Published 22 Jan 2025
Article by
5 min read
What is a GDP Audit Checklist?
A GDP audit checklist is a structured and comprehensive tool used by organizations to assess and ensure adherence to established standards and guidelines for the proper distribution of products, such as medicines. This tool is designed to help inspectors and auditors systematically evaluate various aspects of distribution processes, facilities, and practices to guarantee the quality, safety, and integrity of products as they move through the supply chain.
Why Use a GDP Audit Checklist
GDP acts as a safeguard for product quality and safety during distribution. It ensures that products maintain their intended condition, reducing risks of contamination, degradation, or damage. As a result, companies can uphold product integrity, reduce recalls, and promote transparency in distribution processes, ultimately contributing to consumer safety, brand reputation, and regulatory adherence.
To help them verify their GDP compliance, audits and inspections must be conducted using GDP audit checklists. These serve as essential tools for both internal evaluations and external audits to assist organizations in ensuring safe and quality product handling, storage, and transportation.
Compliance Assurance – provides a structured framework to ensure compliance with legal standards and guidelines governing the distribution of products
Process Optimization – serves as a tool for identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks , or areas for enhancement in their distribution practices, leading to increased operational efficiency
Documentation and Accountability – provides documented evidence of compliance efforts
Cross-Functional Alignment – encourages collaboration among various departments involved in the distribution process
Preparedness for Audits – simplifies the audit process by ensuring that all necessary criteria are met and documented, leading to smoother audits and reduced stress
Key Components of a GDP Audit Checklist
The sections, items, and areas covered in a GDP checklist span various aspects of distribution operations and practices. Here are the most essential elements to include to make it comprehensive:
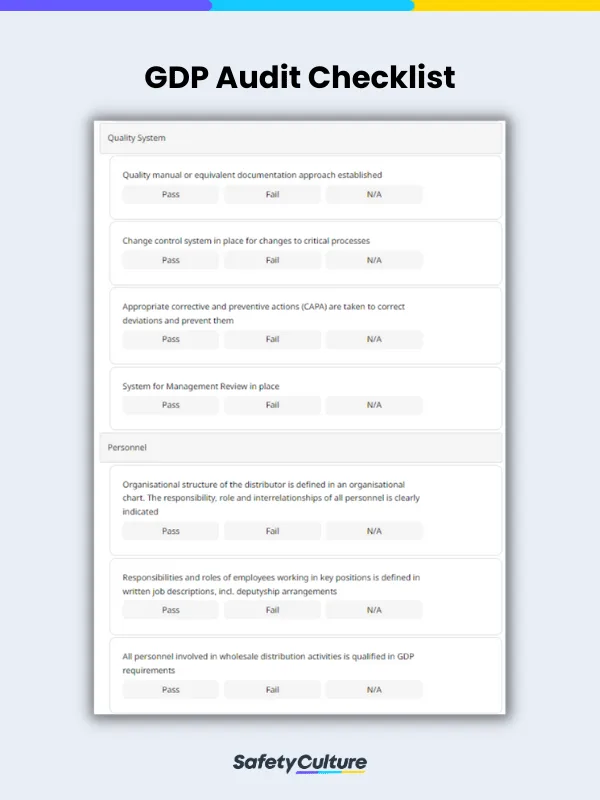
Quality System
Personnel
Premises and Equipment
Outsourcing Activities
Layout of Premises
Hygiene
Temperature and Environment Control
Computer Systems
Documentation
Operations
Qualification of Customers
Storage
Segregation of Goods
Destruction of Obsolete Goods
Picking and Packing
Export (exceptions)
Complaints, Returns, and Recalls
Transportation
Your GDP Audit checklist must also be aligned with relevant regulatory guidelines and standards that govern your industry’s distribution practices. Professionals with expertise in distribution, quality assurance, and compliance should be able to provide insights and input feedback during the checklist development process. On another note, it’s best to integrate risk assessment into the checklist to identify potential risk associated with each aspect of distribution and incorporate risk mitigation strategies.
How to Conduct a GDP Audit Using a Checklist
Keep the following steps and tips in mind when performing a GDP audit with the help of a checklist:
Form an audit team comprising individuals with expertise in distribution, quality assurance, compliance, and relevant departments.
Set a date and time for the audit and notify the relevant teams to ensure their availability.
Provide an overview of the audit process and familiarize the team with the checklist, ensuring they understand the criteria for each item.
Begin the audit proper by following the checklist systematically. Document observations, findings, and evidence for each item by using notes and photos.
Collect supporting evidence to substantiate compliance or non-compliance with each item. This can include records, logs, and other documentation.
Identify areas of non-compliance and recommend corrective actions to address deficiencies.
Prepare a comprehensive report that includes all key findings and results of the conducted audit. Present it to relevant stakeholders and work with responsible teams to implement the recommended corrective actions as needed.
Conduct a follow-up audit to assess the implementation and effectiveness of corrective actions.

GDP Audit Checklist Sample Report | SafetyCulture
Training on GDP Audit Checklist Implementation
Training your employees on the effective use of GDP audit checklists is crucial to ensure that they understand its purpose and can contribute to maintaining high-quality distribution practices. This training should emphasize the significance of GDP compliance and its effect on successful implementation for the organization. Here’s an example training topic points for GDP Audits :
GDP Audit Preparation – Ensure that participants can understand and interpret the checklist easily. Describe how to prepare for an upcoming GDP audit using the checklist.
Documentation and Recordkeeping – Highlight the importance of gathering documentation and evidence in advance. Explain the steps to conduct an audit, including how to accurately document observations, findings, and evidence. Discuss the format and structure of the audit report.
Practical Examples and Use Cases – Present real-world scenarios related to distribution challenges and ask participants to identify checklist items that address those challenges. Discuss instances where non-compliance with the checklist resulted in issues.
Mock GDP Audits and Performance Feedback – During mock GDP audits, provide performance feedback and encourage discussions on best practices and areas for improvement. Emphasize the importance of cross-department collaboration, effective communication, and feedback on the checklist’s usability.
Debriefing – Summarize the key points covered during the training.Reinforce the role of participants in upholding quality distribution practices through checklist implementation.