What is HAZOP?
Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) is a systematic approach to determining potential problems that may be uncovered by reviewing the safety of designs and revisiting existing processes and operations in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil and gas, and nuclear industries.
What is the Purpose of HAZOP?
HAZOP, also known as HAZOP study or HAZOP analysis, is a Process Hazard Analysis (PHA) method recognized in OSHA’s Process Safety Management (PSM) standard. It is a form of risk management to identify, evaluate, and control hazards and risks in complex processes. It involves highly hazardous chemicals that can cause significant injuries to workers and extensive damage to property and company reputation if not properly processed and handled. It helps the organization address:
- potential hazards in business operation;
- past incidents that had likelihood for catastrophic consequences;
- human-controlled factors; and
- consequences of failure of applied control measures including the range of the possible health and safety risks.
Importance of HAZOP for Multiple Industries
HAZOP is a risk assessment approach that has become the de facto industry standard. It is a highly structured method of analyzing any possible deviation that can happen in a complex plant including chemical, pharmaceutical, oil and gas, nuclear, and mining industries. It is a crucial task that helps multiple industries to:
- proactively catch hazards and help formulate risk mitigation early on during the planning or design stage of projects;
- realize risks during modification of current processes and see how deviations may occur from the design intent; and
- investigate how the plant or systems deviate from business goals that create a risk to personnel and operation.
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
Explore nowThe Difference Between HAZOP, Risk Assessment, and HAZID
While risk assessments, HAZID, and HAZOP all aim to uncover safety risks in the workplace, there are differences.
| HAZOP | HAZOP is potentially more time-consuming because it involves the rigorous review of newly designed or already established complex processes in order to uncover potential risks and deviations from the original design intent. |
| HAZOP Template
You can use this HAZOP template when in the process of identifying risks in design, procedure, or operation. Using this HAZOP template to conduct a HAZOP analysis of your processes, you can:
|
|
| Risk Assessment | Risk assessment is the term used for the process of identifying risks, determining the severity of their impact, and coming up with controls to eliminate or mitigate the identified risks. |
| Risk Assessment Template
For identifying hazards and determining their risk rating, use this risk assessment template to record findings and provide some details on the most applicable control measures that can be used to mitigate or eliminate the risks discovered during risk assessments. |
|
| HAZID | Stands for Hazard Identification, HAZID is the process of proactively identifying hazards that can affect people, property, and the environment at the early stages of a project. |
| Hazard Identification Template
This hazard identification template is used to easily identify and document potential sources of injury or damage from performing a task in a specific work area. It helps to implement adequate corrective measures to ensure the health and safety of all employees. |
Study Process
As HAZOP undertakes the careful review of complex processes involved in the handling and processing of chemicals and materials that can potentially harm workers and stakeholders if not properly contained and handled, it is important to follow the following steps:

HAZOP Study Process
1. Build a HAZOP team
Create a multidisciplinary HAZOP team composed of a team leader and members who can collaborate and provide different perspectives based on their fields of expertise at realizing sources of risks and possible deviations from design. An example of HAZOP team members would be design engineers, those who are very familiar with operations, and safety professionals.
2. Identify processes, P&ID, and HAZOP nodes
When beginning a HAZOP study, it is important to identify the processes in operations, be familiar with the process/piping and instrumentation diagram (P&ID), and be aware of all the nodes.
P&ID are drawings or diagrams that provide the visual representation of interconnected processes, equipment, and controls in the physical plant. HAZOP nodes are sections in the entire process where changes happen and they need to be reviewed along with Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) so that parameters can be defined and deviations are identified.
Use this SDS template when identifying chemicals and other materials’ properties that can pose hazards to workers. Completed SDS in SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor) can be easily retrieved during HAZOP reviews.
3. Define the parameters, determine deviations, and select guide words
Define parameters or safe operating limits during the review of nodes so that deviations can be determined and guide words are selected.
Examples of common HAZOP guide words:
- No or not
- More
- Less
- High
- Low
With the use of guide words, workplace hazards can be clearly identified as they are the deviations that go beyond acceptable parameters or safe operating limits.
4. Identify controls and establish safety monitoring
With hazards identified, the corresponding hazard mitigation or elimination strategies should be applied to maintain the safety of the workplace. With ongoing processes and production, monitoring should also be established to ensure that safeguards are still effective and safety procedures are being followed.
Monitoring is only effective when it is actually conducted regularly. With SafetyCulture as mobile safety monitoring software, you can ensure that safety checks and audits are conducted regularly through scheduled inspections and automated notifications. Administrators can schedule and assign inspections and be made aware if inspections are indeed being done on time and on a regular basis. Register here for free.
Another safeguard is to automate safety monitoring through sensors. Sensors can trigger automated notifications for intended personnel whenever safety parameters are exceeded in real-time.
5. Communicate HAZOP results and improve processes
The result of the HAZOP analysis can be used to help elevate safety within the plant and improvements in safety practices and processes should be communicated to as appropriate to employees e.g. occupational safety, chemical safety and hygiene safety processes.
