A Guide to Enterprise Management
Streamline enterprise operations through proper enterprise management.

Published 11 Jun 2025
Article by
6 min read
What is Enterprise Management?
Enterprise management refers to the processes, strategies, and equipment involved in ensuring an enterprise is operating as intended daily. It covers how operations are controlled, how Information Technology (IT) processes are carried out, and how an enterprise’s other tasks align with organizational values and goals.
What is an Enterprise?
In business, an enterprise is any entity that can conduct transactions on its own behalf within itself and with others. It is often a large organization that makes up an enterprise, comprised of multiple levels of management working together to achieve a common goal. Any business can be an enterprise, such as corporations, non-profit organizations, and others.
Enterprises are often categorized by the number of employees they have. According to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), an international forum of different governments with market-based economies, an enterprise with more than 250 employees would be called a Large Enterprise. Meanwhile, enterprises with less than 250 employees will then be sorted into the Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) category. They can be further divided into the following:
Micro enterprises (less than 10 employees)
Small enterprises (10 to 49 employees)
Medium-sized enterprises (50 to 249 employees)
Difference Between Enterprise and General Management
Enterprise management and general management are related concepts, but they have some key differences. While general management focuses on specific functional areas, enterprise management takes a more holistic and strategic perspective, overseeing the entire organization and its long-term success. Here are some ways in which they differ:
Scope
In a business, general management typically refers to overseeing a specific department or function within an organization, such as finance, marketing, or operations. On the other hand, enterprise management has a broader scope and encompasses the management of the entire organization or enterprise as a whole.
Strategic Focus
General management tasks and responsibilities tend to have a more operational and tactical focus. It deals with immediate issues and operational efficiency within a specific domain.
Enterprise management, on the other hand, has a strategic focus, specifically on setting long-term goals, formulating organizational strategies, and making decisions that impact the entire enterprise.
Decision-making
General managers typically have decision-making authority within their specific area of responsibility. They make decisions and implement strategies to achieve the objectives of their department.
In contrast, enterprise managers have broader decision-making authority that cuts across different departments and functions. They make decisions that impact the entire organization, such as resource allocation, investment decisions, and organizational structure.
Risk and Complexity
Enterprise management deals with higher levels of risk and complexity compared to general management. When managing an enterprise, you need to consider the interdependencies and interactions between various functions and departments.
Common Areas and Applications of Enterprise Management
Enterprise management refers to all tasks, tools, strategies, and processes needed to ensure your enterprise is operating as planned. It covers many different areas such as the following:
Data management
Employee health and safety
Finances
Since it covers different aspects of a business’ operations, enterprise management can also be applied in more than one way. The term “management” in business often refers to how business owners and managers carry out specific tasks to meet company goals. For enterprises, some ways it is applied include the following:
Assessing current plans in place for smooth operations regularly
Analyzing and addressing risks in and to the enterprise
Creating and managing a dedicated system within the general enterprise management plan for:
Assets
Fleets
Finances
Documents
Content creation
Designating specific people and teams for managing customers, product and service development, human resources, and communication channels with stakeholders or other enterprises
Establishing deadlines, plans, and budgets for every function of the enterprise
Scale Your Enterprise Operations with Customizable Solutions
✓ Scale ✓ Data ✓ Security ✓ Integration ✓ Teams
What are the 5 Components of Enterprise Management?
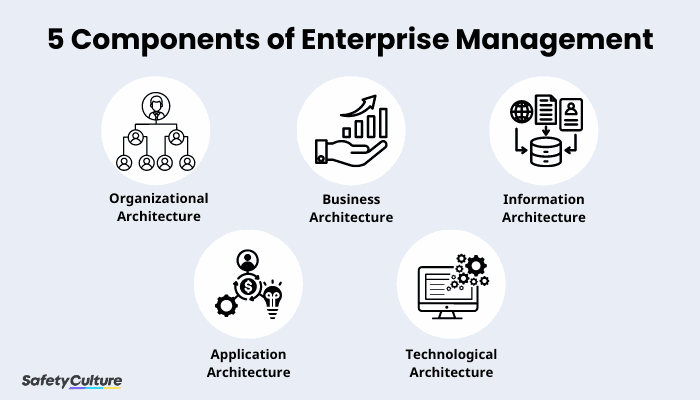
5 Components of Enterprise Management | SafetyCulture
Every enterprise has its own enterprise architecture framework or plan that works for them and their industry. Creating, implementing, and analyzing enterprise architecture involves regularly studying how your enterprise operates on a daily basis, its infrastructure, and the industry you are part of.
Enterprise management consists of the following elements of enterprise architecture:
Organizational Architecture: Managing an enterprise by focusing on its operations from employee positions, tasks, and company goals
Business Architecture: Managing an enterprise through its strategies, business goals, and other proceedings
Information Architecture: Managing an enterprise’s data and the flow and usage of information within it
Application Architecture: Managing how programs should be created, implemented, and maintained within the enterprise
Technological Architecture: Managing the enterprise’s IT infrastructure, hardware, software, and other technological equipment so that goals are achieved better
