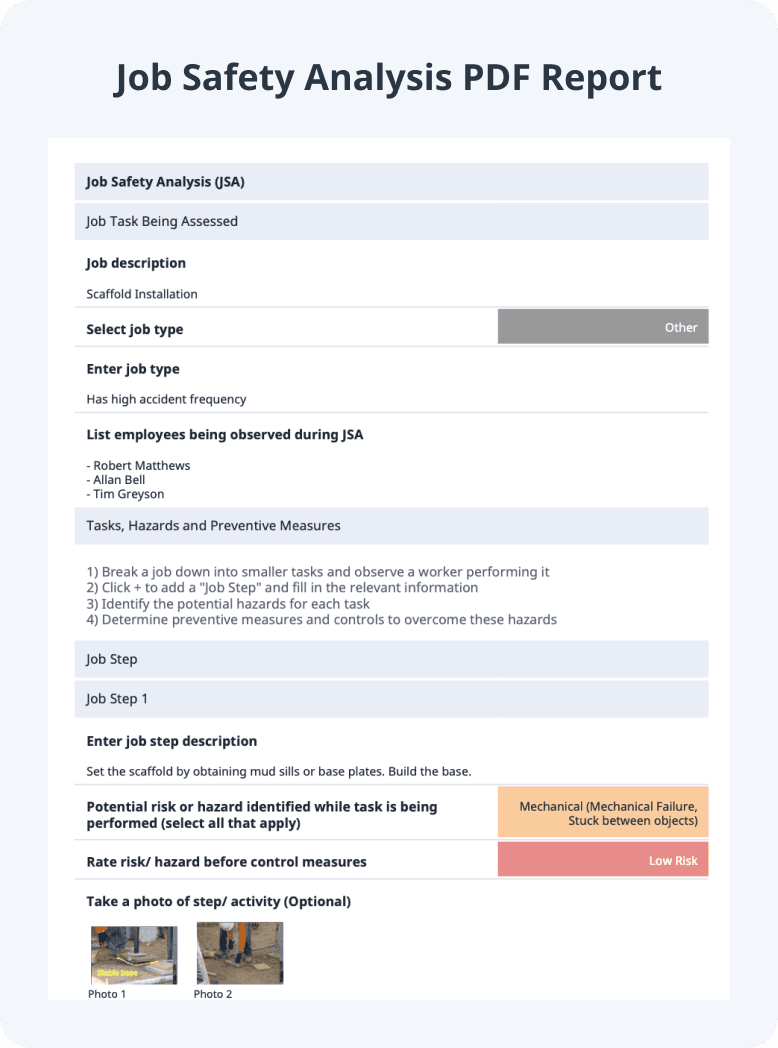
Job Safety Analysis PDF Report

Byblos Construction digitized safety checklists, compliance checks, and risk assessments with SafetyCulture, letting teams quickly notify leaders of risks for faster action and fewer blind spots. This improved risk management, communication, and visibility for safer job sites.

Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.