What is SMETA?
Sedex Members Ethical Trade Audit (SMETA) is a globally recognized social auditing methodology developed by Supplier Ethical Data Exchange (Sedex) in order to provide visibility on suppliers’ business practices in the supply chain.
Importance
Sedex defined SMETA as a “social auditing methodology, enabling businesses to assess their sites and suppliers to understand working conditions in their supply chain.” Social auditing enables brands to demonstrate their commitment to human rights, and monitor worker health and safety. SMETA is relied on by buyers who want their suppliers to be audited, or by suppliers when their customers want them audited to address any issues.
SMETA audits are conducted by third-party companies or organizations approved by Sedex. They are known as a Sedex Affiliate Audit Company (AAC) or independent organizations from Sedex.
Key Areas of Assessment
There are several key areas to consider when evaluating an organization’s socially responsible business operations and meeting social compliance requirements. They are:
SMETA 2-Pillar Audit
A SMETA 2-Pillar audit comprises 2 standard areas:
(1) Labour Standards and;
(2) Health & Safety.
The standards contained in the ETI Base Code govern the 2-Pillars of a SMETA audit. These two are mandatory areas of assessment for any SMETA audit. It covers these areas:
- Management Systems
- Entitlement to work
- Subcontracting and Homeworking
- Shortened Environment assessment
SMETA 4-Pillar
Audit At the request of Sedex members, SMETA has now been extended with “business ethics” and the “environment” being added as optional pillars:
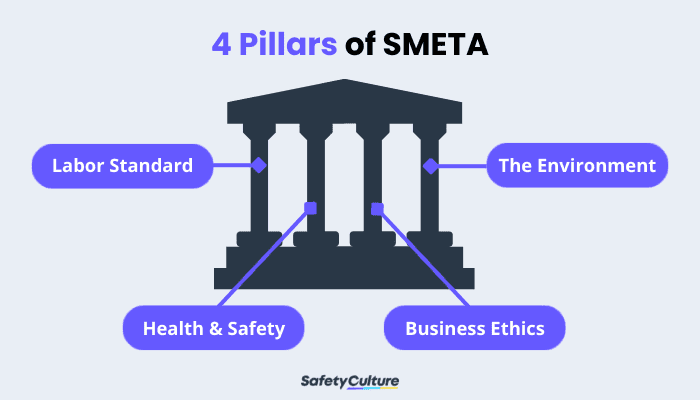
4 Pillars of SMETA
- Labor standards
- Health and safety
- The environment
- Business ethics
Core Documents
SMETA consists of four core documents that support the audits. SMETA may be used by any auditor or audit organization, including those who are not members of the Sedex organization. But an audit can only be referred to as a “SMETA Audit” if and only if it was conducted using the criteria outlined in the following documents:
- SMETA Best Practice Guidance – consists of standard protocols for carrying out a SMETA audit.
- SMETA Measurement Criteria – gives details of the items that should be measured or examined during the SMETA audit.
- SMETA Audit Report – provides the template for conducting the audit in a standardized format which can be uploaded to Sedex website.
- SMETA Corrective Action Plan Report (CAPR) – provides template for audit findings summary that should be used in conjunction with the corresponding corrective actions to ensure that the violation or issue does not occur again.
The information that will be visible to site and customers are those contained in both the SMETA Audit Report and the CAPR.
How Does SMETA Audit Work?
Below is an infographic of how the SMETA audit is done. The auditing process works this way:
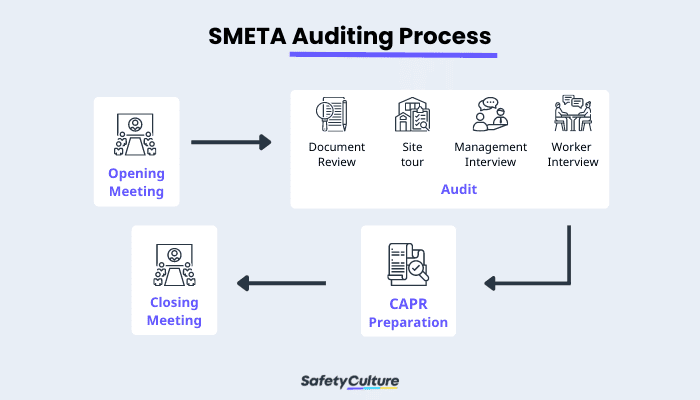
SMETA Auditing Process
- Conduct an opening meeting
- Review business documents–the auditor examines the organization’s existing processes and systems against the Ethical Trading Initiative (ETI) Base Code and local laws.
- Do a site tour–the auditor conducts an inspection of the company’s site to see the working conditions on the ground.
The auditors will be checking the workplace if there is any unsafe working conditions, overwork, discrimination, low pay and forced working conditions which can be found in the conventions of the International Labour Organization (ILO). They will review the following areas according to SMETA:
- Wages
- Right to work
- Working hours
- Health and safety
- Temporary workers
- Provision of rest time
- Fair treatment of staff
- Management interview-conducting interviews with workers (in groups and per person)
- Closing meeting–this involves providing the CAPR.
Benefits of SMETA
Aside from providing visibility to your supply chain, conducting a SMETA audit entails profitable benefits such as:
- Suppliers can share the audit reports to several of their customers which in turn reduces the chance of duplicated audits, saving time, money, and resources.
- SMETA audits is a solution for checking social compliance and meeting standards of your supplier which in turn build transparency in the supply chain.
- SMETA provides the supplier with a CAPR to help address any issues that may occurre.
- Suppliers with SMETA audits signal to their customers that they have zero tolerance for human rights abuses such as child and forced labour and they are compliant with statutory standards on labor.
Be Equipped for a SMETA Audit with SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor)
SMETA can help you understand your business practices in greater depth and identify any areas where you could improve your business ethics. Equip your workplace before a SMETA audit takes place with SafetyCulture, the best mobile inspections and audit app used by auditors for conducting efficient auditing.
With SafetyCulture, you could do the following to support SMETA audits:
- Gather and store the information from your examination and review of the organization’s existing processes and system in a secure cloud which you can view remotely.
- Suppliers can get guidance on how SMETA audits are conducted and prepare for it in advance using the SMETA checklist.
- Conduct compliance checks on your organization and maintain your ethical business practices so that no violations or issues will be found in the audit report.
- Support the CAPR after you’ve received it from the auditor and assign corrective actions to appropriate areas or group of workers.



