Published 4 Jul 2025
Article by
5 min read
What is a Manufacturing Process Audit Checklist?
A manufacturing process audit checklist is used by manufacturing plant managers and compliance officers to help ensure that legal and organizational standards are being met by the operation. A typical manufacturing process audit would include a walkthrough of the site to check if workers are following set protocols and best practices designed to ensure consistent, high-quality output.
What is a Manufacturing Process?
A manufacturing process is a set of principles, protocols, and steps set and followed by manufacturing operations when using raw materials to produce their final products. Manufacturing processes vary, depending mainly on the nature and size of the operation, as well as organizational preference.
Importance
A manufacturing process audit checklist is important for ensuring quality, efficiency, and compliance in manufacturing operations. It serves as a systematic tool to evaluate various production processes, identify areas for improvement, and maintain adherence to industry regulations.
Common Manufacturing Mistakes and How to Prevent Them
A manufacturing plant has many interdependent moving parts that must function efficiently. A mistake, an inefficient process, or a malfunction, even in just one area, will negatively affect the entire production line. Here are some of the most common manufacturing mistakes and some tips on how to prevent them:
Not having a regular inspection schedule
Management should regularly inspect the manufacturing process and floor to ensure that everything is being run as designed and agreed upon. This is also done to ensure that the necessary equipment, facilities, PPE’s, and everything else workers need to do their jobs properly are available. An effective inspection app can assist plant managers and compliance officers in assessing performance, facilities, and task assignments.
Ineffective documentation of data, defects, malfunctions, and non-compliance
Data-gathering can easily be overlooked if, on the surface, your operation is meeting the expected output targets. Good data documentation, however, is essential to knowing the areas where the operation is succeeding and where improvements can be made. Incidents such as identified defects, malfunctions, and non-compliance must be reported immediately and properly documented to contain the problem as long-term solutions are formulated and eventually implemented.
Picking the wrong contract manufacturing organization (CMO) when outsourcing
Complete or partial outsourcing of manufacturing is a popular way to cut costs, and a variety of high-earning industries, including technology and pharmaceuticals, have long enjoyed its benefits. To successfully outsource, however, requires top management to study, compare, and audit different CMOs to assess if their facilities, capabilities, and experience are a good fit for your product.
Lack of accountability
Clear accountability improves the overall manufacturing process and manufacturing system because workers are compelled to be more meticulous when non-compliance can be traced back to them. Ensure that there are official personnel accountable for certain equipment, stages of production, and outputs. By having a point of contact for different manufacturing aspects, information is shared faster and communication becomes easier. A fair system of accountability lowers the chances of human error and neglect that negatively affect production.
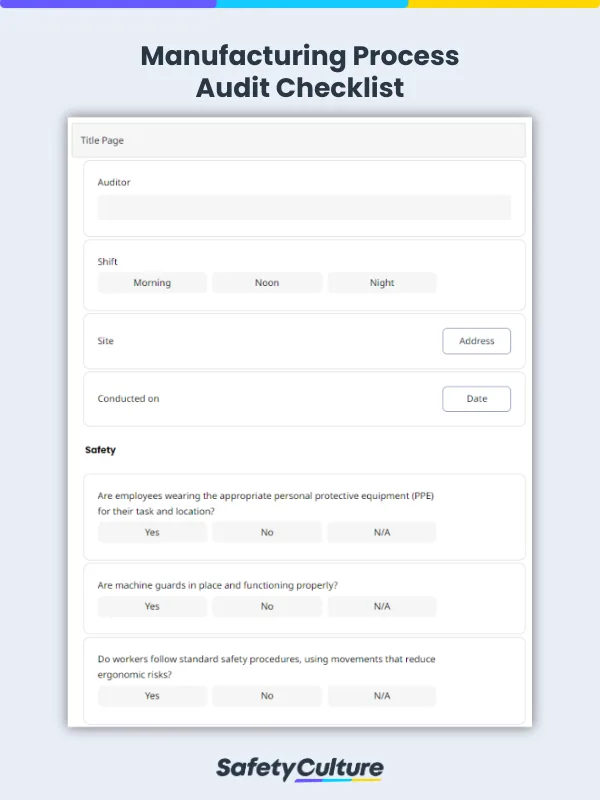
What to Include in a Manufacturing Process Audit Checklist
The key elements to include in a manufacturing process audit checklist vary depending on the task at hand. Here’s an overview of the typical items to be included:
Safety – Make sure that all employees are wearing necessary PPEs , and that the machines and other equipment are safe to use.
Materials and tools – Confirm that staff are utilizing the appropriate tools for each task.
Motions – Consider if the overall movement in the process is efficient enough or it can be improved.
Workstation – Evaluate whether the placement of equipment and materials supports productivity and ergonomics. Also, determine if the workstation is optimized for the specific task being performed.
Reporting process – Verify that there is a clear and accessible escalation procedure for reporting defects, issues, or safety concerns.
Documentation process – Ensure that all employees follow the same format and standard when it comes to tracking and understanding the manufacturing processes.
How to Conduct a Manufacturing Process Audit with a Checklist
Conducting a manufacturing process audit with a checklist is an essential practice for ensuring quality, efficiency, and compliance in manufacturing operations. Here are the steps on conducting an audit with a checklist :
Preparation – Define the audit purpose and scope of the audit. Focus on specific objectives such as improving operations or addressing quality issues
Process Documentation and Control – Verify availability process guidelines. These may include resources such as SOPs, flowcharts, and work instructions
Equipment and Facilities – Check safety features and overall cleanliness of production areas. Ensure that everyone is supplied and uses their PPE.
Quality Control and Assurance – Conduct quality checks at key production stages and review inspection records for non-conforming product handling
Manufacturing Process Audit PDF Report
Once the audit is completed, you can export the results and assign action points when needed. Here’s what a completed report may look like :
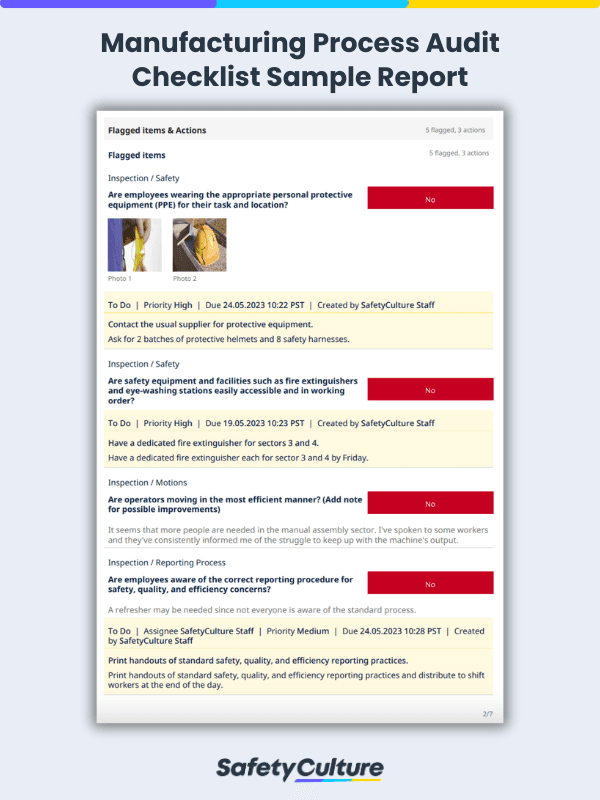
Manufacturing Process Audit Checklist Sample Report | SafetyCulture