Autonomous Maintenance: Benefits, Steps, and Tools
Learn about autonomous maintenance, its seven steps, and why it is beneficial in manufacturing and other industries

Published 26 Nov 2025
Article by
8 min read
What is Autonomous Maintenance?
Autonomous maintenance is a manufacturing concept that empowers machine operators to take responsibility for the routine maintenance of the equipment they use. It aims to reduce dependency on specialized maintenance technicians for routine upkeep and helps in identifying and preventing potential issues before they escalate.
A preventive maintenance strategy and one of the 8 pillars of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), autonomous maintenance equips machine operators with the right training so they can independently identify quality issues and be able to take immediate action to correct them.
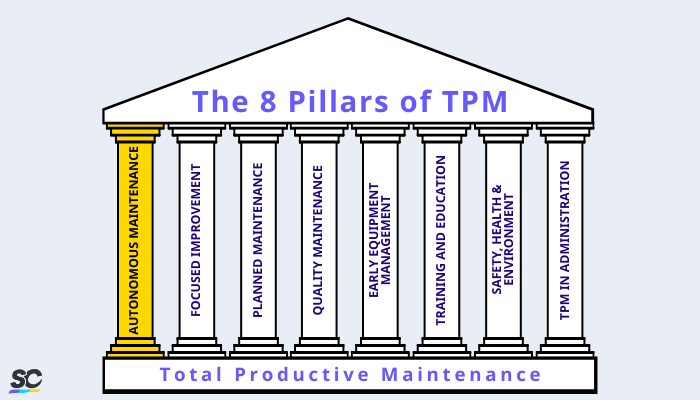
The 8 Pillars of TPM
What are the Benefits of Performing Autonomous Maintenance?
As one of the key TPM pillars, autonomous maintenance is a recognized strategy for preventive and proactive maintenance. It helps prevent costly equipment breakdowns and reduces unplanned downtime or interruptions to operations. Here is a breakdown of how performing autonomous maintenance can benefit any industry:
Prevents Equipment Deterioration
Autonomous maintenance ensures that routine preventive maintenance tasks such as cleaning, lubricating, and oiling are consistently performed on equipment that need them. These simple but crucial tasks help prolong the optimal performance of equipment and company assets.
Autonomous maintenance also helps dedicated maintenance personnel to focus their full attention on other equipment and more pressing maintenance issues in the workplace.
Instills a Sense of Ownership and Responsibility
The operator who uses the machine or equipment day in and day out would have an intimate knowledge of how the machine actually works and if it is not working at its best. That same operator would likely know what’s causing equipment issues and what to do to keep it running smoothly.
Promotes a Culture of Quality and Safety
When operators diligently maintain equipment and other assets, those assets operate at their best. This guarantees that the quality of output meets expectations and that the safety of operating and working around the machines is maintained. Over time, this also helps build a culture of safety for future employees and operators.
Achieve operational excellence
Cultivate a culture of excellence with our digital solutions that enhance efficiency, agility, and continuous improvement across all operations.
The Seven Steps of Autonomous Maintenance
Here are the seven steps of autonomous maintenance and how they help teams take ownership, improve reliability, and reduce downtime:
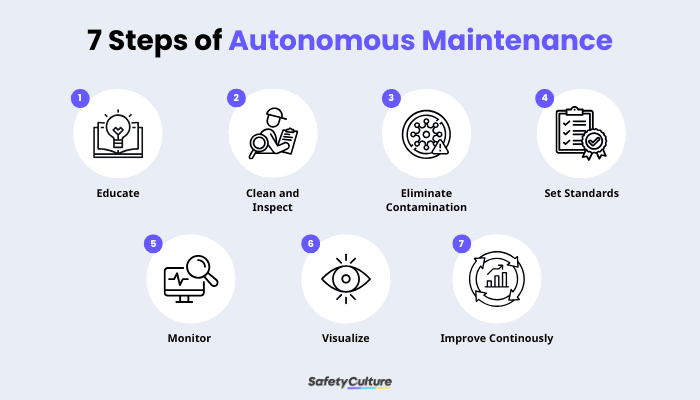
Seven Steps of Autonomous Maintenance
Step 1: Increase Operator Knowledge
The first step in effectively implementing autonomous maintenance is to train operators on how to operate and maintain the equipment that they’re assigned to use. Equip them with knowledge on how the parts of the equipment come together so that they know which parts need periodic maintenance and which parts need to be looked after when it comes to cleaning, lubrication, replacement, and testing.
It’s best to utilize mobile-friendly training tools to increase operator knowledge, as they supplement real-world applications. These also help them understand practical information the fastest and most effective way possible.
Step 2: Initial Cleaning and Inspection
Once operators know the ins and outs of the equipment they are using, they should be able to inspect the equipment and spot any need for cleaning and maintenance. They need to be able to identify any part of the equipment that needs removal of dust and dirt, nuts and bolts that need tightening, oiling and lubrication, and wear and tear that needs fixing.
Step 3: Eliminate Causes of Contamination
Once the equipment is cleaned and back to its optimal working condition, the operator needs to know how to keep it that way. One way to keep the equipment in top condition is to eliminate causes of contamination. Implementing good housekeeping practices and maintaining cleanliness at the workstation helps prevent contamination and keep the working environment safe.
Depending on the type of equipment, cleaning equipment to eliminate contamination may require the use of machine guarding and lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures to keep workers safe.
Step 4: Set Standards for Lubrication and Inspection
Equipment should be cleaned, lubricated, and maintained according to manufacturer specifications to keep it in top condition and performing at its best. To set standards and reinforce those standards, tools and processes should be implemented on what maintenance tasks to do, how to do them, and how often they should be done.
Use digital checklist tools that can help guide operators on what to perform, how to perform those maintenance tasks, as well as notify them to remind them when a task is due.
Step 5: Conduct Inspection and Monitoring
To reinforce good practices like autonomous maintenance, it is recommended to conduct inspection and monitoring. Operators themselves can inspect their equipment and provide information in the form of inspection reports with photos on the current condition of the equipment and maintenance tasks fulfilled.
Data collected through these inspections can be shared and monitored to ensure that all equipment is maintained by operators and in good working condition.
Step 6: Standardize Visual Maintenance Management
