Published 26 Sept 2025
Article by
3 min read
What is a Commissioning Checklist?
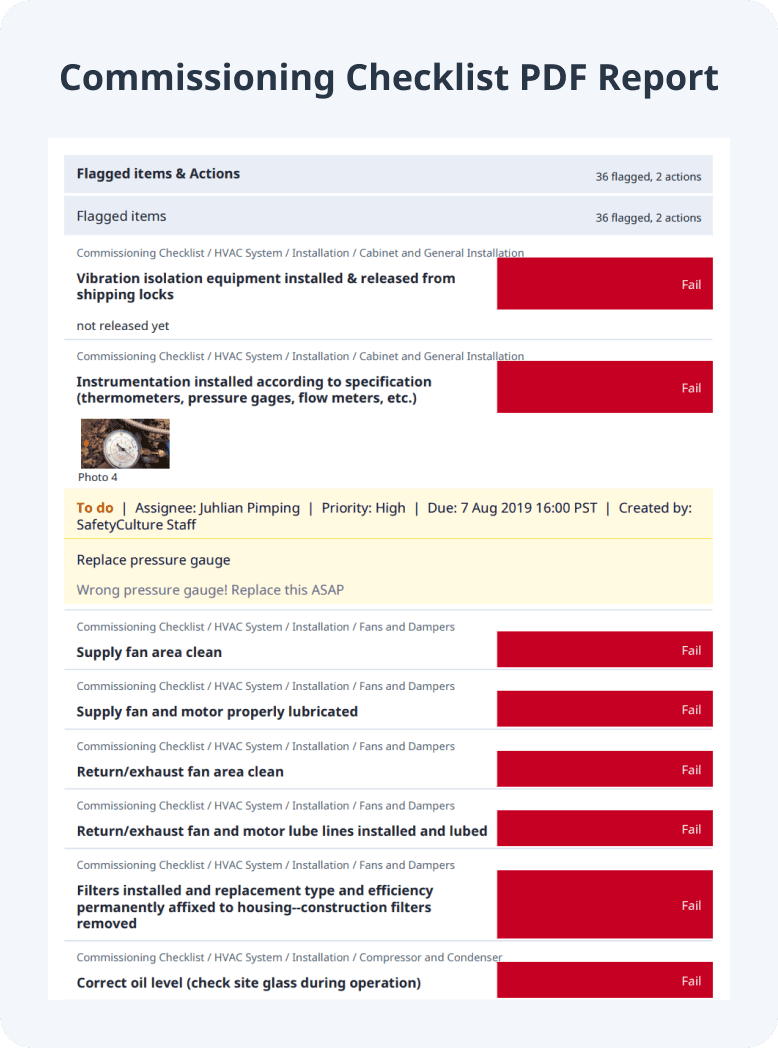
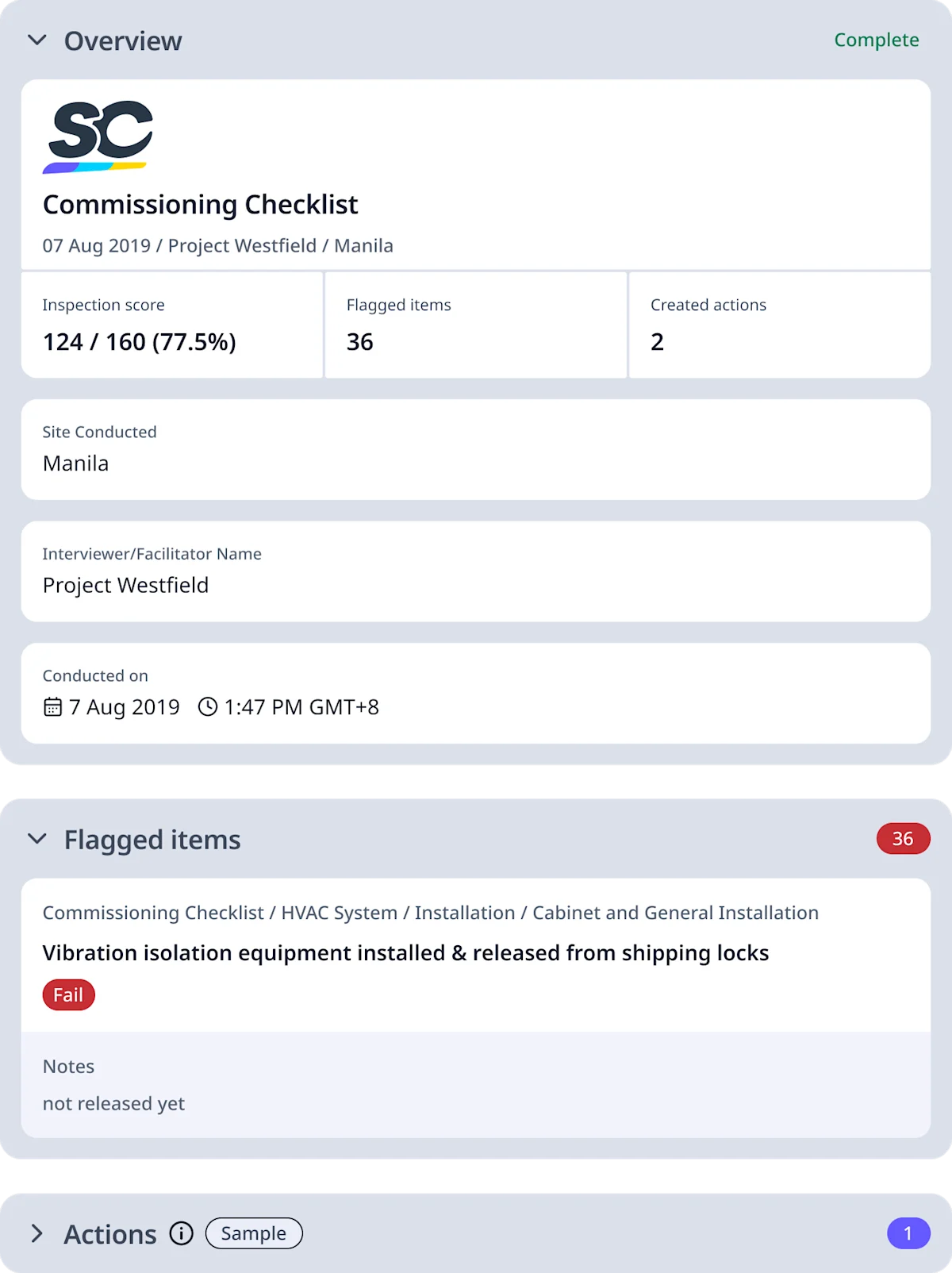
A commissioning checklist is used to easily perform comprehensive installation, functional, and operational inspections of a project equipment, system, or components. This checklist helps resolve any detected failures and ensure full functionality of project assets.
How does a commissioning checklist improve project safety and performance?
Using a commissioning checklist enhances project safety and performance by confirming that HVAC systems are properly installed, operate efficiently, and are compliant with design requirements. This comprehensive check helps prevent equipment failures and safety risks by properly recording the system’s condition and also allowing users to fine-tune controls for functional performance.
At What Point Does Pre-commissioning End and Commissioning Begin?
There are regional differences when it comes to common parlance in pre-commissioning and commissioning. Pre-commissioning is sometimes referred to as Cold Commissioning, Static Commissioning, or Mechanical Completion; on the other hand, commissioning is sometimes referred to as Hot Commissioning, Live/Dynamic Commissioning, or Start-up. Therefore, commissioning teams experience difficulty in determining the proper procedure. Here is a run-down of what needs to be done during pre-commissioning and commissioning, respectively:
Pre-commissioning Procedure
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID) Check , also known as System Check or Walkdown, should be performed by the commissioning team to identify engineering and construction errors. Create a P&ID Punch List and address identified issues before pre-commissioning.
Pre-commissioning activities start from mechanical completion, where running-in of equipment such as control system sequence tests (Dry Commissioning), water or solvent introduction to closed-loop pumps (Wet Commissioning), and other operating scenarios where process fluids are NOT YET used.
