What is Power Line Safety and Why Should It Matter?
This article will give you a quick overview of power line safety and what you need to know to stay safe.

Published 21 Nov 2025
Article by
5 min read
What is Power Line Safety?
Power line safety is about recognizing the risks associated with power cables and working safely around them. Companies are responsible for maintaining power and transmission lines, and for training their teams to work safely around electrical hazards. Meanwhile, workers are also responsible for being aware of the power line dangers and taking precautions to avoid them.
Power lines are a necessary part of our electric grid. They deliver the electricity that keeps our homes and businesses running, but they can also be extremely dangerous. Every year, there are accidents involving power lines that result in serious injury or even death. This is why power line safety is an important issue for both utility companies and the general public.
Importance
Power lines can be extremely dangerous because they carry high voltages of electricity. If you come into contact with a power line, you could be seriously injured or even killed.
According to the US Electronic Library of Construction Occupational Safety and Health (elCOSH), power lines come in second for the cause of electrocutions to electrical workers and other construction workers in the US. Specifically, around 34% of worker electrocutions involve overhead power lines. For non-electrical workers, the rate climbs to 56%. Downed power lines can also create additional hazards by energizing nearby metal objects, such as ladders, pipes, or vehicles, posing a serious public safety risk.
That’s why it’s important to stay clear of power lines and avoid any work that could bring you into contact with them. Line workers, who install, maintain, and repair these lines, must take extra care.
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
Power Line Types and Their Voltages
An electrical grid has three main types of power lines, each operating at different voltages based on how far the electricity needs to go.
The three types are:
Transmission Lines: Being the largest and highest-voltage lines, these carry large amounts of electricity over long distances, from power plants to major substations.
Subtransmission Lines: The middle layer that steps high-voltage electricity down before it reaches the distribution system.
Distribution Lines: As the most commonly used type, these carry lower-voltage electricity to homes, schools, and businesses.
To understand how important power line safety is, you need to understand each power line’s voltage:
Voltage Type | Voltage Range | Use |
Low Voltage (LV) | Up to 1 kV | Mostly used on distribution lines or service lines that carry electricity from transformers to homes and businesses |
Medium Voltage (MV) | 1 kV to 35 kV | Mostly used on local distribution lines that carry electricity from substations to homes and businesses. These can also be overhead or underground |
High Voltage (HV) | 35 kV to 230 kV | Common in sub-transmission and regional transmission lines for distributing electricity to distribution lines |
Extra High Voltage (EHV) | 345 kV to 765 kV | Primarily used in transmission lines for long-distance and bulk power transmission |
Ultra High Voltage (UHV) | Above 765 kV | The largest scale transmission for power grid interconnections |
Hazards and Injuries Associated with Power Lines
Working around power lines comes with serious risks, but most electrical injuries can be prevented by following proper safety procedures. Before starting their work, line workers and their employers should know how to respond to a downed power line and how to install or repair one safely.
Common power line–related injuries include the following:
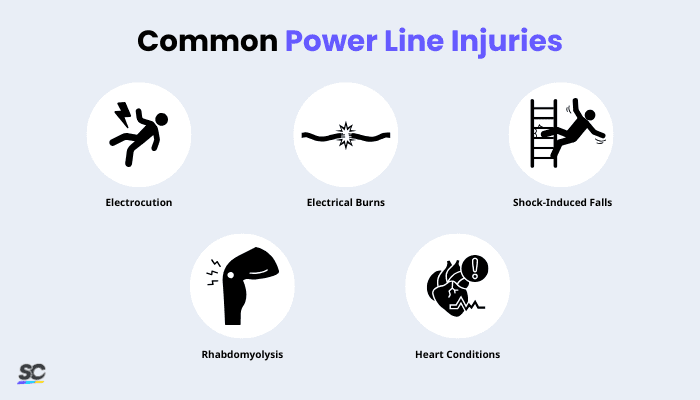
Common Power Line Injuries
Electrocution: A fatal or serious injury caused by direct contact or electrical arcing from an energized power line.
Electrical Burns: Injuries that damage skin and tissue, often caused by arc flashes or falling debris from a power line.
Shock-Induced Falls: Electric shock can cause muscle contractions or loss of consciousness, leading to falls from ladders, scaffolds, or poles.
Rhabdomyolysis: Electricity can burn muscles from the inside, breaking them down and releasing harmful substances into the blood.
Heart Conditions: Electrical current can pass through the chest and disrupt the heart’s rhythm, causing arrhythmia or cardiac arrest.
Power Line Safety Tips
Electrical power lines are vital infrastructure for countries worldwide, as they deliver electricity from power plants to our homes and businesses. While power lines are safe when they are well-maintained, there are some safety hazards that you should be aware of and safety guidelines to follow.
Here are some electrical safety tips to follow when working with or around power lines:
Never climb trees or any tall structure near power lines.
Avoid passing under power lines during a storm or heavy winds.
If you see someone who is in contact with a power line, do not touch them; call 911 immediately.
Never touch a power line with your bare hands or with any conductive object.
Never touch anything that is touching a power line, such as a ladder, pole, or vehicle.
Keep a safe distance from power lines.
In case of wet areas, make sure there are no power lines on the ground. Do not touch them or even go near them.
Always wear proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) when working around power lines, such as the following:
Safety glasses
Face shields
Hard hats
Insulated boots
Rubber gloves with leather protectors
Insulating sleeves
Flame-resistant clothing
Promote Power Line Safety and Awareness with SafetyCulture
Why use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Efficiently manage and streamline health and safety processes across the organization, including incident management, safety audits and inspections, risk assessment, waste management, and more, using a comprehensive EHS software solution.
✓ Save time and reduce costs ✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents ✓ Boost productivity and efficiency ✓ Enhance communication and collaboration ✓ Discover improvement opportunities ✓ Make data-driven business decisions
FAQs about Power Line Safety
Related articles
Food Safety
Safety

Cold Holding: The Ultimate Guide
Learn about cold holding methods for food safety and how it reduces contamination risks across operations.
Food Safety
Safety

A Comprehensive Guide to Natasha’s Law Training
Learn about the process of Natasha’s Law training and how it helps food businesses efficiently meet allergen labeling requirements.
Construction Safety
Safety

A Complete Guide to Scaffolding Safety Training
Learn everything about scaffolding safety training, from topics to best practices, to uphold construction and maintenance safety.