What’s really eating into your team’s time?
Middle managers in manufacturing waste 7 weeks every year on low-value work. See what’s really slowing teams down.

Learn about the role of quality control in manufacturing, its importance in production, and the best strategies for maintaining consistent quality across the board.

Published 22 Aug 2025
Article by
6 min read
Quality control (QC) in manufacturing is a process used to make sure that products and production operations meet specific standards or specifications. It generally involves routine inspections at various stages of production to detect and correct any defects or variations that could compromise quality.
Moreover, quality control within the manufacturing industry is greatly concerned with maintaining safety standards for machinery and production equipment to deliver products that satisfy the necessary regulations.
Quality assurance and quality control are two complementary arms of a manufacturing organization’s quality management system. Here’s how they differ from each other:
Manufacturing QC | Manufacturing QA | |
Purpose | Verify that products meet quality standards by detecting defects | Create and refine processes to prevent systematic issues |
Focus | Product-oriented | Process-oriented |
Approach | Reactive | Proactive |
Scope | Periodic inspections, sampling, and testing | Whole quality management system and product lifecycle |
Responsibility | Dedicated product testing and inspection teams | Cross-functional teams |
Quality control is a necessary step in manufacturing because it involves product checks for things such as specifications, measurements, color and appearance, barcodes, labeling, and packaging. By establishing proper quality control measures, manufacturers can:
Enhance product quality – Rigorous checks help spot and correct defects in the initial production stages, ensuring products meet quality standards and customer expectations.
Lower production costs – Identifying defects early minimizes rework, scrap, and waste, thereby reducing overall production expenses.
Comply with industry regulations – This is especially important in highly regulated subsectors like pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and chemicals, to prevent endangering the lives of consumers.
Prevent recalls – In 2023, product recalls in the US increased by 11% and fines for defective products totaled USD 55.3 million. This can be avoided by enforcing strict quality control checks throughout the production process.
Strengthen brand reputation – Consistently high-quality products build trust and positive customer perception, leading to more loyal customers.
Raise the bar for product quality and exceed customer expectations with standardized checks across all production sites.
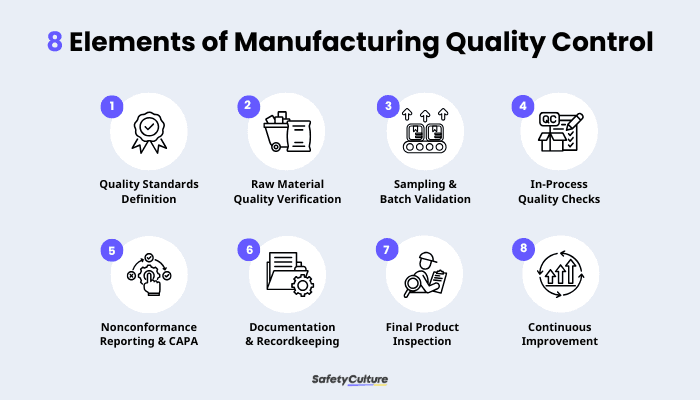
8 Elements of Manufacturing Quality Control
Below is a breakdown of the key components that make up an effective manufacturing quality control process:
Quality standards definition – First, manufacturers must establish clear, measurable quality criteria and standards that the products must meet.
Raw material quality verification – At this stage, incoming raw materials are inspected and tested to ensure they meet the required specifications and quality standards before entering the production process.
Sampling and batch validation – During production, samples from batches are systematically collected and tested to validate that the items within the batch meet quality expectations.
In-process quality checks – Continuous inspections and tests are performed at various stages of manufacturing to monitor quality, catch defects early, and ensure processes remain within control limits.
Nonconformance reporting and Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) – Any defects or deviations detected are recorded through nonconformance reports. Meanwhile, corrective actions are implemented to resolve existing issues, and preventive actions are taken to avoid recurrence.
Documentation and recordkeeping – Throughout the QC process, detailed records of inspections, tests, non-conformances, and corrective actions are maintained to ensure traceability, accountability, and facilitate audits.
Final product inspection – Completed products undergo thorough end-of-line inspection and testing to confirm they meet all quality specifications before release to customers.
Continuous improvement – QC data and feedback are continuously analyzed to identify trends and opportunities for improving manufacturing processes and quality outcomes over time.
Different manufacturing processes require the right quality control approach to ensure desirable results. Here are a few popular ones:
This method involves a straightforward inspection and assessment of all products at any stage of the production process. Inspections can be visual, manual, or automated, using sensors and cameras for consistency. Digital checklists also provide a structured way of performing these quality control assessments.
