Published 5 Aug 2024
Article by
5 min read
What is a GlobalG.A.P. Checklist?
A GlobalG.A.P. checklist is a tool used to assess if farms and crop production units follow Good Agricultural Practices (GAP). It covers food safety, environmental, social, and other benchmarks in line with the GlobalG.A.P. standards to ensure that agricultural processes are safe, socially responsible, and sustainable. The guidelines in this checklist are flexible enough to be adjusted to the size and needs of the farm’s operations.
Benefits
Using a GlobalG.A.P. checklist for internal audits offers many advantages to food producers and farm operators.
For one, it allows them to run operational checks more efficiently and effectively. Instead of manually recalling the standards’ requirements, they can simply refer to the checklist for the things they need to look into. Having a readily available list of items to check helps speed up the audit process while reducing the chances of errors committed along the way.
Moreover, a GlobalG.A.P. checklist is a useful tool for ensuring consistency in carrying out good agricultural practices. Checklists help streamline the internal audit process so that auditors can focus on assessing current practices, spotting nonconformities, and developing ways to address them. In turn, this systematic approach can help:
Improve the quality of agricultural products
Reduce the risk of food safety issues
Sustain operations without compromising the environment
Protect workers and local communities during operations
Earn and maintain a positive reputation among consumers
Types of GlobalG.A.P. Certification Programs
GlobalG.A.P. certifies all types of agricultural producers through the following standards:
Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA)
The GlobalG.A.P. IFA standard is a comprehensive framework for responsible farming practices. It incorporates several farm assurance standards in a single system to streamline operations and simplify compliance for food producers. This global standard covers 4 areas of agricultural practice: livestock, fresh produce, aquaculture, and ornamentals.
Crops for Processing (CfP)
This international standard is designed to ensure that crops meant for food processing are safe for use. It encompasses the primary ingredients for frozen produce, pre-cooked meals, animal feeds, and other processed food items. While CfP is a non-accredited standard, producers can still use it to identify, assess, and mitigate food safety risks associated with these crops.
Harmonized Produce Safety Standard (HPSS)
HPSS is a globally-recognized food safety standard geared toward producers who operate or market their products in the United States. It establishes safeguards for the production of fruits, vegetables, and other crops entering the US market.
Compound Feed Manufacturing (CFM)
The CFM standard assesses the production process of compound feeds for animals covered in IFA’s livestock and aquaculture categories. It consists of social and environmental metrics to verify if feeds are manufactured sustainably. Examples of these benchmarks include responsibly sourcing raw ingredients and keeping workers safe during operations.
Livestock Transport
This GlobalG.A.P. standard integrates animal health and welfare when transporting livestock to and from each part of the supply chain. It anchors itself on the principles and criteria stipulated in the IFA’s Livestock Dispatch section (Section 9). However, the Livestock Transport standard only applies to road vehicle operators and excludes travel by air or sea.
Food manufacturers seeking sustainable alternatives in their supply chain operations can consider looking into these certified haulers for their road transport needs.
Chain of Custody (CoC)
Lastly, the GlobalGAP CoC standard is one of the hallmarks of a sustainable food supply chain —from farms to retail stores. Having this label certifies that the food product is sourced in line with the GlobalG.A.P. standards. Not only does it ensure food safety across the supply network, but it also protects consumers against food fraud.
What to Include in a GlobalG.A.P. Checklist
According to the latest version of the GlobalG.A.P. standard, here are the essential components that your checklist should cover:
Food safety and hygiene policy
Environmental sustainability – biodiversity, water and waste management , energy efficiency, greenhouse gas emissions
Social responsibility – animal and worker health, safety, and welfare
Production processes – equipment and devices, outsourced activities, laboratory testing, stock management
Traceability – ownership, suppliers , food traceability systems , and more
Quality Management System (QMS) – food defense , food fraud, internal documentation, continuous improvement plan, and so forth
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points ( HACCP )
Crop and pest management
Other legal obligations
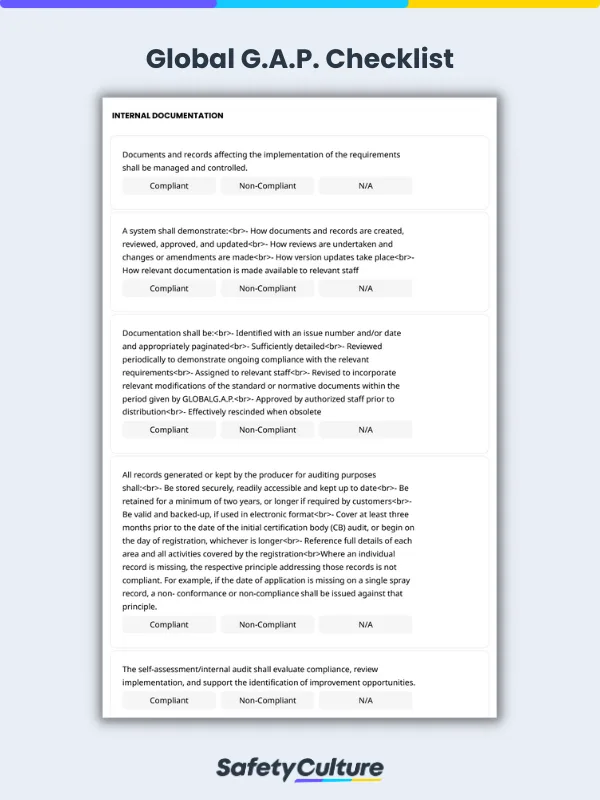
Here’s an example of a completed GlobalG.A.P. checklist that’s filled out using a digital tool:

Global GAP Checklist Sample PDF Report | SafetyCulture
How to Implement This Checklist
After creating a GlobalG.A.P. checklist, the next step is to roll it out across the organization. But before doing so, here’s a helpful guide on using the checklist for your farm operations:
Understand the GlobalG.A.P. standard – Start by familiarizing yourself with the standard and its requirements before carrying things out.
Perform a gap analysis – This process helps you identify non-compliance in your existing farm processes, assess risks, and address areas that require more work.
Develop an action plan – Based on the results of the gap analysis, the next step is to determine corrective actions to address non-compliant items and align operations with GlobalG.A.P. standards.
Implement the plan – Effectively carrying out the plan for GlobalG.A.P. compliance calls for everyone’s active participation. Make sure to involve all relevant stakeholders in the supply chain , including employees, suppliers , and contractors.
Conduct internal audits – It’s important to regularly check if your farm operations follow the GlobalG.A.P. compliance plan consistently and address any lapses before applying for certification.
Prepare the requirements – Before the external audit happens, be sure to have all necessary documents and other prerequisites ready for the auditors to review.
Maintain compliance with the standard – Lastly, continuous compliance with GlobalG.A.P. standards involves regularly reviewing and updating your farm’s procedures, training employees and stakeholders, and monitoring its performance.
Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.