In some cases, enterprise management plans and systems will only focus on one enterprise architecture type, depending on their needs. However, most enterprises would prefer to consider all architectures for a more holistic approach, as each enterprise architecture framework type affects one another.
Managing an Enterprise: Best Practices
Effective enterprise management is the cornerstone of success in today’s dynamic business landscape. As organizations navigate through the complexities of the global market, the significance of strategic and efficient management cannot be overstated.
Leadership
In addition to proper enterprise architecture, there are other things to consider in regard to enterprise management. Strategies, plans, and frameworks are essential to managing an enterprise in the long run, as well as for ensuring employee and organizational safety and growth. This includes having capable leaders, an efficient system of delegating responsibilities, and a smart and effective marketing plan for the business.
Employee Welfare
Employee satisfaction and productivity will affect the enterprise as a whole, so their needs, safety, and well-being must also be considered. There must be a conducive environment for them to work and communicate in, as well as the right opportunities to be empowered. Corporate governance should also be considered.
Customer Relationships
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is an important factor to consider when managing an enterprise. This involves having a good understanding of their lives and concerns, as well as promoting and retaining an amicable relationship with them. You can do this with regular check-ups with your customers and market studies, then collating all data and plans in a place that is easily accessible for conducting planning meetings.
Resource Allocation and Planning
Another essential to managing an enterprise includes conducting regular sessions for Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), which involves integrating different aspects of a business, such as accounting, manufacturing, and sales, into the enterprise’s list of priorities.
Using the right digital tools can also be greatly helpful when creating ways to ensure an effective enterprise management system. There are now digital solutions that can help to streamline your CRM plans, ERP systems, or both. With one platform, you can improve operational efficiency, increase productivity, and ensure a better workplace with less time and effort, allocating them to more important tasks.
Effectively Manage your Enterprise Operations and Processes with SafetyCulture
Why use SafetyCulture?
One proven digital solution you can utilize for enterprise management is SafetyCulture (formerly iAuditor). Used by many enterprises around the world, SafetyCulture can help streamline your operations, empower workers, and improve efficiency within your organization from any device.
SafetyCulture offers checklists to help you and your enterprise conduct safety inspections, ensure compliance with standards and regulations, report problems within the organization, create and collate plans, and manage risks, all in one place. This platform allows you to view your enterprise from all aspects to easily address concerns and simplify complex processes.
With SafetyCulture, you can work anytime and anywhere, allowing you and your enterprise to collaborate regardless of size and location. From the field, office, or anywhere else in the world, you can do the following:
Work from anywhere with a mobile, tablet, or laptop
Identify risks, problems, and concerns directly from the frontline teams across multiple sites through checklists and forms
Unlock opportunities for business growth and efficiency using insights from the Analytics dashboard
Communicate company-wide updates, best practices, and other information with your workers all at once with Heads Up
Ensure the privacy of critical data and files by setting the right access controls and permissions fit for the right worker level
Create a seamless work experience by customizing workflows and integrating other work software into the SafetyCulture platform
Gain visibility over the usage, maintenance, and activities of enterprise equipment and assets
Enhance employee productivity and competency for their jobs by providing training on a team and an enterprise level and monitor their progress
Proactively protect your business and workers from internal and external risks with SafetyCulture Care
Ensure that all work gets done at the right time by the right people by scheduling inspections and meetings with your staff or stakeholders in the platform
Keep track of raised issues and corrective actions in one place
Keep lone workers safe with SHEQSY by SafetyCulture
FAQs about Enterprise Management
In this article
- What is Enterprise Management?
- What is an Enterprise?
- Difference Between Enterprise and General Management
- Common Areas and Applications of Enterprise Management
- What are the 5 Components of Enterprise Management?
- Managing an Enterprise: Best Practices
- Effectively Manage your Enterprise Operations and Processes with SafetyCulture
- FAQs about Enterprise Management
Related articles
Operations
Human Resources

The Role of HR in Workplace Health and Safety Management
Learn what an HR health and safety program covers, its key responsibilities, and the best practices for creating safer working environments.
Operations
Performance Evaluation

The RICE Framework: A Strategic Approach to Prioritization
Learn how the RICE framework and prioritization method helps put focus on high-ROI tasks to streamline workflows.
Operations
Business Processes

Implementing Value Management for Better Business Outcomes
Explore value management, its principles, benefits, and helpful strategies to drive peak performance and cost-efficiency.