An effective approach to safety training or program will also help hasten the implementation of changes and reinforce safety across the board.
HAZOP is rigorous and can take a lot of time and resources to complete, but by following HAZOP steps and using tools that can help hasten the process without compromising the quality of the process and its result, HAZOP can be effectively conducted and completed sooner and the workplace can be made safer and more efficient.
Digitize the way you Work
Empower your team with SafetyCulture to perform checks, train staff, report issues, and automate tasks with our digital platform.
Get Started for Free4 Phases of Analysis
A HAZOP analysis is conducted by a suitably experienced multi-disciplinary team to thoroughly examine a planned or existing process. It helps identify and evaluate health hazards that may endanger people or hinder efficient operation of the business. A HAZOP analysis is executed in four phases, as follows:
1. Definition Phase
The definition phase typically begins with the preliminary selection of risk assessment team members. After building the team, they must clearly define their responsibilities and identify their objective and assessment scope including study boundaries, key interfaces, and assumptions.
2. Preparation Phase
During the preparation phase, the team should identify and locate supporting data and information to plan the study. They have to prepare the schedule, timelines, and template format for recording study outputs.
3. Examination Phase
The examination phase begins with the identification of all elements such as parts or steps of the system or process to be examined. The team has to classify deviation using guide words on each element and identify consequences and causes of problems. They have to establish protection, detection process, and supporting mechanisms.
4. Documentation and Follow-up Phase
The documentation and follow-up phase utilizes HAZOP templates to finalize the output reports. It involves the review of recorded examinations, follow-up on implemented action plans, and re-study of any system parts if necessary before signing off the documentation.
How SafetyCulture Can Help
Identifying hazards and deviations in plant environments is traditionally conducted using pen and paper. It is a cumbersome task that requires a lot of time and effort collating evidence into one document to hand over HAZOP reports. With SafetyCulture (iAuditor), a mobile inspection app, you can streamline the process of data gathering and reporting. SafetyCulture as a HAZOP Software can help the organization to:
- complete and document HAZOP study using smartphone/ tablet while on-site with your expert team without returning to the office;
- take unlimited photo evidence and annotations of design systems and deviations;
- schedule and notify teams on planned facility walkthrough;
- assign respective teams to collaborate on the spotted issues; and
- securely save all your reports in the cloud and easily access them online.
To get you started on risk control, check the below HAZOP example report.
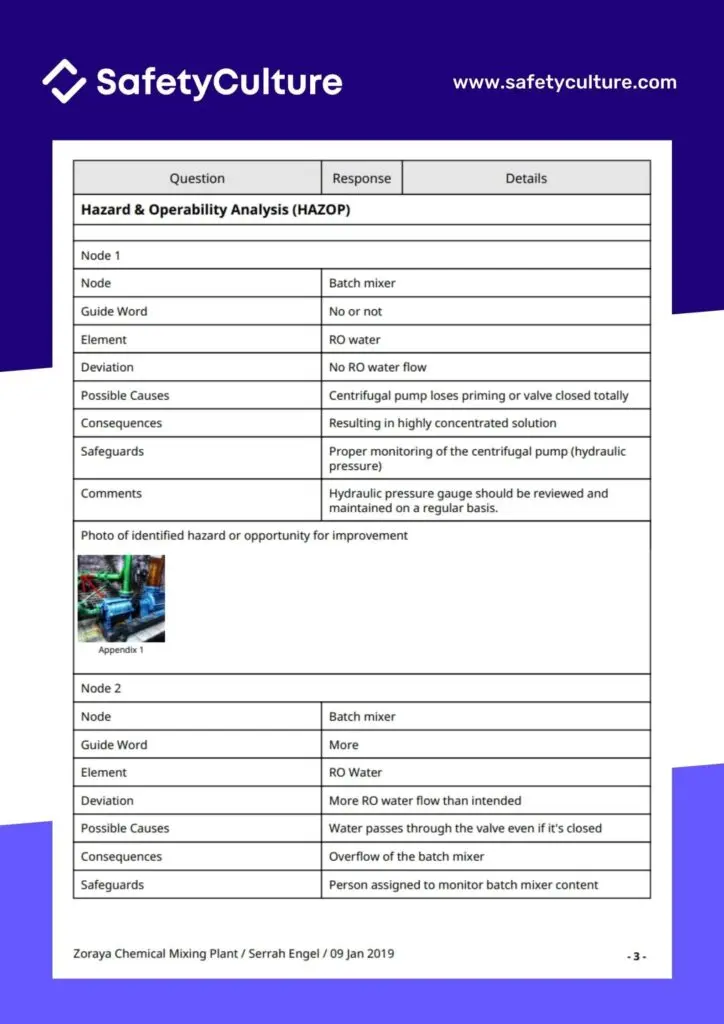
This HAZOP example is a result of using this HAZOP template that you can download for free through the SafetyCulture app or as PDF.




