SMETA Audit: Visibility for Responsible Business Practices
Learn what is SMETA social audit, its pillars, importance, and benefits. Understand how SMETA audits can give visibility on business processes and help improve working conditions and the supply chain.

Published 18 Dec 2024
Article by
4 min read
What is SMETA?
Sedex Members Ethical Trade Audit (SMETA) is a globally recognized social auditing methodology developed by Supplier Ethical Data Exchange (Sedex) in order to provide visibility on suppliers’ business practices in the supply chain.
Importance
Sedex defined SMETA as a “social auditing methodology, enabling businesses to assess their sites and suppliers to understand working conditions in their supply chain.” Social auditing enables brands to demonstrate their commitment to human rights, and monitor worker health and safety. SMETA is relied on by buyers who want their suppliers to be audited, or by suppliers when their customers want them audited to address any issues.
SMETA audits are conducted by third-party companies or organizations approved by Sedex. They are known as a Sedex Affiliate Audit Company (AAC) or independent organizations from Sedex.
Key Areas of Assessment
There are several key areas to consider when evaluating an organization’s socially responsible business operations and meeting social compliance requirements. They are:
SMETA 2-Pillar Audit
A SMETA 2-Pillar audit comprises 2 standard areas:(1) Labour Standards and;(2) Health & Safety.
The standards contained in the ETI Base Code govern the 2-Pillars of a SMETA audit. These two are mandatory areas of assessment for any SMETA audit. It covers these areas:
Management Systems
Entitlement to work
Subcontracting and Homeworking
Shortened Environment assessment
SMETA 4-Pillar
Audit At the request of Sedex members, SMETA has now been extended with “business ethics” and the “environment” being added as optional pillars:
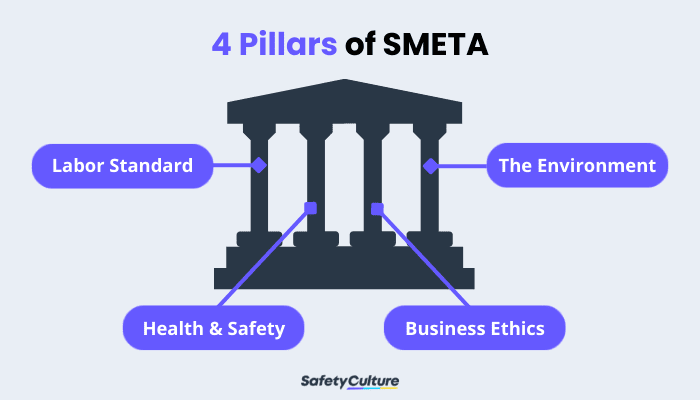
4 Pillars of SMETA
Labor standards
Health and safety
The environment
Business ethics
Core Documents
SMETA consists of four core documents that support the audits. SMETA may be used by any auditor or audit organization, including those who are not members of the Sedex organization. But an audit can only be referred to as a “SMETA Audit” if and only if it was conducted using the criteria outlined in the following documents:
SMETA Best Practice Guidance – consists of standard protocols for carrying out a SMETA audit.
SMETA Measurement Criteria – gives details of the items that should be measured or examined during the SMETA audit.
SMETA Audit Report – provides the template for conducting the audit in a standardized format which can be uploaded to Sedex website.
SMETA Corrective Action Plan Report (CAPR) – provides template for audit findings summary that should be used in conjunction with the corresponding corrective actions to ensure that the violation or issue does not occur again.
The information that will be visible to site and customers are those contained in both the SMETA Audit Report and the CAPR.
How Does SMETA Audit Work?
Below is an infographic of how the SMETA audit is done. The auditing process works this way:
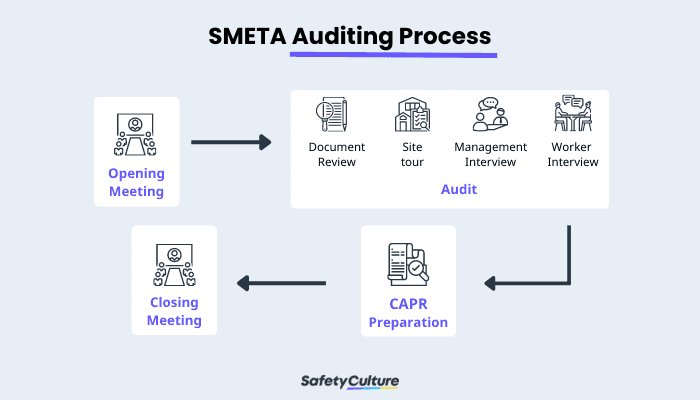
SMETA Auditing Process
Conduct an opening meeting
Review business documents –the auditor examines the organization’s existing processes and systems against the Ethical Trading Initiative (ETI) Base Code and local laws.
Do a site tour –the auditor conducts an inspection of the company’s site to see the working conditions on the ground.The auditors will be checking the workplace if there is any unsafe working conditions, overwork, discrimination, low pay and forced working conditions which can be found in the conventions of the International Labour Organization (ILO) . They will review the following areas according to SMETA:
Wages
Right to work
Working hours
Health and safety
Temporary workers
Provision of rest time
Fair treatment of staff
Management interview -conducting interviews with workers (in groups and per person)
Closing meeting –this involves providing the CAPR.
Benefits of SMETA
Aside from providing visibility to your supply chain, conducting a SMETA audit entails profitable benefits such as:
Suppliers can share the audit reports to several of their customers which in turn reduces the chance of duplicated audits, saving time, money, and resources.
SMETA audits is a solution for checking social compliance and meeting standards of your supplier which in turn build transparency in the supply chain.
SMETA provides the supplier with a CAPR to help address any issues that may occur.
Suppliers with SMETA audits signal to their customers that they have zero tolerance for human rights abuses such as child and forced labour and they are compliant with statutory standards on labor. Additionally, SMETA audits performed with a comprehensive audit checklist ensure that no essential area is overlooked.
Efficient SMETA Audits with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SMETA can help you understand your business practices in greater depth and identify any areas where you could improve your business ethics. Equip your workplace before a SMETA audit takes place with SafetyCulture, the best mobile inspection and audit app used by auditors for conducting efficient auditing.
Optimize your organization’s operations and workflow with SafetyCulture. Our digital platform enables you to:
Simplify processes by automating manual and repetitive tasks
Maintain safety, quality, and compliance standards with digital checklists
Create powerful workflows by integrating your existing systems and software
Gain greater visibility and transparency with real-time reporting
Take advantage of our comprehensive features to transform your organization’s capabilities towards operations excellence.
Article by
SafetyCulture Content Team
SafetyCulture Content Contributor, SafetyCulture
View author profileRelated articles
Digital Tool
Operations

Types of Forms: What You Need to Know
Learn about the types of forms your business can use to standardize processes, collect valuable and actionable data, and ensure compliance.
Logistics
Operations

Warehousing Logistics (Storage Logistics)
Understand warehousing logistics and manage the storage, movement, and handling of inventory to effectively meet supply and demand.
Operations
Human Resources

The Role of HR in Workplace Health and Safety Management
Learn what an HR health and safety program covers, its key responsibilities, and the best practices for creating safer working environments.