Make it easier for operators to complete maintenance tasks by using visual cues like color-coded tags, visual aids, flagged items in your Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS), and simple signs or posters that outline key steps when working with equipment. These reminders help everyone stay consistent and reduce the chance of missed tasks.
Step 7: Establish Continuous Improvement
One of the most crucial pillars of TPM is long-term improvement. As processes, equipment, and operators change, it’s important to keep continuous improvement at the core of autonomous maintenance. Using a CMMS to collect and manage this data gives you useful insights into equipment performance and maintenance strategies.
Any training feedback gathered from operators in step 1, as well as inspection and monitoring data collected through their reports in step 5 can be used to continuously improve procedures for equipment maintenance.
How It Improves Overall Equipment Effectiveness
OEE or Overall Equipment Effectiveness is a manufacturing best practice that enables businesses to calculate how much of an equipment’s potential is being used in accordance with the calculated percentage. This method helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement in maintaining and maximizing equipment to its full potential. The metric used in calculating OEE is based on the factors of availability, performance, and quality.
Here are several points on how to improve OEE:
Calculate effectiveness accurately – Follow guidelines and implement calculation strategies on how to best compute the OEE score. Note that an OEE score of 40% is generally considered low, 60% as the average score, while an 85% score is considered high or world-class.
Collect and report production data – Streamline data collection by digitizing the methods performed in gathering OEE information. Automating data collection and utilizing new technologies provides more accurate details for OEE reports , allowing businesses to gain a timely overview of each equipment or situation to avoid errors caused by manual processes.
Implement regular assessments – Relevant people should consistently strategize, collaborate, and discuss best practices to apply in improving OEE. This makes sure that everyone is on the same page and hastens the response time needed to address an equipment issue.
Minimize Six Big Losses – If businesses cannot completely eliminate the reasons for the Six Big Losses, they should at least find ways to minimize their negative impact. The Six Big Losses are composed of unplanned downtime, planned downtime, small stops, slow cycles, production rejects, and start-up rejects.
Perform Root Cause Analysis – Doing a Root Cause Analysis (RCA) helps to get to the bottom of the encountered issues and understand them in an in-depth manner. Performing RCA also gives the opportunity to identify which solutions to recommend and which preventive measures to implement.
Create your own Root Cause Analysis template
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
How Technology can Help in Performing Autonomous Maintenance?
One of the key steps in autonomous maintenance is inspection and monitoring. Modern manufacturing equipment has it easier than ever thanks to AI-powered systems, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, machine learning, telematics, and autonomous industrial vehicles—all helping teams perform maintenance more efficiently.
Another simple way to perform autonomous maintenance right now, is with the use of digital solutions such as SafetyCulture can make this easier by turning your mobile device into a powerful inspection and monitoring platform. With this tool, teams can capture data in real time, track whether maintenance tasks are complete or flagged, and schedule preventive maintenance.
Technology like these helps streamline processes, reinforce best practices, and drive continuous improvement for more effective autonomous maintenance.
Power Autonomous Maintenance with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, enhance resource utilization, and build an agile and scalable infrastructure with SafetyCulture. Strive for operational excellence to boost competitive advantage, foster sustainable growth, and deliver long-term value.
Save time and reduce costs
Stay on top of risks and incidents
Boost productivity and efficiency
Enhance communication and collaboration
Discover improvement opportunities
Make data-driven business decisions
FAQs About Autonomous Maintenance
Article by
SafetyCulture Content Team
SafetyCulture Content Contributor, SafetyCulture
View author profileIn this article
- What is Autonomous Maintenance?
- What are the Benefits of Performing Autonomous Maintenance?
- The Seven Steps of Autonomous Maintenance
- How It Improves Overall Equipment Effectiveness
- How Technology can Help in Performing Autonomous Maintenance?
- Power Autonomous Maintenance with SafetyCulture
- FAQs About Autonomous Maintenance
Related articles
Facility Management
Maintenance

A Guide to Retail Facility Management
Improve store performance with effective retail facility management, and learn its key components, challenges, and top solutions for success.
Equipment Maintenance
Maintenance

Autonomous Vehicle Maintenance for Safety and Asset Performance
Discover how autonomous vehicle maintenance supports safety, reliability, and asset performance through preventative workflows.
Maintenance
Equipment Maintenance

Understanding Mechanical Integrity and Its Importance
Understand the meaning of mechanical integrity, its fundamental components, and how to develop a mechanical integrity plan for the team.