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
Also known as stress testing, this method evaluates product durability and performance under extreme conditions such as temperature, pressure, or tension until they break. It’s a straightforward way to expose product flaws, so it’s easier to address potential vulnerabilities and improve product quality.
The Six Sigma method works by defining the problem, assessing the current process, and identifying the potential cause of variations, defects, and issues. It involves 5 steps ( Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control ) to achieve high-quality standards.
Root cause analysis in manufacturing is another popular method for quality control. This technique identifies the primary cause of an issue and analyzes different factors that contribute to quality failures. This way, long-term damage from persistent or emerging problems can be avoided.
SPC uses statistical methods to monitor and control the manufacturing process. By collecting and analyzing quantitative data, it’s easier to identify trends, variations, and potential issues, allowing for adjustments before defects occur. This methodology helps uncover problems that will be addressed through corrective measures.
Lean manufacturing is a systematic approach that focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing value by continuously improving processes. As a quality control method, it emphasizes identifying and eliminating defects and inefficiencies in production to ensure high quality and consistent output.
TQM integrates a strategic and systematic approach where every employee understands their role in the process. This holistic approach not only reduces defects but also lowers costs, improves customer satisfaction, and builds a culture deeply committed to quality.
Besides identifying a quality control method that works for their organizational needs, manufacturers must support this process by implementing practices that deliver top-quality products.
Every moment counts — the industry loses roughly $25.8 billion each year in middle-manager productivity due to unclear workflows and limited visibility. Tightening up these processes doesn’t just protect quality, it gives time back to teams.
Here are some key best practices:
Define clear quality standards : Set specific, measurable quality standards that align with industry regulations and customer expectations. Thoroughly document these standards so that all team members understand the requirements and are aligned with overall manufacturing goals.
Implement Standard Operating Procedures ( SOPs ) : Develop and enforce SOPs to standardize production processes. SOPs reduce variation, improve efficiency, and ensure that all employees follow consistent practices.
Use data for decision making : Collect and analyze data throughout the manufacturing process to identify patterns and root causes of defects. Conduct routine inspections and audits to ensure accuracy over observations and use real-time monitoring systems to track key quality metrics at every stage.
Invest in employee training : Regular training on quality standards , inspection techniques, and equipment use ensures that employees are skilled and knowledgeable about maintaining product quality. Empowering employees with problem-solving skills also helps identify and address issues early.
Listen to customer feedback : Gather and analyze customer feedback regularly. Use this information to make necessary quality adjustments and enhance product reliability and customer satisfaction .
What’s really eating into your team’s time?
Middle managers in manufacturing waste 7 weeks every year on low-value work. See what’s really slowing teams down.

SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, enhance resource utilization, and build an agile and scalable infrastructure with SafetyCulture. Strive for operational excellence to boost competitive advantage, foster sustainable growth, and deliver long-term value.
✓ Save time and reduce costs✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents✓ Boost productivity and efficiency✓ Enhance communication and collaboration✓ Discover improvement opportunities✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Compliance
Construction Site Compliance

Find out how caisson construction can provide a stable foundation for your next project in a quick, cost-effective, and reliable manner.
Compliance
ISO

Explore the factors, requirements, and best practices for delivering impactful ISO 22000 training and implementing systems effectively.
ISO
Compliance

Explore the benefits of delivering ISO 45001 training across multiple industries and choose what works best for your team.