Understanding and Meeting the Common GRC Standards
Explore the most common GRC standards, the typical implementation challenges, and the strategies for success.

Published 11 Feb 2025
Article by
7 min read
What are GRC Standards?
GRC standards refer to the frameworks, guidelines, and best practices that organizations adopt to streamline their Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) efforts. These standards are designed to ensure that businesses operate ethically, manage risks effectively, and adhere to legal, regulatory, and industry requirements.
Benefits
By integrating a unified GRC approach into their processes, businesses can better identify vulnerabilities, enhance corporate governance, and build a culture of accountability. Here are the benefits of following these standards:
Improved risk management – Implementing GRC standards equips organizations with robust frameworks to identify, assess, and mitigate risks effectively. These standards provide structured approaches for addressing potential vulnerabilities. By proactively managing risks, businesses can avoid costly disruptions , enhance decision-making , and maintain business continuity in a competitive landscape.
Enhanced compliance and legal assurance – Adhering to GRC standards ensures that organizations meet legal, regulatory, and industry-specific requirements. This minimizes the risk of penalties, lawsuits, and reputational damage caused by non-compliance. Beyond legal obligations, following these standards fosters a culture of accountability, ensuring that compliance is integrated into daily operations rather than treated as a one-off task.
Streamlined governance processes – GRC standards help organizations establish clear governance structures, improving accountability and transparency across all levels. They enable better alignment of corporate objectives with day-to-day operations, ensuring optimal resource management . By adopting these standards, businesses can create a strong foundation for ethical leadership and stakeholder trust.
Common GRC Standards
By understanding these standards and regulations, organizations can build a robust framework to ensure compliance, manage risks effectively, and enhance governance practices. Below are the common standards and regulations according to each aspect of GRC:
Governance
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) – The SOX Act is a US federal law designed to improve corporate governance and enhance transparency in financial reporting. It mandates strict internal controls , auditing standards, and executive accountability to protect shareholders and the public from corporate fraud.
Corporate Governance Code – These varying codes depending on the jurisdiction, such as the UK Corporate Governance Code, provide guidelines for board responsibilities, shareholder rights, and ethical business conduct. They aim to foster accountability and align corporate strategies with stakeholder interests.
OECD Principles of Corporate Governance – The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) offers international benchmarks for effective corporate governance. They focus on fairness, transparency, responsibility, and accountability in managing organizations.
Risk
Basel III – This is a global regulatory framework for banks, focusing on risk management and financial stability. It introduces capital adequacy requirements and stress testing to reduce risks in the banking sector.
ISO 31000 – Providing a comprehensive framework for risk identification, assessment, and mitigation, ISO 31000 applies to organizations of all sizes and industries, promoting a structured approach to risk management.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework – This framework provides guidelines for cybersecurity risk management and emphasizes risk assessment, incident response , and ongoing monitoring to safeguard critical infrastructure and sensitive data.
Compliance
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – This is a European Union regulation designed to protect personal data and privacy. It mandates organizations to implement strict data protection measures and obtain explicit consent for data processing. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) – This governs the protection of sensitive health information in the US It requires healthcare providers to implement security measures to ensure data confidentiality and integrity.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Regulations -This set of regulations aims to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. These require organizations, particularly in the financial sector, to conduct due diligence , report suspicious activities, and establish robust compliance programs.
Standardize Policies for Seamless Operations
Centralize policies and procedures to maintain consistency, reduce compliance risks, and ensure governance strategies align with organizational goals.
How to Follow the GRC Standards
By implementing GRC standards, organizations can establish a unified approach to decision-making, accountability, and resource allocation. They provide a roadmap for managing risks and compliance obligations, fostering trust among stakeholders, and improving overall operational resilience. Below are the steps in following the GRC standards:
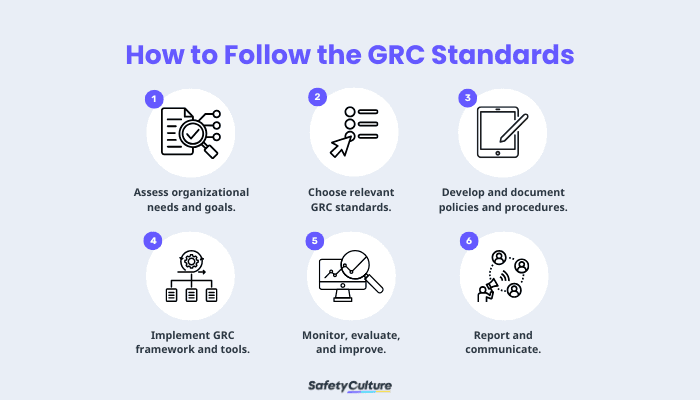
How to Follow the GRC Standards
1. Assess organizational needs and goals.
Evaluate existing processes, regulatory obligations, and risk exposure to determine where these GRC standards can add value.
Best Practices :
Conduct a comprehensive compliance gap analysis to identify current GRC strengths and weaknesses.
Involve stakeholders across departments to ensure a holistic understanding of organizational needs.