The Defining Point: Pre-Startup Safety Review (PSSR)
PSSR is a thorough safety inspection of a new or modified facility to be conducted before commissioning. This is the point where pre-commissioning ends and commissioning begins. Correct any system failure, resolve all safety risks, and re-take the PSSR to comply with health and safety regulations prior to commissioning.
Commissioning Procedure
Commissioning is the overall performance testing of the facility and its systems such as HVAC , pumps, piping, and lighting. Outstanding punch points should be resolved before routine operation. During a manufacturing plant commissioning, process conditions are established and process fluids (the actual raw materials to be used for routine production) are introduced into the system.
Initial Operation, or the first production run, aims to determine if the production process manufactures output that meets design requirements. Easily identify non-conformance and adjust the system or optimize the process by performing a first article inspection prior to routine production.
What is Included in a Commissioning Checklist
A commissioning checklist is an essential tool used in various industries to ensure that systems, equipment, and processes are installed and functioning as intended. The contents of a commissioning checklist can vary based on the project type and assets involved, but typically include several key elements:
Pre-Installation Checks: Verify design, equipment, and site conditions.
Installation Verification: Ensure proper installation and secure connections.
System Testing: Test functionality, safety systems, and performance.
Adjustments and Calibration (TAB): Balance and calibrate systems for optimal performance.
Documentation and Compliance: Ensure proper documentation and regulatory compliance.
Training and Handover: Train staff and provide operational resources.
Post-Commissioning Follow-Up: Address any outstanding issues and schedule follow-ups.