Published 26 Sept 2025
Article by
4 min read
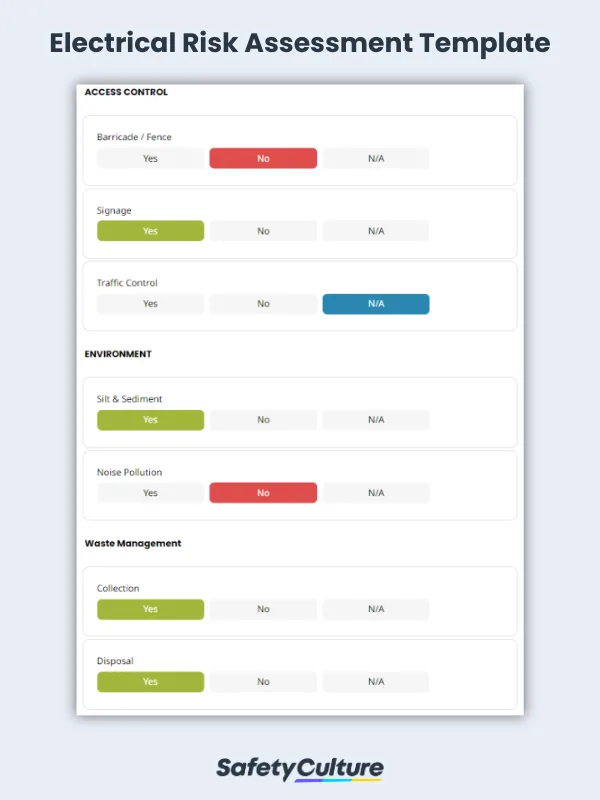
What is an Electrical Risk Assessment Checklist
An Electrical Risk Assessment Checklist serves as an essential tool for organizations to ensure the safety of personnel interacting with electrical systems. It involves cataloging all electrical equipment, identifying potential hazards, designing preventative measures, and conducting periodic reviews. Regular training and awareness programs complement the checklist, emphasizing best practices and safety protocols, thereby highlighting an organization’s commitment to operational excellence.
Importance and Benefits
This template is important for organizations as it serves as a safeguard against potential electrical hazards. It ensures worker safety, aids in regulatory compliance, promotes proactive measures, and standardizes safety protocols across different operational units. Additionally, it boosts operational efficiency, reinforces employee confidence, and can lead to financial savings by preventing costly mishaps and legal liabilities.
Components of an Electrical Risk Assessment Template
An effective Electrical Risk Assessment Template is designed to provide a structured approach to identifying, evaluating, and controlling electrical hazards. Following the prescribed outline:
1. Identifying Potential Hazards and Risks
This is the foundational step of the assessment. It involves:
Assessing the surrounding environment for general hazards.
Cataloging electrical equipment and systems within an organization or facility.
Noting areas with exposed electrical parts, overloaded circuits, or outdated wiring.
Recognizing scenarios where personnel might come into contact with electrical components, whether during routine operations or maintenance.
2. Evaluating the Severity and Likelihood of Risks
Post identification, each hazard is assessed based on:
Severity: How harmful can the hazard be? This could range from minor shocks to life-threatening electrocutions or fires.
Likelihood: What’s the probability of the hazard leading to an incident? This considers factors like frequency of interaction with the hazard and existing safety measures.
3. Implementing Preventive Measures and Controls
With risks identified and evaluated, the next step is mitigation. This involves:
Designing and instituting safety protocols, such as lockout/tagout procedures.
Ensuring regular maintenance and timely replacement of faulty equipment.
Incorporating safety equipment, such as circuit breakers, ground fault circuit interrupters, and arc fault circuit interrupters.
Offering continuous training and awareness programs to keep personnel informed and vigilant.
Providing action points that can be assigned to responsible personnel and have notified and accomplished within minutes, not days.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting an Electrical Risk Assessment
When you are ready to conduct your electrical risk assessment, make sure to have your digital checklist in-hand. Divide the tasks into different sections to make sure you don’t miss anything. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use this template :
Preparing for the assessment process
Assembling the Assessment Team : Gather a team of experts and stakeholders who can contribute their knowledge and insights to the assessment. This may include electricians, safety officers, engineers, and relevant management personnel.
Defining the Scope and Objectives : Clearly define the scope of the assessment. Determine what areas, systems, and equipment will be included in the assessment. Set specific objectives, such as identifying potential hazards, evaluating existing safety measures, and proposing improvements.
Gathering necessary information and data
Identifying Electrical Systems and Components : List all the electrical systems, equipment, and components present in the area under assessment. This includes power sources, distribution panels, wiring, outlets, and machinery.
Reviewing Electrical Documentation : Gather relevant documents such as electrical drawings, diagrams, maintenance records, and previous risk assessment reports. These documents provide insights into the existing electrical setup and any previous identified risks.
Conducting On-Site Inspections : Physically inspect the area to identify any visible hazards such as exposed wires, damaged equipment, or improper wiring. This step involves assessing the condition of equipment and identifying potential sources of electrical leakage or short circuits.
Analyzing findings and identifying priorities
Assessing Potential Hazards : Analyze the collected data to identify potential electrical hazards, such as overloaded circuits, inadequate grounding, and improper storage of flammable materials near electrical sources.
Evaluating Existing Safety Measures : Review the effectiveness of current safety measures in place, such as circuit protection devices, grounding systems, and emergency shutdown procedures.
Prioritizing Risks : Rank the identified risks based on their severity and likelihood of occurrence. This step helps determine which risks need immediate attention and which can be addressed through long-term strategies.
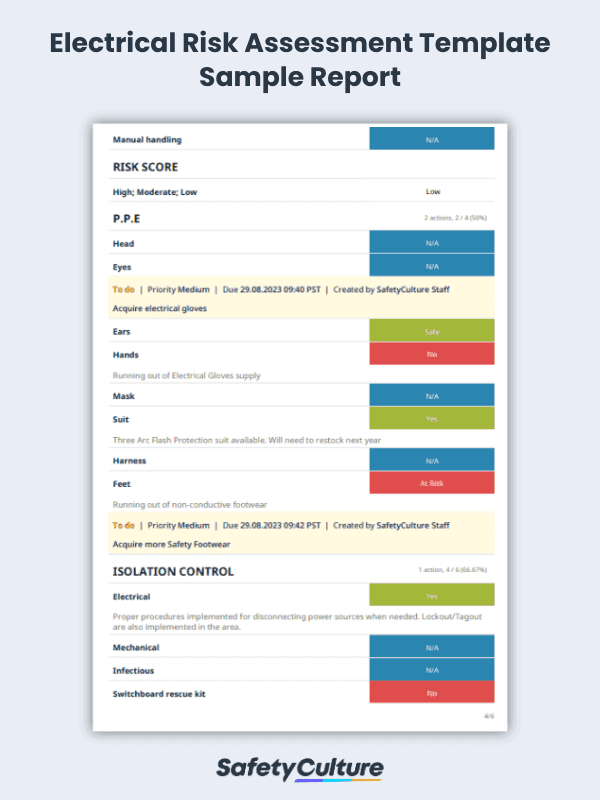
Check out how a sample of a completed checklist report looks like. Note that this checklist and sample report is for enterprise applications only.
Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.