Make sure your GRC goals are in sync with the broader business objectives so they stay relevant and deliver real value.
2. Choose relevant GRC standards.
Select the most appropriate GRC standards based on your industry, regulatory landscape, and risk profile.
Best Practices :
Research industry benchmarks to identify the standards commonly adopted by competitors.
Prioritize standards that integrate seamlessly with your organization’s existing processes.
Consult with legal and compliance experts to ensure chosen standards meet all regulatory requirements.
3. Develop and document policies and procedures.
Create clear, actionable policies and procedures aligning with the chosen GRC standards. These should outline roles, responsibilities, and workflows to embed GRC practices into daily operations.
Best Practices :
Use a policy management tool to centralize and streamline documentation.
Ensure policies are written in simple, accessible language for better adoption across teams.
Regularly review and update policies to align with evolving business needs, industry standards, and regulatory requirements.
4. Implement GRC framework and tools.
Deploy a GRC framework and supporting tools to facilitate monitoring, reporting, and decision-making. These tools help integrate GRC activities into a cohesive system.
Best Practices :
Invest in a robust GRC platform to automate processes and reduce manual errors.
Start with a pilot implementation to identify potential challenges and refine processes before a full rollout.
Provide training for employees to ensure proper utilization of tools and adherence to the framework.
5. Monitor, evaluate, and improve.
Keep a close eye on GRC activities to track their impact and spot opportunities for improvement. Regular GRC audits, assessments, and feedback loops are essential for maintaining alignment with these standards.
Best Practices :
Schedule periodic internal audits to ensure compliance with GRC standards.
Leverage dashboards and analytics tools to track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) .
Promote a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging feedback from employees and stakeholders.
6. Report and communicate.
Regularly report GRC performance to key stakeholders, including management, board members, and external auditors. Open and honest communication fosters trust and demonstrates accountability.
Best Practices :
Use standardized reporting templates to ensure consistency and clarity.
Highlight progress, successes, and areas for improvement in reports.
Keep an open dialogue with regulators to address any concerns early and proactively.
Overcoming Challenges
While following the GRC standards greatly benefits organizations, businesses may face a few challenges. Addressing these requires proactive planning, continuous improvement, and leveraging the right tools and expertise. By overcoming these barriers, organizations can achieve the full advantages of following GRC standards.
Resource constraints – Limited budgets, staffing, or technological resources can hinder the effective adoption of GRC standards, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. Prioritizing adherence to high-impact standards, leveraging scalable GRC software, and outsourcing certain business functions are some ways to address such constraints.
Resistance to change – Employees and management may resist adopting new policies and procedures due to perceived complexity or disruption to existing workflows. To help deal with this, foster a culture of change by clearly communicating the benefits of following GRC standards (e.g., operational efficiency ) and engage employees during the planning and implementation stages to gain their support.
Keeping up with regulatory changes – Regulations evolve frequently , making it challenging for organizations to comply with the latest requirements. Falling behind can result in penalties or reputational damage. Investing in GRC tools that include automated alerts and updates for relevant laws and standards is a practical strategy to consider.
Data overload and poor reporting – Managing and analyzing large volumes of data related to GRC can be overwhelming, leading to poor decision-making and missed insights. Hence, it’s best to simplify data management and focus on tracking KPIs relevant to your organization’s objectives using advanced GRC software.
Consistently Meet the Highest Standards with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Promote a culture of accountability and transparency within your organization where every member takes ownership of their actions toward meeting GRC standards. Align governance practices, enhance operational risk management protocols, and ensure compliance with legal requirements and internal policies by streamlining and standardizing workflows through a unified platform.
✓ Save time and reduce costs ✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents ✓ Boost productivity and efficiency ✓ Enhance communication and collaboration ✓ Discover improvement opportunities ✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Related articles
Quality Management
Quality

Critical to Quality (CTQ): Guide to Customer-Driven Excellence
Learn the basics of Critical to Quality, its benefits, parameters, and specific applications in this comprehensive guide.
Quality
Quality Management

A Guide to Understanding Management Reviews
Learn about what a management review is, its importance, its key inputs and outputs, its process, and some FAQs.
Quality
Quality Management

5 Core Tools of Quality: The Ultimate Guide
Learn how the 5 core tools of quality work together to reduce risk, improve consistency, and drive continuous operational improvement.